
Concept explainers
A 1.00-kg glider on a horizontal air track is pulled by a string at an angle θ. The taut string runs over a pulley and is attached to a hanging object of mass 0.500 kg as shown in Figure P5.40. (a) Show that the speed vx of the glider and the speed vy of the hanging object are related by vx = uvy, where u = z(z2 − h02)−1/2. (b) The glider is released from rest. Show that at that instant the acceleration ax of the glider and the acceleration ay of the hanging object are related by ax = uay. (c) Find the tension in the string at the instant the glider is released for h0 = 80.0 cm and θ = 30.0°.
Figure P5.40
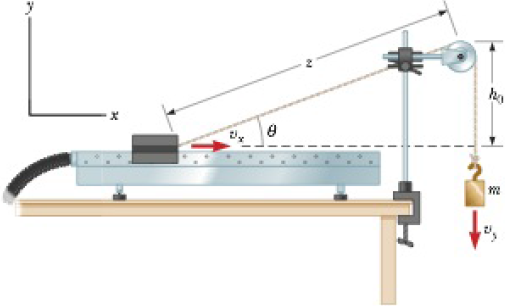
(a)
The relation between the speed of the glider and the speed of the hanging object.
Answer to Problem 40AP
The relation between the speed of the glider and the speed of the hanging object is
Explanation of Solution
The mass of the glider is
The free body diagram of the given case is as shown below.
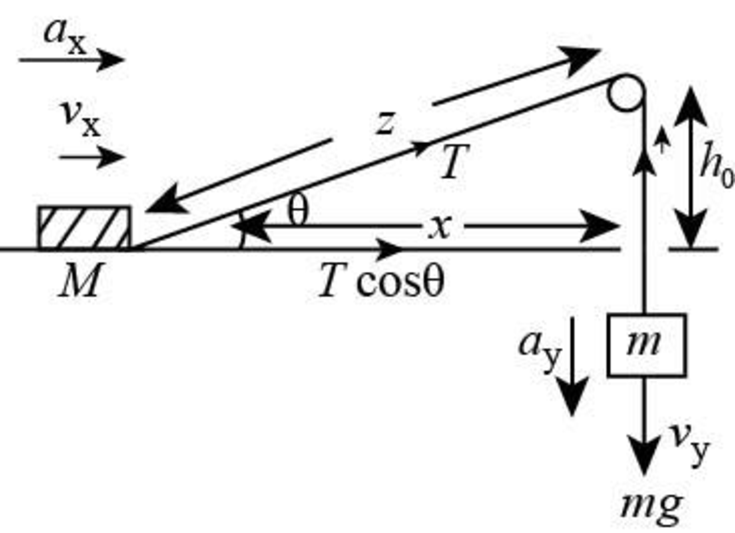
Figure (1)
Form the above figure (1).
Write the expression for the length of the string using Pythagorean Theorem,
Here,
Rearrange the above equation for
Write the expression for the speed of the glider
Here,
Substitute
The term
Write the expression for the speed of the hanging object.
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the relation between the speed of the glider and the speed of the hanging object is
(b)
The relation between the acceleration of the glider and the speed of the hanging object.
Answer to Problem 40AP
The relation between the acceleration of the glider and the speed of the hanging object is
Explanation of Solution
From equation (2), the relation of
Write the expression for the acceleration of the glider
Substitute
The initial velocity of the hanging object is zero.
Substitute
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the relation between the acceleration of the glider and the speed of the hanging object is
(c)
The tension of the string.
Answer to Problem 40AP
The tension of the string is
Explanation of Solution
From the free body diagram in figure (1) the net direction in
From part (a) the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the value of
The net force in
Here,
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for
The net force in the
Here,
Form part (b) substitute
From equation (3) substitute
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the tension in the string is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 10th, Multi-Term
- Frictionless surfarrow_forward71. A 2.1-kg mass is connected to a spring with spring constant 72 k = 150 N/m and unstretched length 18 cm. The two are mounted on a frictionless air table, with the free end of the spring attached to a frictionless pivot. The mass is set into circular mo- tion at 1.4 m/s. Find the radius of its path. cor moving at 77 km/h negotiat CH —what's the minimum icient of frictioarrow_forward12. Two forces act on a 3.1-kg mass that undergoes acceleration = 0.91 0.27 m/s². If one force is -1.2î – 2.5ĵ N, what's the other?arrow_forward
- 36. Example 5.7: You whirl a bucket of water around in a vertical circle of radius 1.22 m. What minimum speed at the top of the circle will keep the water in the bucket?arrow_forwardPassage Problems Laptop computers are equipped with accelerometers that sense when the device is dropped and then put the hard drive into a protective mode. Your computer geek friend has written a program that reads the accel- erometer and calculates the laptop's apparent weight. You're amusing yourself with this program on a long plane flight. Your laptop weighs just 5 pounds, and for a long time that's what the program reports. But then the "Fasten Seatbelt" light comes on as the plane encounters turbu- lence. Figure 4.27 shows the readings for the laptop's apparent weight over a 12-second interval that includes the start of the turbulence. 76. At the first sign of turbulence, the plane's acceleration a. is upward. b. is downward. c. is impossible to tell from the graph. 77. The plane's vertical ac- celeration has its greatest magnitude a. during interval B. b. during interval C. c. during interval D. 78. During interval C, you can conclude for certain that the plane is Apparent…arrow_forwardIf the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere? Assume you can treat both the person and the metal sphere as point charges a distance 25 cm from each otherarrow_forward
- If the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere? Assume you can treat both the person and the metal sphere as point charges a distance 25 cm from each other (so that you can use Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force).arrow_forwardUsing Coulomb's Law, calculate the magnitude of the electrical force between two protons located 1 meter apart from each other. (Give your answer as the number of Newtons but as usual you only need to include the number, not the unit label.)arrow_forwardPart A You want to get an idea of the magnitude of magnetic fields produced by overhead power lines. You estimate that a transmission wire is about 12 m above the ground. The local power company tells you that the line operates at 12 kV and provide a maximum of 60 MW to the local area. Estimate the maximum magnetic field you might experience walking under such a power line, and compare to the Earth's field. [For an ac current, values are rms, and the magnetic field will be changing.] Express your answer using two significant figures. ΟΤΕ ΑΣΦ VAΣ Bmax= Submit Request Answer Part B Compare to the Earth's field of 5.0 x 10-5 T. Express your answer using two significant figures. Ο ΑΣΦ B BEarth ? ? Tarrow_forward
- Ho propel 9-kN t. Boat 27. An elevator accelerates downward at 2.4 m/s². What force does the elevator's floor exert on a 52-kg passenger?arrow_forward16. 17 A CUIN Starting from rest and undergoing constant acceleration, a 940-kg racing car covers 400 m in 4.95 s. Find the force on the car.arrow_forward----- vertical diste Section 4.6 Newton's Third Law 31. What upward gravitational force does a 5600-kg elephant exert on Earth?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





