
a.
To calculate: The EPS of Lopez-Portillo Company before the expansion, if EBIT is 9% on total assets.
Introduction:
Earning per share (EPS):
It is the profit per outstanding share of a public company. A higher EPS indicates higher value of the company because investors are ready to pay higher price for one share of the company.
a.
Answer to Problem 25P
The calculation of EPS of current plan, plan D, and plan E of Lopez-Portillo Company is shown below.
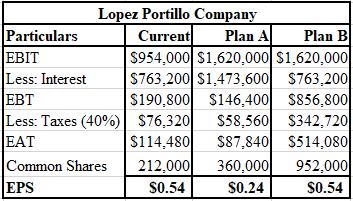
Explanation of Solution
The formulae used for the computation of EPS of current plan, plan D, and plan E are shown below.
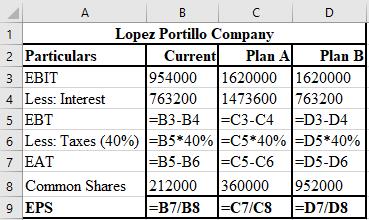
Working notes:
Calculation of interest on current plan:
Calculation of common shares of current plan:
Calculation of interest of plan A:
Calculation of common shares of plan A:
Calculation of common shares of plan B:
Note : The interest of plan B is unchanged.
b.
To calculate: The DFL of Lopez-Portillo company of each plan.
Introduction:
Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL):
It refers to the leverage ratio that evaluates the company’s EPS to the variations in its operating income. This ratio indicates that higher DFL leads to the higher earnings of the firm.
b.
Answer to Problem 25P
The DFL of current plan is 5 times , plan A is 11.07 times, and plan B is 1.89 times.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of DFL of current plan:
Computation of DFL of plan A:
Computation of DFL of plan B:
c.
To calculate: The EPS of each Plan and also determine the impact of each plan of Lopez-Portillo company.
Introduction:
Earning per share(EPS):
It is the profit per outstanding share of a public company. A higher EPS indicates higher value of the company because investors are ready to pay higher price for one share of the company.
c.
Answer to Problem 25P
The calculation of EPS of plan A and plan B of Lopez-Portillo Company is shown below.
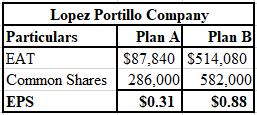
Explanation of Solution
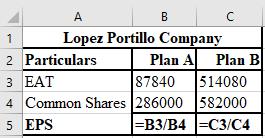
The formula used for the computation of EPS of Plan A and Plan B are shown below.
Plan B will provide a higher EPS on a constant basis.
Working notes:
Calculation of common shares of plan A:
Calculation of common shares of plan B:
d.
To explain: The reason behind the concern of CFO about the stock values of Lopez-Portillo Company.
Introduction:
Share price:
The highest price of one share of a company that an investor is willing to pay is termed as the share’s price. It is the current price used for the trading of such shares.
d.
Answer to Problem 25P
The CFO of the company is concerned about the value of the stock because it impacts capital budgeting decisions and it also influences the ability to finance projects.
Explanation of Solution
The reason behind CFO’s concern about the common stock values are as follows:
(a) Common stock creates shareholder’s wealth.
(b) It impacts the capital budgeting decisions.
(c) It also influences the potential of financing any undertaken projects either at a high or low cost of capital.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Foundations Of Financial Management
- What is ethical dilemma?arrow_forward$1.35 Million for the below question is incorrect, Machine A is $1.81 and Machine B is $0.46 Million. The Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $1.35 millionarrow_forwardBuggies-Are-Us Steady Freddie, Inc Gang Buster Group g = 0 g = 55% Year 1 $3.51 (i.e., dividends are expected to remain at $3.053.05/share) (for the foreseeable future) Year 2 $4.04 Year 3 $4.63 Year 4 $5.36 Year 5 $6.15 Year 6 and beyond: g = 55%arrow_forward
- Project S has a cost of $10,000 and is expected to produce benefits (cash flows) of $3,000 per year for 5 years. Project L costs $25,000 and is expected to produce cash flows of $7,400 per year for 5 years. Calculate the two projects' NPVs, assuming a cost of capital of 12%. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Calculate the two projects' PIs, assuming a cost of capital of 12%. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to three decimal places. Project L is not 1.07arrow_forwardWilbur and Orville are brothers. They're both serious investors, but they have different approaches to valuing stocks. Wilbur, the older brother, likes to use the dividend valuation model. Orville prefers the free cash flow to equity valuation model. As it turns out, right now, both of them are looking at the same stock-Wright First Aerodynmaics, Inc. (WFA). The company has been listed on the NYSE for over 50 years and is widely regarded as a mature, rock-solid, dividend-paying stock. The brothers have gathered the following information about WFA's stock: Current dividend (D) = $2.30/share Current free cash flow (FCF) = $1.5 million Expected growth rate of dividends and cash flows (g) = 5% Required rate of return (r) = 14% Shares outstanding 500,000 shares How would Wilbur and Orville each value this stock?arrow_forwardCompany P/S Multiples Facebook 13.33 Snap 18.22 Twitter 13.27arrow_forward
- The Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $ millionarrow_forwardWilbur and Orville are brothers. They're both serious investors, but they have different approaches to valuing stocks. Wilbur, the older brother, likes to use the dividend valuation model. Orville prefers the free cash flow to equity valuation model. As it turns out, right now, both of them are looking at the same stock-Wright First Aerodynmaics, Inc. (WFA). The company has been listed on the NYSE for over 50 years and is widely regarded as a mature, rock-solid, dividend-paying stock. The brothers have gathered the following information about WFA's stock: Current dividend (D) = $3.30/share Current free cash flow (FCF) = $1.5 million Expected growth rate of dividends and cash flows (g)=8% Required rate of return (r) = 13% Shares outstanding 500,000 shares How would Wilbur and Orville each value this stock? The stock price from Wilbur's valuation is $ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forwardThe Perez Company has the opportunity to invest in one of two mutually exclusive machines that will produce a product it will need for the foreseeable future. Machine A costs $8 million but realizes after-tax inflows of $4.5 million per year for 4 years. After 4 years, the machine must be replaced. Machine B costs $17 million and realizes after-tax inflows of $4 million per year for 8 years, after which it must be replaced. Assume that machine prices are not expected to rise because inflation will be offset by cheaper components used in the machines. The cost of capital is 13%. Using the replacement chain approach to project analysis, by how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better machine? Round your answer to two decimal places. 1.) $ million What is the equivalent annual annuity for each machine? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. 2.) Machine A: $ million 3.) Machine B: $ millionarrow_forward
- You expect to have $29,865. You plan to make X savings contribution of $1,690 per month. The expected return is 0.92 percent per month and the first regular savings contribution will be made later today. What is X? Round to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardCompany P/S Multiples Facebook 13.67 Snap 18.76 Twitter 13.55arrow_forwardEnergy Resources generated an EPS of $4.38 over the last 12 months. The company's earnings are expected to grow by 30.7% next year, and because there will be no significant change in the number of shares outstanding, EPS should grow at about the same rate. You feel the stock should trade at a P/E of around 30 times earnings. Use the P/E approach to set a value on this stock. Using the P/E approach, the value on this stock is $ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
