
MICROBIOLOGY-MASTERING MICRO.-ACCESS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780321802705
Author: Tortora
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 2R
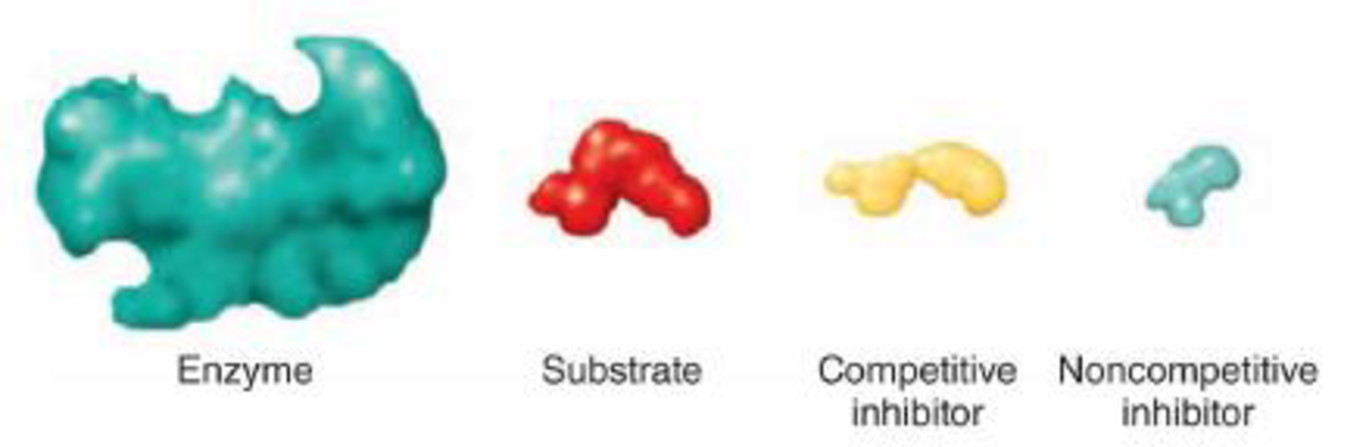
DRAW ITUsing the diagrams below, show each of the following:
- a. where the substrate will bind
- b. where the competitive inhibitor will bind
- c. where the noncompetitive inhibitor will bind
- d. which of the four elements could be the inhibitor in feedback inhibition
- e. What effect will the reactions in (a), (b), and (c) have?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Analyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.
I have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.
13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a
viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then
calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by
both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages.
3 colonies
56
cells
10 μL
10 μL
100 μL
500 με
m
OS
A
B
D
5.0 mL
990 με
990 με
900 με
500 μL
EN
2
100 με
100 μL
118
colonies
12
colonies
Chapter 5 Solutions
MICROBIOLOGY-MASTERING MICRO.-ACCESS
Ch. 5 - Prob. 1RCh. 5 - DRAW ITUsing the diagrams below, show each of the...Ch. 5 - DRAW IT An enzyme and substrate are combined. The...Ch. 5 - Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the...Ch. 5 - There are three mechanisms for the phosphorylation...Ch. 5 - All of the energy-producing biochemical reactions...Ch. 5 - Fill in the following table with the carbon source...Ch. 5 - Write your own definition of the chemiosmotic...Ch. 5 - Why must NADH be reoxidized? How does this happen...Ch. 5 - NAME IT What nutritional type is a colorless...
Ch. 5 - Explain why, even under ideal conditions,...Ch. 5 - The following graph shows the normal rate of...Ch. 5 - Compare and contrast carbohydrate catabolism and...Ch. 5 - How much ATP could be obtained from the complete...Ch. 5 - The chemoautotroph Acidithiobacillus can obtain...Ch. 5 - Which substance in the following reaction is being...Ch. 5 - Which of the following reactions produces the most...Ch. 5 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 5 - Which of the following compounds has the greatest...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5MCQCh. 5 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 5 - Which culture produces the most lactic acid? Use...Ch. 5 - Which culture produces the most ATP? Use the...Ch. 5 - Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices...Ch. 5 - Which culture uses the most glucose? Use the...Ch. 5 - Haemophilus influenzae requires hemin (X factor)...Ch. 5 - The drug Hivid, also called ddC, inhibits DNA...Ch. 5 - The bacterial enzyme streptokinase is used to...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
True or false? Some trails are considered vestigial because they existed long ago.
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Identify me theme or themes exemplified by (a) the sharp quills of a porcupine (b) the development of a multice...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Describe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?arrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward
- 1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forwardwhat measures can a mother to take to improve the produce of her to milk to her newborn baby ?arrow_forward1. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Eastern white pine tree green (but only the ancestral line NOT shared with other organisms) 2. Oncle the last common ancestor of the Colorado blue spruce tree and Eastern white pine tree. 3. Put a box around the last common ancestor of the sugar maple tree and the dogwood tree. 4. Put a triangle around the last common ancestor of the red pine tree and the american holly bush. 5. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Ponderosa pine tree red (including all shared ancestors). 6. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the American elm tree blue (including all shared ancestors). 7 Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Sabal palm tree purple (including all shared ancestors) 8. Using a yellow highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all pine trees. 9. Using a orange highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all gymnosperms 10. Can you tell…arrow_forward
- You have been hired as a public relations specialist to give invertebrates a good name. After all, they are much more than just creepy crawly bugs! Your first task though is to convince yourself that is true. The best way to do that is to start close to home. Find something in your house that is a product obtained directly from an invertebrate or only due to an invertebrate’s actions. Describe the product, its function and utility, as well as any human manufactured alternatives. Be sure to highlight the advantages of obtaining this directly from nature. Keep in mind, a product can be something you use, wear, eat, or enjoy for its visual appeal.arrow_forwardUse the following tree diagram to answer Questions #8-10. 8) Which of the following two animals are the most closely related based on the tree to the left? a) Pig and camel b) Hippo and pig c) Deer and cow 9) CIRCLE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a hippo and a cow is. 10) Put a SQUARE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a pig and a peccary is.arrow_forwardExplain: Healthy Cell Function Overview→ Briefly describe how a healthy cell usually works: metabolism (ATP production), pH balance, glycogen storage, ion transport, enzymes, etc. Gene Mutation and Genetics Part→ Focus on the autosomal recessive mutation and explain: How gene mutation affects the cell. How autosomal inheritance works. Compare the normal and mutated gene sequences simply. → Talk about possible consequences of a faulty hydrolytic enzyme.arrow_forward
- Can you fill out those termsarrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forwardAn 1100 pound equine patient was given 20 mg/kg sucralfate 3 times a day, 2.8 mg/kg famotidine twice a day, and 10mg/kg doxycycline twice a day. Sucralfate comes as a 1 gm tablet, famotidine as 20 mg tablets, and doxycycline as 100mg tablets. All are in bottles of 100 tablets.How many total mg are needed for the patient and how many tablets of each would be needed to provide each dose?How many bottles of each would be needed to have available if this patient were to be on this drug regimen for 5 days?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Enzyme Kinetics; Author: MIT OpenCourseWare;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FXWZr3mscUo;License: Standard Youtube License