
Concept explainers
Two blocks of masses m1 and m2, are placed on a table in contact with each other as discussed in Example 5.7 and shown in Figure 5.13a. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block of mass m1 and the table is μ1, and that between the block of mass m2 and the table is μ2. A horizontal force of magnitude F is applied to the block of mass m1. We wish to find P, the magnitude of the contact force between the blocks. (a) Draw diagrams showing the forces for each block. (b) What is the net force on the system of two blocks? (c) What is the net force acting on m1? (d) What is the net force acting on m2? (e) Write Newton’s second law in the x direction for each block. (f) Solve the two equations in two unknowns for the acceleration a of the blocks in terms of the masses, the applied force F, the coefficients of friction, and g. (g) Find the magnitude P of the contact force between the blocks in terms of the same quantities.
(a)
The free body diagram of each block with forces.
The free body diagram of an object represents the direction and magnitude of forces acting on the body.
Explanation of Solution
The mass of block
The free body diagram of the book is given below.
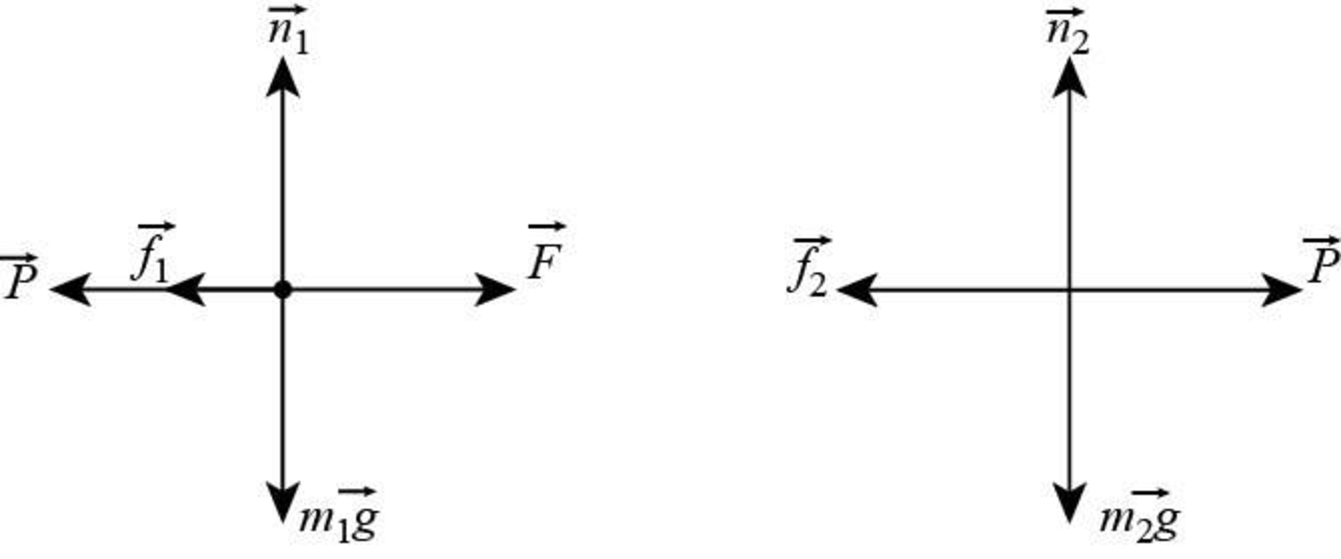
Figure (1)
The sum of all vertical forces is zero because the block moves on a horizontal surface. So the vertical acceleration,
Write the net force in the y-direction for mass
Here,
Write the net force in the y-direction for mass
Here,
Write the equation for kinetic friction for block
Here,
Write the equation for kinetic friction for block
Here,
In the figure,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the free body diagram of each block to show the forces is given in figure I.
(b)
The net force on the system of two blocks.
Answer to Problem 39AP
The net force on the system of two blocks is the external force applied minus the frictional force.
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the net force in x-direction for the system of two blocks from the figure I,
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net force on the system of two blocks is the external force applied minus the frictional force.
(c)
The net force acting on
Answer to Problem 39AP
The net force acting on
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the net force in x-direction for the system of two blocks from the figure I,
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net force acting on
(d)
The net force acting on
Answer to Problem 39AP
The net force acting on
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the net force in x-direction for the system of two blocks from the figure I,
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net force acting on
(e)
The Newton’s second law in the
Answer to Problem 39AP
The Newton’s second law in the
Explanation of Solution
The block has on a horizontal acceleration
Write the Newton’s second law for block
Substitute
Substitute
Write the Newton’s second law for block
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the Newton’s second law in the
(f)
The acceleration of the blocks.
