
Concept explainers
A 1.00-kg glider on a horizontal air track is pulled by a string at an angle θ. The taut string runs over a pulley and is attached to a hanging object of mass 0.500 kg as shown in Figure P5.40. (a) Show that the speed vx of the glider and the speed vy of the hanging object are related by vx = uvy, where u = z(z2 − h02)−1/2. (b) The glider is released from rest. Show that at that instant the acceleration ax of the glider and the acceleration ay of the hanging object are related by ax = uay. (c) Find the tension in the string at the instant the glider is released for h0 = 80.0 cm and θ = 30.0°.
Figure P5.40
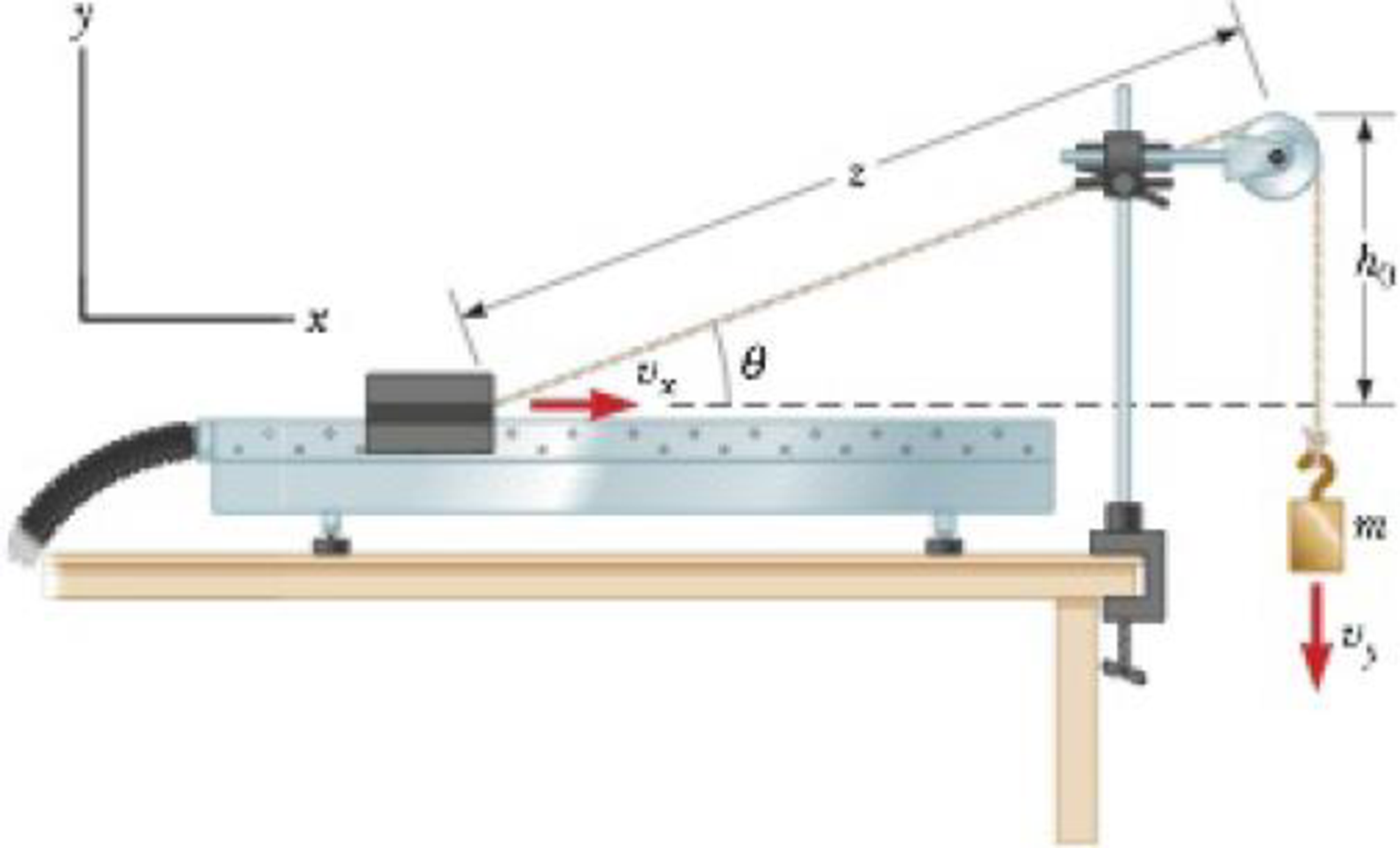
(a)
To show: The speed of the glider and the speed of the hanging object are related by
Answer to Problem 40AP
The speed of the glider and the speed of the hanging object are related by
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the glider is
The free body diagram of the given case is as shown below.
