
(a)
Record the acceptance of the note on March 1, when the note had interest of 6%.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Note receivable: Note receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
Prepare
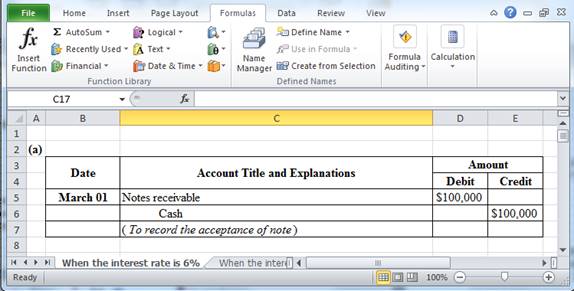
Table (1)
March 01: To record the acceptance of note.
- Notes receivable is an asset. Lending of cash increases notes receivable balance. Thus, notes receivable is debited with $100,000.
- Cash is an asset. Lending of cash decreases the cash balance. Thus, it is credited with $100,000.
(b)
Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, when the note had interest of 6%.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Interest revenue: Interest revenue is the amount charged on the principal value of notes receivable for the privilege of borrowing money. Interest is to be paid by the borrower and to be received by the lender. Interest revenue is calculated as follows:
Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, when the note had interest of 6%.
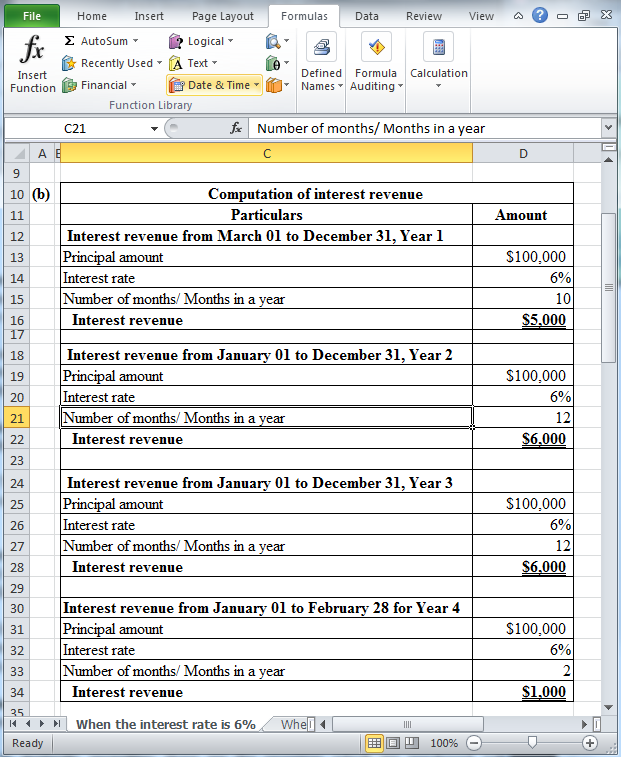
Table (2)
Hence, the interest revenue for Year 1 (for 10 months), Year 2, Year 3 and Year 4 (for 2 months) are $5,000, $6,000, $6,000 and $1,000 respectively.
Working note:
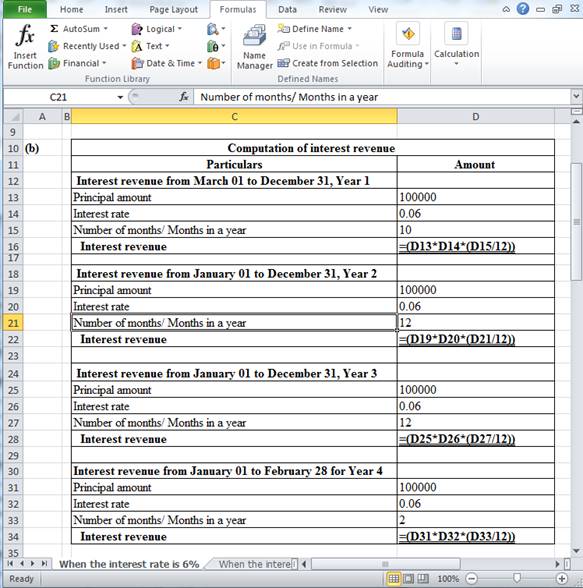
Table (3)
(c)
Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year, when the note had interest of 6%.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Interest revenue: Interest revenue is the amount charged on the principal value of notes receivable for the privilege of borrowing money. Interest is to be paid by the borrower and to be received by the lender. Interest revenue is calculated as follows:
Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year.
