
Delsing Canning Company is considering an expansion of its facilities. Its current income statement is as follows:
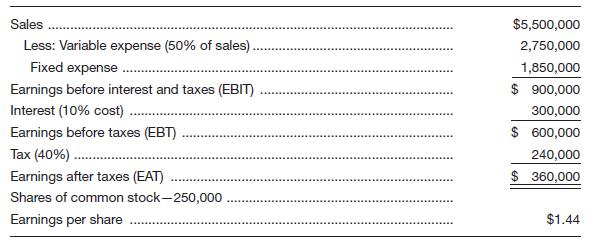
The company is currently financed with 50 percent debt and 50 percent equity (common stock, par value of $10). In order to expand the facilities, Mr. Delsing estimates a need for $2.5 million in additional financing. His investment banker has laid out three plans for him to consider:
Variable costs are expected to stay at 50 percent of sales, while fixed expenses will increase to
Delsing is interested in a thorough analysis of his expansion plans and methods of financing. He would like you to analyze the following:
a. The break-even point for operating expenses before and after expansion (in sales dollars).
b. The degree of operating leverage before and after expansion. Assume sales of
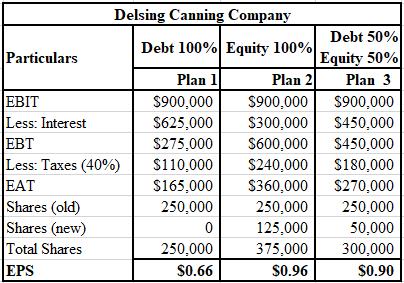
c. The degree of financial leverage before expansion and for all three methods of financing after expansion. Assume sales of
d. Compute EPS under all three methods of financing the expansion at
e. What can we learn from the answer to part d about the advisability of the three methods of financing the expansion?
a.
To calculate: The BEP (in dollars) for the operating expenses of Delsing Canning Company prior to and post expansion.
Introduction:
Break-even point (BEP):
It refers to the production level at which the revenue of the product is equal to the cost of the product. It is calculated by dividing the total fixed cost with the difference between the revenue per unit and variable cost per unit.
Answer to Problem 27P
The BEP of sales prior to the expansion of Delsing Canning Company is $3,700,000 and that post expansion is $4,700,000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of BEP before expansion:
Calculation of BEP after expansion:
Working Notes:
Calculation of the contribution margin ratio prior to expansion:
Calculation of the contribution margin ratio post expansion:
b.
To calculate: The DOL before and after expansion for Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL):
It refers to the ratio that measures the change in the operating income of the company with the change in sales volume.
Answer to Problem 27P
The DOL of Delsing Canning Company before expansion is 3.06 times and that after expansion is 3.61 times.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of DOL before expansion with sales of $5,500,000:
Calculation of DOL after expansion with sales of $6,500,000:
c.
To calculate: The DFL before and after expansion for Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Degree of financial leverage (DFL):
It refers to the leverage ratio that evaluates the EPS of the company with respect to variations in its operating income. This ratio indicates that a higher DFL leads to higher earnings for the firm.
Answer to Problem 27P
The DFL before expansion for Delsing Canning Company is 1.50 times and that after expansion for plan 1 is 3.27 times, that for plan 2 is 1.50 times, and that for plan 3 is 2 times.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of DFL before expansion:
Calculation of DFL after expansion for plan 1:
Calculation of DFL after expansion for plan 2:
Calculation of DFL after expansion for plan 3:
Working Notes:
Calculation of EBIT for plan 1 with 100% debt:
Calculation of EBIT for plan 2 with 100% equity:
Calculation of EBIT for plan 3 with 50% debt and 50% equity:
Calculation of interest for plan 1 with 100% debt:
Calculation of interest for plan 2 with 100% equity:
Calculation of interest for plan 3 with 50% debt and 50% equity:
d.
To calculate: The EPS, given that the sales in the first year were $6,500,000 and that in the last year were $10,000,000, using the three methods of financing after the expansion of Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Earnings per share (EPS):
It is the profit per outstanding share of a public company. A higher EPS indicates a higher value of the company because investors are ready to pay a higher price for one share of the company.
Answer to Problem 27P
The calculation of EPS with sales of $6,500,000 for Delsing Canning Company is shown below.
