
Concept explainers
To name:
The pathways diagrammed in parts (a), (b), and (c) of the given figure.
Introduction:
Cellular mechanisms involved in many reactions in which the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another take place by means of
Explanation of Solution
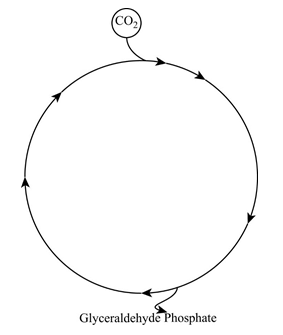
- The given diagram is the Calvin-Benson cycle. In this cycle, three molecules of carbon dioxide are fixed and one molecule of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is produced. After that, it leaves the cycle is shown in the below diagram.
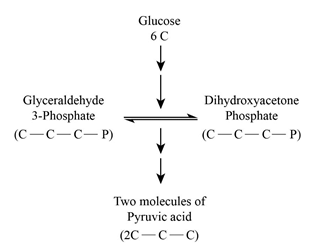
- The given b diagram resembles the Glycolysis pathway. In this pathway, the oxidation of glucose yields two molecules of pyruvic acid as its end product.
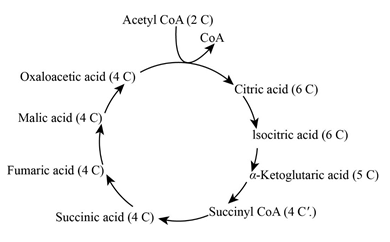
- The below-given diagram is the Kreb’s cycle. Here, the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid produces one carbon dioxide molecule and one acetyl group.
To review:
The anabolic and catabolic mechanisms in the given pathways.
Introduction:
The cellular mechanism of all living organisms requires the energy for its
Explanation of Solution
Glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle are the major pathways for anabolic and catabolic mechanisms of all organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Glycerol is catabolized as Dihydroxyacetone phosphate in the Glycolysis pathway (a) and fatty acids are catabolized as acetyl CoA int he TCA cycle (b).
Glutamic acid is catabolized in the Krebs cycle (c). Glutamic acid is an amino acid which is catabolized by Kreb’s cycle at α-ketoglutaric acid which is formed from isocitric acid.
In the Calvin-Benson cycle, Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is the end product, which enters into glycolysis. In glycolysis, the glucose is oxidized into pyruvate which is decarboxylated to acetyl group and entered into the Kreb’s cycle.
The Calvin cycle requires 18 molecules of ATP between glucose and glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate.
Three molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) is released in the Kreb’s cycle,
- Between pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
- Between isocitric acid to α-ketoglutarate (TCA cycle).
- Between α-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA.
The long chain hydrocarbon like such as acetyl group is catabolized in the TCA cycle at acetyl CoA. This acetyl group like hydrocarbons are catabolized by beta-oxidation which enters into the Kreb’s cycle.
The production of NADH, FADH2 or NADH in glycolysis, Calvin-Benson and TCA cycles are,
The anabolic and catabolic pathways are integrated between,
- In glycolysis, the anabolic and catabolic pathways integrated into dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
- In the TCA cycle, the anabolic and catabolic pathways integrated into acetyl, oxaloacetic acid and ketoglutaric acid.
| Utilizes | Produces | |
| Glycolysis | 2 NADH | |
| Calvin-Benson cycle | 6 NADPH | |
| Pyruvate to acetyl CoA | 1 NADH | |
| Isocitrate to α-ketoglutaric acid | 1 NADH | |
| α-keto-glutaric to succinyl CoA | 1 NADH | |
| Succinate to fumarate | 1 FADH2 | |
| Malate to oxalate | 1 NADH |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
MICROBIOLOGY-ACCESS >CUSTOM<
- There is a species of eagle, which lives in a tropical forest in Brazil. The alula pattern of its wings is determined by a single autosomal gene with four alleles that exhibit an unknown hierarchy of dominance. Genetic testing shows that individuals 1-1, 11-4, 11-7, III-1, and III-4 are each homozygous. How many possible genotypes among checkered eagles in the population?arrow_forwardwhat is this called?arrow_forwardcan you help me identify this it's based on onion rootarrow_forward
- Which evidence-based stress management techniques are most effective in reducing chronic stress and supporting college students’ academic success?arrow_forwardstudents in a science class investiged the conditions under which corn seeds would germinate most successfully. BAsed on the results which of these factors appears most important for successful corn seed germination.arrow_forwardI want to write the given physician orders in the kardex formarrow_forward
- Amino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forwardWhat is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