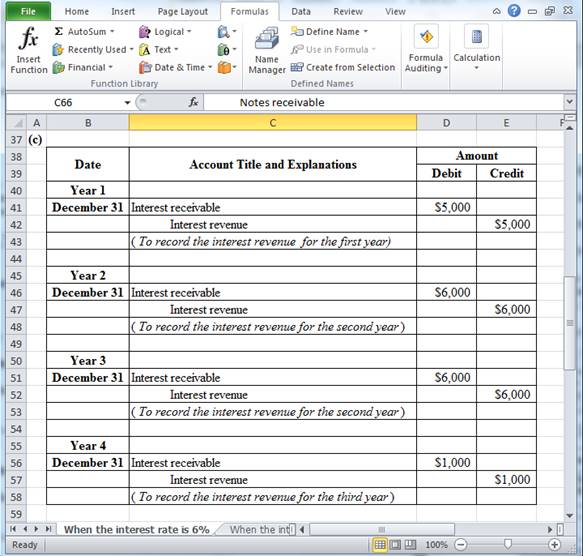
Table (4)
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the first year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $5,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of
retained earnings . It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $5,000.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the second year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $6,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $6,000.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the third year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $1,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $1,000.
(d)
Record the entry for cash received at maturity, when the note had interest of 6%.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Notes receivable: Note receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
Record the entry for cash received at maturity, when the note had interest of 6%.
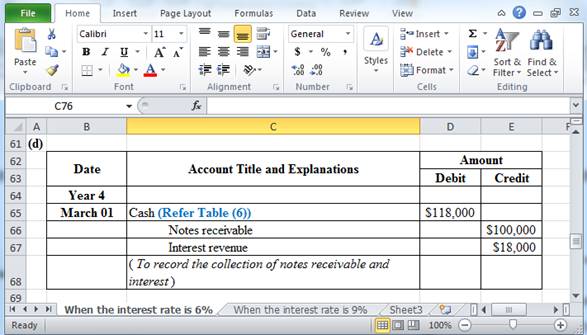
Table (5)
Hence, the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity is $118,000.
Working Note:
Determine the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity.
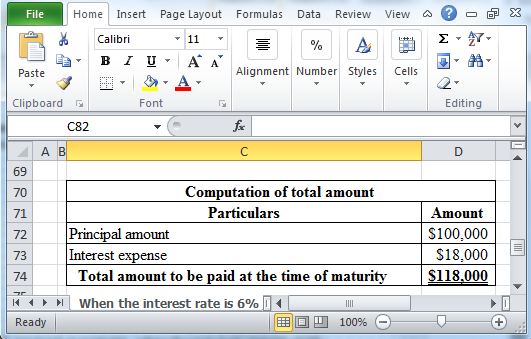
Table (6)
(a) Record the acceptance of the note on March 1, if the note had interest of 9%.
(b) Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, if the note had interest of 9%.
(c) Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year, if the note had interest of 9%.
(d) Record the entry for cash received at maturity, if the note had interest of 9%.
Explanation of Solution
(a) Record the acceptance of the note on March 1, if the note had interest of 9%.
Notes receivable: Notes receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
Prepare journal entry.