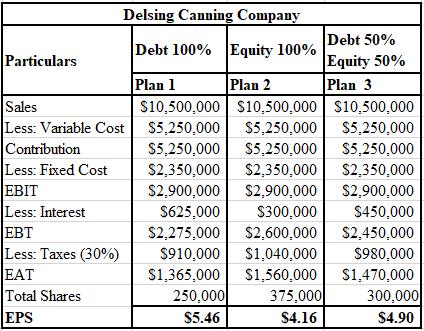
The calculation of EPS with sales of $10,500,000 for Delsing Canning Company is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the calculation of EPS with sales of $6,500,000 are shown below.
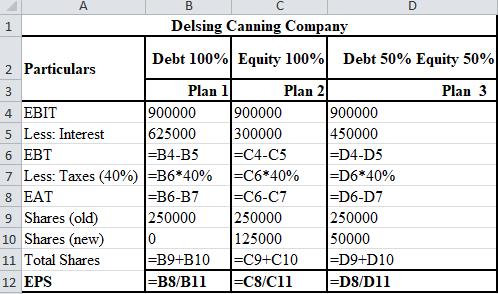
The formulae used for the calculation of EPS with sales of $10,500,000 are shown below.
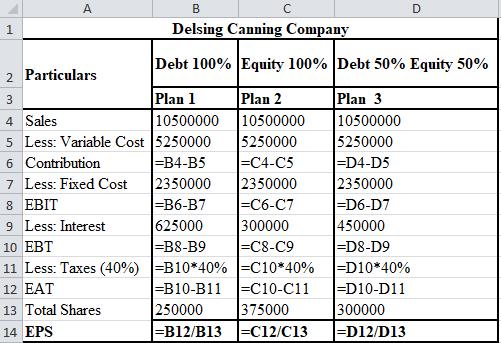
e.
To determine: The outcome of the calculation of part (d) using the three methods of financing the expansion for the Delsing Canning Company.
Introduction:
Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT):
It is the profit of a firm that includes all operating and non-operating expenses. It is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold and operating expenses from the revenue of the corporation.
Answer to Problem 27P
When sales and profits are comparatively low, plan 2, that is, the plan with 100% equity, seems to be the best alternative in the first year. However, after expansion, when sales and profits are high, plan 1, that is, the one with 100% debt, seems to be the best one on the basis of higher yield.
Explanation of Solution
Plan 2 with 100% equity is comparatively the best alternative for the first year when there are low profits as well as sales. Moreover, with the increase in the level of sales of approximately $10.5 million, it is clear that the financial leverage has started producing results as it increased the EBIT in plan 1, which has 100% debt.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
BUS 225 DAYONE LL
- Could you explain what are the Biblical principles researchers that can follow to mitigate researcher bias? How to use of Biblical ethics to synthesize the literature to avoid misrepresentation of the literature? How researchers can demonstrate Biblical ethics when collecting and analyzing data?arrow_forwardThe manager of company A is thinking about adding an air conditioner to the office. The AC will cost $1630 to buy and install. The manager plans to use the AC for 5 years and each year's depreciation rate is 18% of the purchase price. The manager expects to sell the AC in 5 years for $880.The tax rate is 15% and the company's WACC is 15%. If the manager considers this purchase of AC as an investment, what is the NPV (keep two decimal places and assume that the AC will not affect the operations of the company)?arrow_forwardProblem 5-5 Calculating IRR A firm has a project with the following cash flows: Year Cash Flow 0 -$27,700 1 23 11,700 14,700 10,700 The appropriate discount rate is 18 percent. What is the IRR for this project? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) IRR %arrow_forward
- Could you help to explain: How researchers can demonstrate Biblical ethics when conducting a literature review? How researchers can demonstrate Biblical ethics when communicating with a research team or university committee? How researchers can demonstrate Biblical ethics when recruiting participants. Provide Biblical and/or scholarly support for all assertions?arrow_forwardCould you please help explain what is the Biblical ethics in research? How do they establish a firm ethical foundation based on Biblical principles? What should they do to reduce the researcher bias as well as misrepresenting the literature and study findings? How Christians would like to ensure of being obedient to God in the research and study conduct?arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forward
- < When you purchased your car, you took out a 5-year annual-payment loan with an interest rate of 5% per year. The annual payment on the car is $5,200. You have just made a payment and have now decided to pay off the loan by repaying the outstanding balance. What is the payoff amount for the following scenarios? a. You have owned the car for 1 year (so there are 4 years left on the loan)? b. You have owned the car for 4 years (so there is 1 year left on the loan)? a. You have owned the car for 1 year (so there are 4 years left on the loan)? The payoff if there are 4 years left on the loan is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) b. You have owned the car for 4 years (so there is 1 year left on the loan)? The payoff if there is 1 year left on the loan is $ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forwardVictoria Exports (Canada). A Canadian exporter, Victoria Exports, will