
MICROBIOLOGY-MASTERING MICRO.-ACCESS
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780321802705
Author: Tortora
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 1MCQ
Which substance in the following reaction is being reduced?
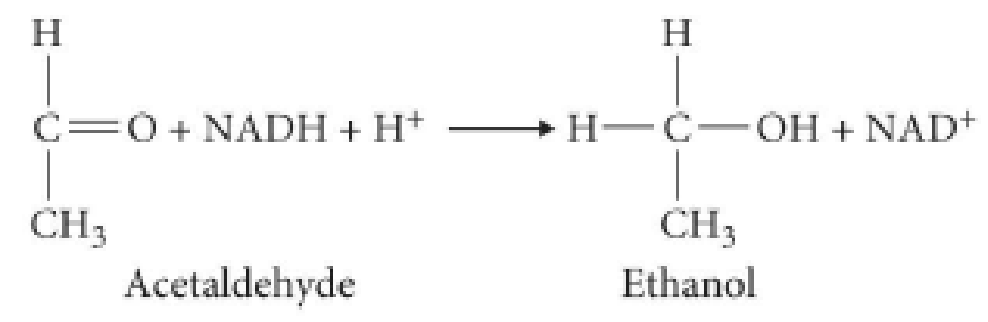
- a. acetaldehyde
- b. NADH
- c. ethanol
- d. NAD+
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Ch.23
How is Salmonella able to cross from the intestines into the blood?
A. it is so small that it can squeeze between intestinal cells
B. it secretes a toxin that induces its uptake into intestinal epithelial cells
C. it secretes enzymes that create perforations in the intestine
D. it can get into the blood only if the bacteria are deposited directly there, that is, through a puncture
—
Which virus is associated with liver cancer?
A. hepatitis A
B. hepatitis B
C. hepatitis C
D. both hepatitis B and C
—
explain your answer thoroughly
Ch.21
What causes patients infected with the yellow fever virus to turn yellow (jaundice)?
A. low blood pressure and anemia
B. excess leukocytes
C. alteration of skin pigments
D. liver damage in final stage of disease
—
What is the advantage for malarial parasites to grow and replicate in red blood cells?
A. able to spread quickly
B. able to avoid immune detection
C. low oxygen environment for growth
D. cooler area of the body for growth
—
Which microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans?
A. Toxoplasma gondii
B. Cytomegalovirus
C. Francisella tularensis
D. Plasmodium falciparum
—
explain your answer thoroughly
Ch.22
Streptococcus pneumoniae has a capsule to protect it from killing by alveolar macrophages, which kill bacteria by…
A. cytokines
B. antibodies
C. complement
D. phagocytosis
—
What fact about the influenza virus allows the dramatic antigenic shift that generates novel strains?
A. very large size
B. enveloped
C. segmented genome
D. over 100 genes
—
explain your answer thoroughly
Chapter 5 Solutions
MICROBIOLOGY-MASTERING MICRO.-ACCESS
Ch. 5 - Prob. 1RCh. 5 - DRAW ITUsing the diagrams below, show each of the...Ch. 5 - DRAW IT An enzyme and substrate are combined. The...Ch. 5 - Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the...Ch. 5 - There are three mechanisms for the phosphorylation...Ch. 5 - All of the energy-producing biochemical reactions...Ch. 5 - Fill in the following table with the carbon source...Ch. 5 - Write your own definition of the chemiosmotic...Ch. 5 - Why must NADH be reoxidized? How does this happen...Ch. 5 - NAME IT What nutritional type is a colorless...
Ch. 5 - Explain why, even under ideal conditions,...Ch. 5 - The following graph shows the normal rate of...Ch. 5 - Compare and contrast carbohydrate catabolism and...Ch. 5 - How much ATP could be obtained from the complete...Ch. 5 - The chemoautotroph Acidithiobacillus can obtain...Ch. 5 - Which substance in the following reaction is being...Ch. 5 - Which of the following reactions produces the most...Ch. 5 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 5 - Which of the following compounds has the greatest...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5MCQCh. 5 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 5 - Which culture produces the most lactic acid? Use...Ch. 5 - Which culture produces the most ATP? Use the...Ch. 5 - Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices...Ch. 5 - Which culture uses the most glucose? Use the...Ch. 5 - Haemophilus influenzae requires hemin (X factor)...Ch. 5 - The drug Hivid, also called ddC, inhibits DNA...Ch. 5 - The bacterial enzyme streptokinase is used to...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
True or false? Some trails are considered vestigial because they existed long ago.
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is this?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology A-C components of the question are corresponding to attached image labeled 1. D component of the question is corresponding to attached image labeled 2. For a eukaryotic mRNA, the sequences is as follows where AUGrepresents the start codon, the yellow is the Kozak sequence and (XXX) just represents any codonfor an amino acid (no stop codons here). G-cap and polyA tail are not shown A. How long is the peptide produced?B. What is the function (a sentence) of the UAA highlighted in blue?C. If the sequence highlighted in blue were changed from UAA to UAG, how would that affecttranslation? D. (1) The sequence highlighted in yellow above is moved to a new position indicated below. Howwould that affect translation? (2) How long would be the protein produced from this new mRNA? Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Explain why the cell doesn’t need 61 tRNAs (one for each codon). Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology You discover a disease causing mutation (indicated by the arrow) that alters splicing of its mRNA. This mutation (a base substitution in the splicing sequence) eliminates a 3’ splice site resulting in the inclusion of the second intron (I2) in the final mRNA. We are going to pretend that this intron is short having only 15 nucleotides (most introns are much longer so this is just to make things simple) with the following sequence shown below in bold. The ( ) indicate the reading frames in the exons; the included intron 2 sequences are in bold. A. Would you expected this change to be harmful? ExplainB. If you were to do gene therapy to fix this problem, briefly explain what type of gene therapy youwould use to correct this. Please help. Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you Explain what is meant by the term “defective virus.” Explain how a defective virus is able to replicate.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain why changing the codon GGG to GGA should not be harmful. Please help . Thank youarrow_forward
- Stage Percent Time in Hours Interphase .60 14.4 Prophase .20 4.8 Metaphase .10 2.4 Anaphase .06 1.44 Telophase .03 .72 Cytukinesis .01 .24 Can you summarize the results in the chart and explain which phases are faster and why the slower ones are slow?arrow_forwardCan you circle a cell in the different stages of mitosis? 1.prophase 2.metaphase 3.anaphase 4.telophase 5.cytokinesisarrow_forwardWhich microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forward
- Select all of the following that the ablation (knockout) or ectopoic expression (gain of function) of Hox can contribute to. Another set of wings in the fruit fly, duplication of fingernails, ectopic ears in mice, excess feathers in duck/quail chimeras, and homeosis of segment 2 to jaw in Hox2a mutantsarrow_forwardSelect all of the following that changes in the MC1R gene can lead to: Changes in spots/stripes in lizards, changes in coat coloration in mice, ectopic ear formation in Siberian hamsters, and red hair in humansarrow_forwardPleiotropic genes are genes that (blank) Cause a swapping of organs/structures, are the result of duplicated sets of chromosomes, never produce protein products, and have more than one purpose/functionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College


Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

KINE 2310-Chapter 4: Philosophy of Physical Activity; Author: HBU Online Course Development;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Ky6t3nvP_4;License: Standard youtube license