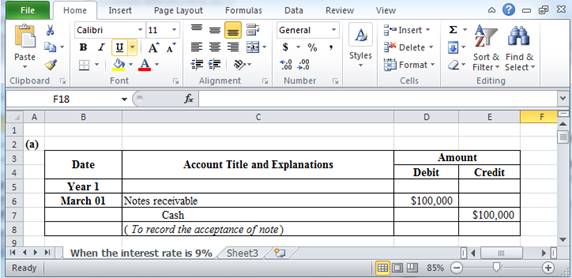
Table (7)
March 01: To record the acceptance of note.
- Notes receivable is an asset. Issuance of notes increases the notes receivables balance. Thus, notes receivable is debited with $100,000.
- Cash is an asset. Lending of cash decreases the cash balance. Thus, it is credited with $100,000.
(b) Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, if the note had interest of 9%.
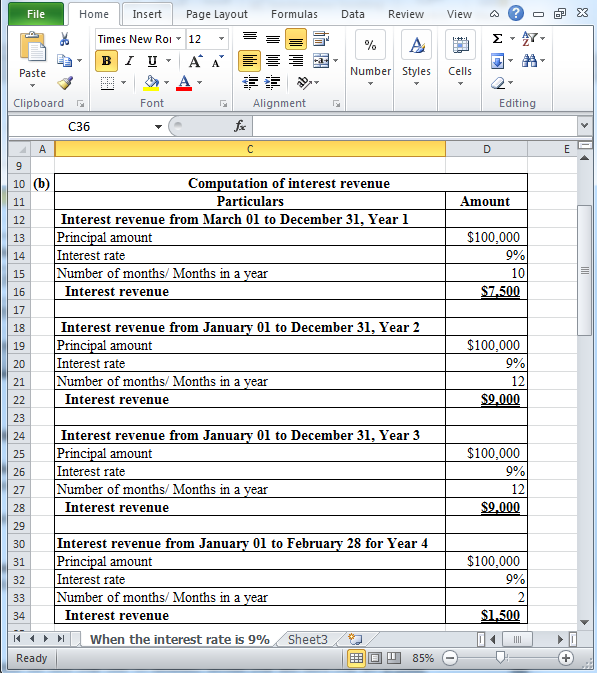
Table (8)
Hence, the interest revenue for Year 1 (for 10 months), Year 2, Year 3 and Year 4 (for 2 months) are $7,500, $9,000, $9,000 and $1,500 respectively.
Working note:
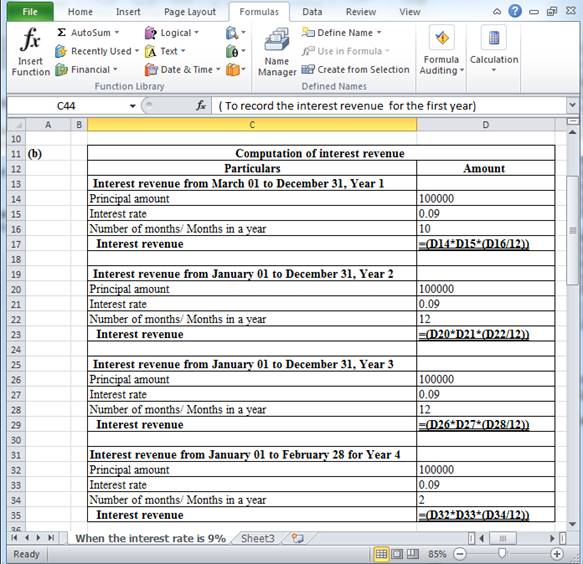
Table (9)
(c) Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year, if the note had interest of 9%.