Answer to Problem 39AP
The acceleration of the blocks is
Explanation of Solution
Write the Newton’s second law is for block
Write the Newton’s second law is for block
Conclusion:
Add the equation (I) and equation (II) and solve for
Therefore, the acceleration of the blocks is
(g)
The magnitude of the contact force between the blocks in terms of acceleration, mass, applied force and the friction coefficient.
Answer to Problem 39AP
The magnitude
Explanation of Solution
Recall the equation (II).
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 10th, Multi-Term
- below the horizontal, and land 55 m horizontally from the end of the jump. Your job is to specify the slope of the ground so skiers' trajectories make an angle of only 3.0° with the ground on land- ing, ensuring their safety. What slope do you specify? T 9.5° -55 marrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch and a free body diagram. DO NOT give me examples but ONLY the solutionarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch AND draw a Free body diagramarrow_forward
- P -3 ft 3 ft. O A B 1.5 ft Do 1.5 ft ✓ For the frame and loading shown, determine the magnitude of the reaction at C (in lb) if P = 55 lb. (Hint: Use the special cases: Two-force body and Three-force body.)arrow_forwardA convex mirror (f.=-6.20cm) and a concave minor (f2=8.10 cm) distance of 15.5cm are facing each other and are separated by a An object is placed between the mirrors and is 7.8cm from each mirror. Consider the light from the object that reflects first from the convex mirror and then from the concave mirror. What is the distance of the image (dia) produced by the concave mirror? cm.arrow_forwardAn amusement park spherical mirror shows park spherical mirror shows anyone who stands 2.80m in front of it an upright image one and a half times the person's height. What is the focal length of the minor? m.arrow_forward
- An m = 69.0-kg person running at an initial speed of v = 4.50 m/s jumps onto an M = 138-kg cart initially at rest (figure below). The person slides on the cart's top surface and finally comes to rest relative to the cart. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the person and the cart is 0.440. Friction between the cart and ground can be ignored. (Let the positive direction be to the right.) m M (a) Find the final velocity of the person and cart relative to the ground. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s (b) Find the friction force acting on the person while he is sliding across the top surface of the cart. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) N (c) How long does the friction force act on the person? S (d) Find the change in momentum of the person. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) N.S Find the change in momentum of the cart. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) N.S (e) Determine the displacement of the…arrow_forwardSmall ice cubes, each of mass 5.60 g, slide down a frictionless track in a steady stream, as shown in the figure below. Starting from rest, each cube moves down through a net vertical distance of h = 1.50 m and leaves the bottom end of the track at an angle of 40.0° above the horizontal. At the highest point of its subsequent trajectory, the cube strikes a vertical wall and rebounds with half the speed it had upon impact. If 10 cubes strike the wall per second, what average force is exerted upon the wall? N ---direction--- ▾ ---direction--- to the top to the bottom to the left to the right 1.50 m 40.0°arrow_forwardThe magnitude of the net force exerted in the x direction on a 3.00-kg particle varies in time as shown in the figure below. F(N) 4 3 A 2 t(s) 1 2 3 45 (a) Find the impulse of the force over the 5.00-s time interval. == N⚫s (b) Find the final velocity the particle attains if it is originally at rest. m/s (c) Find its final velocity if its original velocity is -3.50 î m/s. V₁ m/s (d) Find the average force exerted on the particle for the time interval between 0 and 5.00 s. = avg Narrow_forward
- ••63 SSM www In the circuit of Fig. 27-65, 8 = 1.2 kV, C = 6.5 µF, R₁ S R₂ R3 800 C H R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 0.73 MQ. With C completely uncharged, switch S is suddenly closed (at t = 0). At t = 0, what are (a) current i̟ in resistor 1, (b) current 2 in resistor 2, and (c) current i3 in resistor 3? At t = ∞o (that is, after many time constants), what are (d) i₁, (e) i₂, and (f) iz? What is the potential difference V2 across resistor 2 at (g) t = 0 and (h) t = ∞o? (i) Sketch V2 versus t between these two extreme times. Figure 27-65 Problem 63.arrow_forwardThor flies by spinning his hammer really fast from a leather strap at the end of the handle, letting go, then grabbing it and having it pull him. If Thor wants to reach escape velocity (velocity needed to leave Earth’s atmosphere), he will need the linear velocity of the center of mass of the hammer to be 11,200 m/s. Thor's escape velocity is 33532.9 rad/s, the angular velocity is 8055.5 rad/s^2. While the hammer is spinning at its maximum speed what impossibly large tension does the leather strap, which the hammer is spinning by, exert when the hammer is at its lowest point? the hammer has a total mass of 20.0kg.arrow_forwardIf the room’s radius is 16.2 m, at what minimum linear speed does Quicksilver need to run to stay on the walls without sliding down? Assume the coefficient of friction between Quicksilver and the wall is 0.236.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





