
Concept explainers
A link in a
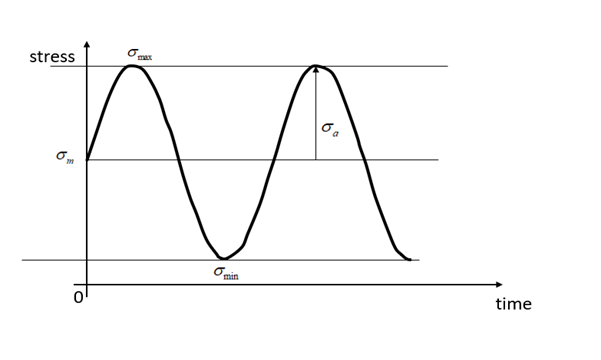
The minimum stress, maximum stress, mean stress, stress ratio, and alternating stress.
Answer to Problem 1P
Maximum stress is 44.6 MPa
Minimum stress is 6.37 MPa
Mean stress is 25.5 MPa
Alternating stress = 19.11 MPa
Stress ratio is 0.143
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Diameter of the bar, D = 10 mm
Maximum tensile force =
Minimum tensile force =
Area of the bar, A
Stress in the bar is defined as,
For maximum stress,
For minimum stress,
Mean stress,
Alternating stress,
Stress Ratio, R
Stress vs time plot
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Machine Elements in Mechanical Design (6th Edition) (What's New in Trades & Technology)
- 6/94 Determine the minimum coefficient of static friction for which the bar can be in static equilibrium in the config- uration shown. The bar is uniform and the fixed peg at C is small. Neglect friction at B. A L PROBLEM 6/94 B L 22arrow_forwardQ2. For the following situation, estimate the minimum required compressive strength of 20/40 proppant. If intermediate-strength proppant is used, estimate the permeability of the proppant pack: Formation depth: 10,000 ft Overburden density: 165lbm/ft3 Poison’s ratio: 0.25 Biot constant: 0.7 Reservoir pressure: 6,500 psi Production drawdown: 2,000 and 4,000 psiarrow_forwardA 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 5-in.-radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that at the instant shown. point A has a velocity of 4.875 in./sin./s and an acceleration of 15.50 in./s2in./s2 , both directed to the right, determine the accelerations of points A, B, and C of the drums. The cord is wound around the 3 inch radius drum. Point B is at the bottom of the 5 inch radius drum. Point A is at the bottom of the 3 inch radius drum. Point C is on the right edge of the 5 inch radius drum. The accelerations of point B is______ in./s2 . The accelerations of point A is ______ in./s2 ______ ⦨ °. at what angle/direction The accelerations of point C is______ in./s2 ______ ⦪ °. at what angle/direction?arrow_forward
- A total volume of mud is 1,000 bbls that has a mud weight of 9.1 ppg. Calculate the volumefractions of water, Bentonite, and the weight of Bentonite used. Density of powder Bentonite is 156 lbm/ft3arrow_forwardA 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 5-in.-radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that at the instant shown. point A has a velocity of 4.875 in./sin./s and an acceleration of 15.50 in./s2in./s2 , both directed to the right, determine the accelerations of points A, B, and C of the drums. The cord is wound around the 3 inch radius drum. Point B is at the bottom of the 5 inch radius drum. Point A is at the bottom of the 3 inch radius drum. Point C is on the right edge of the 5 inch radius drum. The accelerations of point B is ______ in./s2 The accelerations of point A is ______ in./s2 _____⦨ °. The accelerations of point C is _______ in./s2 ____ ⦪ °.arrow_forwardThe average heat transfer coefficent for airflow over an odd shaped body is to be determined by mass transfer measurements and using the Chilton-Colburn analogy btwn heat and mass transfer. The experiemnt is conducted by blowing dry air at 1 atm at a free-stream velocity of 2 m/s over a body covered with a layer of naphthalene. The surface area of the body is .75 m^2, and it is observed that 100 g of maphthalene has sublimated in 45 min. During the experiemnt, both the body and the air were kep at 25oC, at which the vapor pressure and mass diffusivity of naphthalene are 11 Pa and Dab=0.61*10^-5 m^2/s respectively. Determine the heat transfer coefficent under the same flow conditions over the same geometry.arrow_forward
- Auto Controls Design a PID controller for thefollowing system so that the modified system satisfies the followingspecifications : 1. settling time ,ts = 1.96 s and % Overshoot Mp = 70.7 % Assume a non-dominant pole at s = -15 to solve the problem The plot the compensated andThen plot the uncompensated system in MATLAB. what can you see from the plot ? what is your observation ?arrow_forwardAuto Controls The figure is a schematic diagram of an aircraft elevator control system. The input to the systemin the deflection angle of the control lever , and the output is the elevator angle phi.show that for each angle theta of the control lever ,there is a corresponding elevator angle phi. Then find Y(s)/theta(s) and simplify the resulting transfer function . Also note from the diagram that y and phi is relatedarrow_forwardFresh water is planned to be pumped in a certain pipe at constant pumping rate of 6.5 gpm. If water density and viscosity are 8.34 ppg and 1.0 cp, what is the minimum pipe inside diameter that make the fluid flow behave as turbulent flow?arrow_forward
- USE MATLAB ONLY provide typed code Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),... axis([-1 6 -4 4]), ... title('Velocity Triangle'), ... xlabel('x'),ylarrow_forwardConsider a 12 cm internal diameter, 14 m long circular duct whose interior surface is wet. The duct is to be dried by forcing dry air at 1 atm and 15oC throught it at an average velocity of 3m/s. The duct passes through a chilled roo, and it remains at an average temp of 15oC at all time. Determine the mass transfer coeeficient in the duct.arrow_forwardConsider a 5m by 5m wet concret patio with an average water film thickness of .2mm. Now wind at 50 km/h is blowing over the surface. If the air is at 1 atm, 15oC and 35 percent relative humidity, determine how long it will take for the patio to completely dry.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