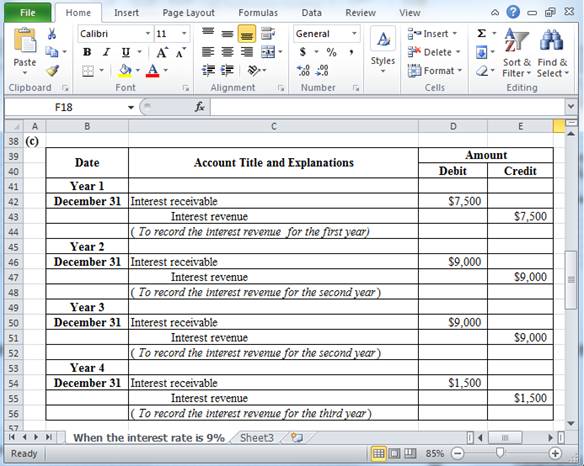
Table (10)
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the first year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $7,500.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $7,500.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the second year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $9,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $9,000.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the third year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $1,500.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $1,500.
(d) Record the entry for cash received at maturity, if the note had interest of 9%.
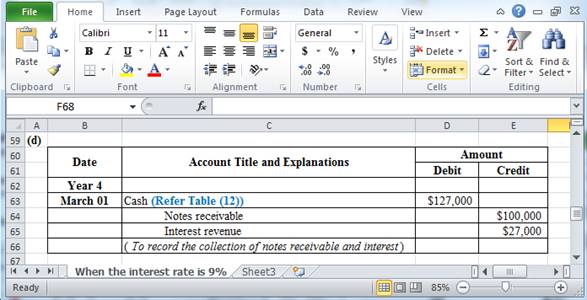
Table (11)
Hence, the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity is $127,000.
Working Note:
Determine the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity.
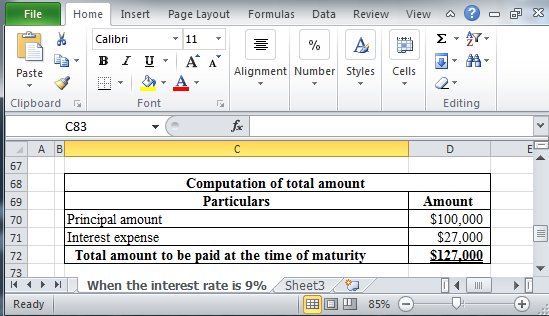
Table (12)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCT(LOOSELEAF)>CUSTOM<-W/COD
- Assess the role of the Conceptual Framework in financial reporting and its influence on accounting theory and practice. Discuss how the qualitative characteristics outlined in the Conceptual Framework enhance financial reporting and contribute to decision-usefulness. Provide examplesarrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress Cullumber Corporation has income from continuing operations of $464,000 for the year ended December 31, 2025. It also has the following items (before considering income taxes). 1. An unrealized loss of $128,000 on available-for-sale securities. 2. A gain of $48,000 on the discontinuance of a division (comprised of a $16,000 loss from operations and a $64,000 gain on disposal). Assume all items are subject to income taxes at a 20% tax rate. Prepare a partial income statement, beginning with income from continuing operations. Income from Continuing Operations Discontinued Operations Loss from Operations Gain from Disposal Net Income/(Loss) CULLUMBER CORPORATION Income Statement (Partial) For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 Prepare a statement of comprehensive income. Net Income/(Loss) $ CULLUMBER CORPORATION Statement of Comprehensive Income For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 = Other Comprehensive Income Unrealized Loss of Available-for-Sale Securities ✰…arrow_forwardPlease make a trial balance, adjusted trial balance, Income statement. end balance ,owners equity statement, Balance sheet , Cash flow statement ,Cash end balancearrow_forward
- Activity Based Costing - practice problem Fontillas Instrument, Inc. manufactures two products: missile range instruments and space pressure gauges. During April, 50 range instruments and 300 pressure gauges were produced, and overhead costs of $89,500 were estimated. An analysis of estimated overhead costs reveals the following activities. Activities 1. Materials handling 2. Machine setups Cost Drivers Number of requisitions Number of setups Total cost $35,000 27,500 3. Quality inspections Number of inspections 27,000 $89.500 The cost driver volume for each product was as follows: Cost Drivers Instruments Gauge Total Number of requisitions 400 600 1,000 Number of setups 200 300 500 Number of inspections 200 400 600 Insructions (a) Determine the overhead rate for each activity. (b) Assign the manufacturing overhead costs for April to the two products using activity-based costing.arrow_forwardBodhi Company has three cost pools and two doggie products (leashes and collars). The activity cost pool of ordering has the cost drive of purchase orders. The activity cost pool of assembly has a cost driver of parts. The activity cost