
a
Calculate the cost per unit for each product.
a
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of
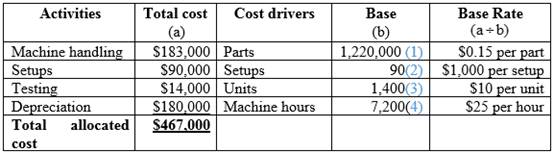
Table (1)
Hence, the total allocated cost is $467,000.
Calculation of total allocated cost and cost per unit for Model W:
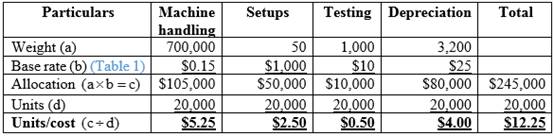
Table (2)
Calculation of total allocated cost and cost per unit for Model M:
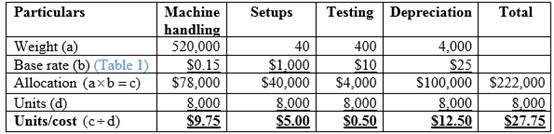
Table (3)
Calculation of cost per unit consumption:
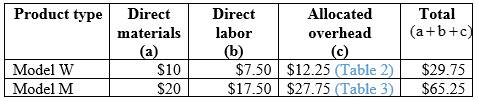
Table (4)
Hence, the costs per unit of Model W and Model M are $29.75 and $65.25.
Working notes:
Calculation of base for material handling:
Hence, the base for material handling is 1,220,000 hours.
(1)
Calculation of base for machine setup:
Hence, the base for machine setups is 90 setups.
(2)
Calculation of base for product testing:
Hence, the base product level is 1,400 units.
(3)
Calculation of
Hence, the base of depreciation is 2,500 hours.
(4)
b
Calculate whether Company K earns a profit or loss for the next year.
b
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of profit or loss earned by the company previous month:
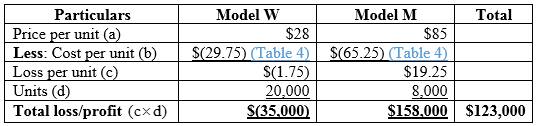
Table (5)
Hence, the company has a loss of -$35,000 on Model W and earns a profit of $123,000 on Model M.
c
Calculate the target cost for each product and total target profit.
c
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of target cost:
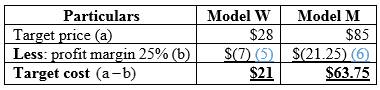
Table (6)
Hence, the target costs of Model W and Model M are $21 and $63.75.
Calculation of total target profit:
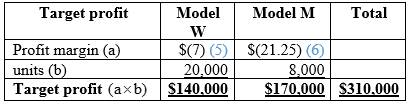
Table (7)
Hence, the total target profit from both the models is $310,000.
Working notes:
Calculation of profit margin for the Model ZM:
Hence, the profit margin for Model W is $7.
(5)
Calculation of profit margin for the Model M:
Hence, the profit margin for Model M is $21.25.
(6)
d
Whether the new process allows Company K to attain its target cost.
d
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of overhead cost under ABC system using new process:
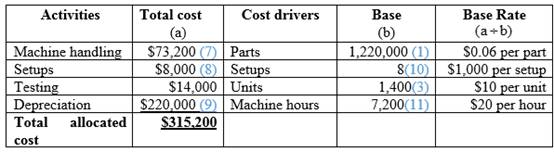
Table (8)
Hence, the total allocated cost is $315,200.
Calculation of total allocated cost and cost per unit for Model W:
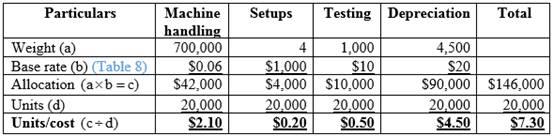
Table (9)
Calculation of total allocated cost and cost per unit for Model W:
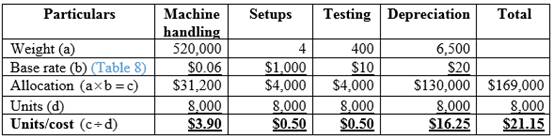
Table (10)
Calculation of cost per unit consumption:
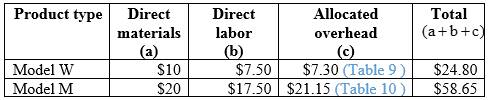
Table (11)
Hence, the costs per unit of Model W and Model M are $24.80 and $58.65.
Company K will not achieve its target with a new process because the cost per unit of Model W is above the target cost.
Working notes:
Calculation of machine handling cost for a new process:
Hence, the machine handling data for a new process is $73,200.
(7)
Calculation of setup cost for new process:
Hence, the setup cost for new process is $8,000.
Note:
The cost per setup is not affected.
(8)
Calculation of depreciation cost for new process:
Hence, the depreciation cost for new process is $220,000.
(9)
Calculation of base for setup for a new process:
Hence, the base for setup is 1,220,000 hours.
(10)
Calculation of base for machine hours for a new process:
Hence, the base for machine hours is 11,000 hours.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts
- provide correct answerarrow_forwardInternal control refers to the processes and procedures implemented by an organization to ensure the integrity of financial and accounting information, promote accountability, and prevent fraud. These controls are designed to provide reasonable assurance that the organization achieves its objectives in operational efficiency, financial reporting reliability, and compliance with laws and regulations. Internal control is a comprehensive system that includes a variety of checks and balances, such as segregation of duties, authorization and approval processes, reconciliations, and physical security measures. It is an integral part of an organization's governance framework, helping to safeguard assets, improve operational efficiency, and ensure accurate and timely financial reporting. Respond to the above postarrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forward
- You are a team of accounting consultants hired by the company VinGrenDom Ltd., a regional utility and manufacturing firm expanding into the Eastern Caribbean. The Board of Directors is requesting an accounting report that addresses three critical areas in their financial statements. Part A: Working Capital 1. Define working capital and explain its importance in financial health and liquidity management. 2. Assess how the matching concept and accrual basis affect the reporting of current assets and liabilities. 3. Using a hypothetical balance sheet (you may create one), identify at least 5 current assets and 5 current liabilities and analyze how changes in these elements affect liquidity ratios. 4. Recommend at least two strategies VinGrenDom Ltd. can implement to optimize working capital.arrow_forwardProvide best solution accountingarrow_forwardGeneral Accounting solve this problemarrow_forward
- Explain the theoretical concepts underlying equity (e.g., residual interest, stewardship, and proprietary theories)arrow_forwardGeneral Accounting Questionarrow_forwardSea Harbor, Inc. has a marginal tax rate of 35 percent and an average tax rate of 22 percent. If the firm earns $79,500 in taxable income, how much will it owe in taxes? a. $10,335. b. $16,695. c. $17,490. d. $27,030. e. $27,825.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





