
a.
Record these events in a horizontal statements model and indicate whether the item is an operating activity (OA), an investing activity (IA), or a financing activity (FA) or not affected (NA).
a.
Explanation of Solution
Horizontal statements model: The model that represents all the financial statements,
Record these events in a horizontal statements model and indicate whether the item is an operating activity (OA), an investing activity (IA), or a financing activity (FA) or not affected (NA):
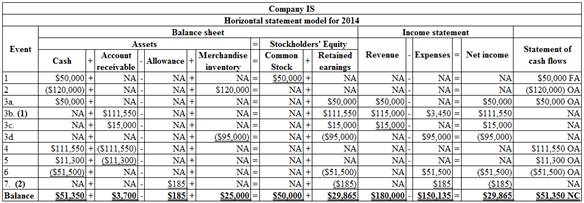
Table (1)
Note:
OA refers to operating activities.
FA refers to financing activities.
NA refers to does not affected.
3a. this transaction records the cash sale.
3b. this transaction records the credit card sale.
3c. this transaction records the sales made on account.
3d. this transaction records the cost of merchandise sold.
Working Note 1: Calculate the amount of credit card sales made to customers:
The merchandise sold to credit card customers for $115,000 and the company charges a fee of 3% on sales. So, the credit card expense (A) is
Working Note 2: Calculate the amount for uncollectible accounts expense:
b)
Prepare income statement, statement of changes in
b)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Statement of changes in the stockholders’ equity: This statement reflects whether the components of stockholders’ equity have increased or decreased during the period.
Statement of Cash flows: Statement of cash flows is a statement reports the source and application of cash between two balance sheet dates. It shows how the cash is sourced and used for the company’s operating, investing, and financing activities.
Prepare the income statement for Company IS for the year ended 2014.
| Company IS | ||
| Statement of income | ||
| For the year ended 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Service revenue | $180,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ($95,000) | |
| Gross margin | $85,000 | |
| Operating expenses | ||
| Credit card expense | $3,450 | |
| Selling and administrative expenses | $51,500 | |
| Uncollectible accounts expense | $185 | |
| Total operating expenses | ($55,135) | |
| Net income | $29,865 | |
Table (2)
Hence, the net income of Company IS for the year ended December 31, 2014 is $29,865.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity of Company IS for the year ended December 31, 2014.
| Company IS | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders' equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Beginning Common Stock | $0 | |
| Add: Stock Issued | $50,000 | |
| Ending Common Stock | $50,000 | |
| Beginning | $0 | |
| Add/Less: Net Income (Loss) | $29,865 | |
| Ending Retained Earnings | $29,865 | |
| Total stockholder's equity | $79,865 | |
Table (3)
Hence, the total stockholders’ equity of Company IS for the year ended December 31, 2014 is $79,865.
Prepare the balance sheet of Company IS as on December 31, 2014.
| Company IS | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As on December 31, 2014 | ||
| Assets | Amount | Amount |
| Cash | $51,350 | |
| $3,700 | ||
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | ($185) | $3,515 |
| Merchandise Inventory | $25,000 | |
| Total Assets | $79,865 | |
| Liabilities and stockholders' equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Total Liabilities | $0 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common Stock | $50,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | $29,865 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $79,865 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $79,865 | |
Table (4)
Hence, the total of assets and liabilities and stockholders’ equity of Company IS as on December 31, 2014 is $79,865.
Prepare the statement of cash flows of Company IS for the year ended December 31, 2014.
| Company IS | ||
| Statement of cash flows | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Customers | $172,850 | |
| Outflow for inventory | ($120,000) | |
| Outflow for expenses | ($51,500) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | $1,350 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | ||
| Net Cash Flow From Investing Activities | $0 | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Stock Issue | $50,000 | |
| Net Cash Flow From Financing Activities | $50,000 | |
| Net Change in Cash | $51,350 | |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | $0 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | $51,350 | |
Table (5)
Hence, the net change in cash of Company IS during 2014 is $51,350.
Working note:
Determine the amount of cash collected from customers.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNTING-ACCESS
- Solve with explanation and accounting questionarrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardIf Sierra Manufacturing had their total liabilities increased by $8,400 and stockholders' equity decreased by $3,700 during a period of time. Then total assets must have changed by what amount and direction during that same period? helparrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this financial accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardI am searching for a clear explanation of this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardA $5,000 bond issued in 2020 pays $275 in interest each year. What is the current yield on the bond if it can be purchased for $4,200?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





