
A toy car rolls off tables of various heights at different speeds as shown.
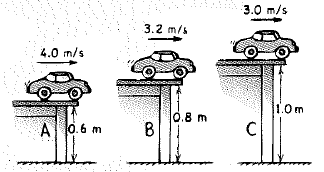
a. Rank them for the time in the air, from greatest to least.
b. Rank them for horizontal range, from greatest to least.
(a)
To Rank: The cars for the time in air.
Answer to Problem 15A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
For car A:
Acceleration in vertical direction
Time interval
Initial velocity along the vertical direction
Vertical displacement
For car B:
Acceleration in vertical direction
Time interval
Initial velocity along the vertical direction
Vertical displacement
For car C:
Acceleration in vertical direction
Time interval
Initial velocity along the vertical direction
Vertical displacement
Formula Used:
According to kinematics equation, displacement is given as
Where,
a is he acceleration
t is the time
Calculation:
For car A:
Using the kinematics equation for the vertical motion of car
For car B:
Using the kinematics equation for the vertical motion of car
For car C:
Using the kinematics equation for the vertical motion of car
Conclusion:
Hence, the ranking comes out to be
(b)
To Rank:The cars as per their horizontal range.
Answer to Problem 15A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
For car A:
Acceleration in horizontal direction
Time interval
Initial velocity along the horizontal direction
Horizontal displacement
For car B:
Acceleration in horizontal direction
Time interval
Initial velocity along the horizontal direction
Horizontal displacement
For car C:
Acceleration in horizontal direction
Time interval
Initial velocity along the horizontal direction
Horizontal displacement
Formula Used:
According to kinematics equation, displacement is given as
Where
Calculation:
For car A:
Using the kinematics equation for the horizontal motion of car
For car B:
Using the kinematics equation for the horizontal motion of car,
For car C:
Using the kinematics equation for the horizontal motion of car
Conclusion:
Hence, the ranking comes out to be
Chapter 5 Solutions
EP CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS-ONLINE ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Use the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. a Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) 1) Determine the angle of refraction of the ray of light in the water. Barrow_forwardHi can u please solvearrow_forward6. Bending a lens in OpticStudio or OSLO. In either package, create a BK7 singlet lens of 10 mm semi-diameter and with 10 mm thickness. Set the wavelength to the (default) 0.55 microns and a single on-axis field point at infinite object distance. Set the image distance to 200 mm. Make the first surface the stop insure that the lens is fully filled (that is, that the entrance beam has a radius of 10 mm). Use the lens-maker's equation to calculate initial glass curvatures assuming you want a symmetric, bi-convex lens with an effective focal length of 200 mm. Get this working and examine the RMS spot size using the "Text" tab of the Spot Diagram analysis tab (OpticStudio) or the Spd command of the text widnow (OSLO). You should find the lens is far from diffraction limited, with a spot size of more than 100 microns. Now let's optimize this lens. In OpticStudio, create a default merit function optimizing on spot size.Then insert one extra line at the top of the merit function. Assign the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer .arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forward
- Good explanation it sure experts solve it.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Asaparrow_forwardA satellite has a mass of 100kg and is located at 2.00 x 10^6 m above the surface of the earth. a) What is the potential energy associated with the satellite at this loction? b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCorrect answer No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardStatistical thermodynamics. The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesa) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberb) must always be greater than Avogadro's number.c) has no relation to Avogadro's number.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