pool of supervising has the cost driver of labor hours. The accumulated data relative to those cost drivers is as follows: Expected Use of Estimated Cost Drivers by Product Cost Drivers Overhead Leashes Collars Purchase orders $260,000 70,000 60,000 Parts 400,000 300,000 500,000 Labor hours 300,000 15,000 10,000 $960,000 Instructions: (a) Compute the activity-based overhead rates. (b) Compute the costs assigned to leashes and collars for each activity cost pool. (c) Compute the total costs assigned to each product.arrow_forwardTorre Corporation incurred the following transactions. 1. Purchased raw materials on account $46,300. 2. Raw Materials of $36,000 were requisitioned to the factory. An analysis of the materials requisition slips indicated that $6,800 was classified as indirect materials. 3. Factory labor costs incurred were $55,900, of which $51,000 pertained to factory wages payable and $4,900 pertained to employer payroll taxes payable. 4. Time tickets indicated that $50,000 was direct labor and $5,900 was indirect labor. 5. Overhead costs incurred on account were $80,500. 6. Manufacturing overhead was applied at the rate of 150% of direct labor cost. 7. Goods costing $88,000 were completed and transferred to finished goods. 8. Finished goods costing $75,000 to manufacture were sold on account for $103,000. Instructions Journalize the transactions.arrow_forward
- Chapter 15 Assignment of direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead Stine Company uses a job order cost system. During May, a summary of source documents reveals the following. Job Number Materials Requisition Slips Labor Time Tickets 429 430 $2,500 3,500 $1,900 3,000 431 4,400 $10,400 7,600 $12,500 General use 800 1,200 $11,200 $13,700 Stine Company applies manufacturing overhead to jobs at an overhead rate of 60% of direct labor cost. Instructions Prepare summary journal entries to record (i) the requisition slips, (ii) the time tickets, (iii) the assignment of manufacturing overhead to jobs,arrow_forwardSolve accarrow_forwardSolve fastarrow_forward
- Assume that none of the fixed overhead can be avoided. However, if the robots are purchased from Tienh Inc., Crane can use the released productive resources to generate additional income of $375,000. (Enter negative amounts using either a negative sign preceding the number e.g. -45 or parentheses e.g. (45).) Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead 1A Fixed overhead Opportunity cost Purchase price Totals Make A Buy $ SA Net Income Increase (Decrease) $ Based on the above assumptions, indicate whether the offer should be accepted or rejected? The offerarrow_forwardThe following is a list of balances relating to Phiri Properties Ltd during 2024. The company maintains a memorandum debtors and creditors ledger in which the individual account of customers and suppliers are maintained. These were as follows: Debit balance in debtors account 01/01/2024 66,300 Credit balance in creditors account 01/01/2024 50,600 Sunday credit balance on debtors ledger Goods purchased on credit 724 257,919 Goods sold on credit Cash received from debtors Cash paid to suppliers Discount received Discount allowed Cash purchases Cash sales Bad Debts written off Interest on overdue account of customers 323,614 299,149 210,522 2,663 2,930 3,627 5,922 3,651 277 Returns outwards 2,926 Return inwards 2,805 Accounts settled by contra between debtors and creditors ledgers 1,106 Credit balances in debtors ledgers 31/12/2024. 815 Debit balances in creditors ledger 31/12/2024.698 Required: Prepare the debtors control account as at 31/12/2024. Prepare the creditors control account…arrow_forwardSolnarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