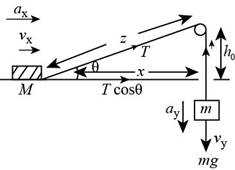
Figure (1)
Form the above figure (1).
From the Pythagorean Theorem,
Here,
Rearrange the above equation for
The speed of the glider is.
Substitute
The term
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of the glider and the speed of the hanging object are related by
(b)
To show: The acceleration of the glider and the speed of the hanging object are related by.
Answer to Problem 40AP
The acceleration of the glider and the speed of the hanging object are related by.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the glider is
From equation (2), the relation of
The acceleration of the glider is,
Substitute
The initial velocity is zero.
Substitute
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the acceleration of the glider and the speed of the hanging object are related by.
(c)
The tension of the string.
Answer to Problem 40AP
The tension of the string is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the glider is
From the free body diagram in figure (1) the net direction in
From part (a) the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the value of
The net force in
Here,
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for
The net force in the
Here,
Form part (b) substitute
From equation (3) substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the tension in the string is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Chemistry: Atoms First
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- the cable may break and cause severe injury. cable is more likely to break as compared to the [1] ds, inclined at angles of 30° and 50° to the vertical rings by way of a scaled diagram. [4] I 30° T₁ 3cm 3.8T2 cm 200 N 50° at it is headed due North and its airspeed indicat 240 km/h. If there is a wind of 100 km/h from We e relative to the Earth? [3]arrow_forwardCan you explain this using nodal analysis With the nodes I have present And then show me how many KCL equations I need to write, I’m thinking 2 since we have 2 dependent sourcesarrow_forwardstate the difference between vector and scalar quarrow_forward
- Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe shear leg derrick is used to haul the 200-kg net of fish onto the dock as shown in. Assume the force in each leg acts along its axis. 5.6 m. 4 m- B Part A Determine the compressive force along leg AB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB = Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the compressive force along leg CB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FCB= Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in the winch cable DB. Express your answer with the appropriate units. 2marrow_forward
- Part A (Figure 1) shows a bucket suspended from a cable by means of a small pulley at C. If the bucket and its contents have a mass of 10 kg, determine the location of the pulley for equilibrium. The cable is 6 m long. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 4 m B НА x = Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback < 1 of 1 T 1 m Units ?arrow_forwardThe particle in is in equilibrium and F4 = 165 lb. Part A Determine the magnitude of F1. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ tvec F₁ = Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the magnitude of F2. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ It vec F2 = Submit Request Answer Part C Determine the magnitude of F3. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ? ? lb lb F₂ 225 lb 135° 45° 30° -60°-arrow_forwardThe 10-lb weight is supported by the cord AC and roller and by the spring that has a stiffness of k = 10 lb/in. and an unstretched length of 12 in. as shown in. Part A Determine the distance d to maintain equilibrium. Express your answer in inches to three significant figures. 節 ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ d = *k J vec 5 t 0 ? d C A in. 12 in. Barrow_forward
- The members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in . The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F = Value Submit Request Answer Part B 0 ? Units Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? T₂ = Value Units T₁ Carrow_forwardpls help on botharrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