be receiving six payments of €13,800, ranging from now to 12 months in the future. Since the company keeps cash balances in both Canadian dollars and U.S. dollars, it can choose which currency to exchange the euros for at the end of the various periods. Which currency appears to offer the better rates in the forward market? (Click on the icon to import the table into a spreadsheet.) Period Days Forward spot 1 month C$/euro 1.3347 1.3370 US$/euro 1.3219 1.3224 m 2 months 3 months 1.3392 30 60 1.3229 90 1.3235 180 1.3438 12 months 360 1.3464 1.3239 1.3269 6 months 1.3416 Calculate the forward premium, the Canadian dollar proceeds, and the difference from the spot rate proceeds in the C$/Euro forward market below: (Round the forward premium to three decimal places and the Canadian dollar amounts to the nearest cent.) Days Forward Premium C$ Proceeds of Difference Period Forward C$/euro on the C$/euro €13,800 Over Spot…arrow_forwardidentify the primary sources of financing, both traditional and alternative, accessible to companies seeking sources of funding. To do so, you should: Collect and curate data and documentary resources from various sources (magazine articles, newspapers, online content, working papers from various institutions, activity reports, performance reports, legal regulations, speeches, appearances, press conferences, etc.). Analyze the documentary content you have previously curated and collected. During your analysis, consider the context, location, timing, and target audience of the texts. Reference Article: One Park Financial. (2022). Best alternative business loans and financing for entrepreneurs. https://www.oneparkfinancial.com/blog/alternative-business-funding Questions: Identify and summarize the traditional financial avenues available to businesses. What are the most innovative financing options they could find? Open-ended question: if you were in the opposite position, as an…arrow_forward
- XYZ stock price and dividend history are as follows: Beginning-of- $ 130 Dividend Paid at Year Year Price Year-End 2021 $ 2 2022 2023 153 2 2024 128 133 2 2 An investor buys five shares of XYZ at the beginning of 2021, buys another two shares at the beginning of 2022, sells one share at the beginning of 2023, and sells all six remaining shares at the beginning of 2024. Required: a. What are the arithmetic and geometric average time-weighted rates of return for the investor? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Arithmetic time-weighted average returns Geometric time-weighted average returns % % b-1. Prepare a chart of cash flows for the four dates corresponding to the turns of the year for January 1, 2021, to January 1, 2024. Note: Negative amounts should be indicated by a minus sign. Date 01/01/2021 01/01/2022 Cash Flow 01/01/2023 01/01/2024 b-2. What is the dollar-weighted rate of return? (Hint. If your calculator cannot calculate…arrow_forwardConsider the following two banks: Bank 1 has assets composed solely of a 10-year, 11.50 percent coupon, $1.5 million loan with a 11.50 percent yield to maturity. It is financed with a 10-year, 10 percent coupon, $1.5 million CD with a 10 percent yield to maturity. Bank 2 has assets composed solely of a 7-year, 11.50 percent, zero-coupon bond with a current value of $1,108,283.85 and a maturity value of $2,374,515.87. It is financed with a 10-year, 5.75 percent coupon, $1,500,000 face value CD with a yield to maturity of 10 percent. All securities except the zero-coupon bond pay interest annually. a. If interest rates rise by 1 percent (100 basis points), what is the difference in the value of the assets and liabilities of each bank? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Negative amounts should be indicated by a minus sign. Enter the answers in dollars, not millions of dollars. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. (e.g., 32.16) Before Interest Asset Value After Interest…arrow_forwardTIME TO REACH A FINANCIAL GOAL You have $42,180.53 in a brokerage account, and you plan to deposit an additional $5,000 at the end of every future year until your account totals $250,000. You expect to earn 12% annually on the account. How many years will it take to reach your goal? Round UP to the nearest year. (Example 5.01 years = 6 years) Your answer should include numerical value only.arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

