
University Physics Volume 2
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168161
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 125AP
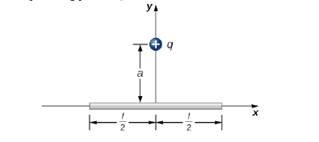
The charge per unit length on the thin rod shown here is
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 5 Solutions
University Physics Volume 2
Ch. 5 - Check Your Understanding What would be different...Ch. 5 - Check Your Understanding What would be different...Ch. 5 - Check Your Understanding What is the electric...Ch. 5 - Check Your Understanding How would the strategy...Ch. 5 - Check Your Understanding How would the above limit...Ch. 5 - Check Your Understanding the electric field 100k...Ch. 5 - There are very large numbers of charged particles...Ch. 5 - Why do most objects tend to contain nearly equal...Ch. 5 - A positively charged It'd attracts a small piece...Ch. 5 - Two bodies attract each other electrically. Do...
Ch. 5 - How would you determine whether the charge on a...Ch. 5 - An eccentlic inventor attempts to levitate a cork...Ch. 5 - When a glass rod is lubbed with silk, it becomes...Ch. 5 - Why does a car always attract dust right after it...Ch. 5 - Does the uncharged conductor shown below...Ch. 5 - While walking on a mg, a person frequently becomes...Ch. 5 - Compare charging by conduction to charging by...Ch. 5 - Small pieces of tissue are attracted to a charged...Ch. 5 - Trucks that cany gasoline often have chains...Ch. 5 - Why do electrostatic experiments work so poorly in...Ch. 5 - Why do some clothes cling together after being...Ch. 5 - Can induction be used to produce charge on an...Ch. 5 - Suppose someone tells you that rubbing quartz with...Ch. 5 - A handheld copper rod does not acquire a charge...Ch. 5 - Suppose you place a charge q near a large metal...Ch. 5 - Would defining the charge on an electron to be...Ch. 5 - An atomic nucleus contains positively charged...Ch. 5 - Is the fore between two fixed charges influenced...Ch. 5 - When measuring an electlic field, could we use a...Ch. 5 - During fair weather, the electric field due to the...Ch. 5 - If the electric field at a point on the line...Ch. 5 - Two charges lie along the x-axis. Is it nue that...Ch. 5 - Give a plausible argument as to why the electric...Ch. 5 - Compare the electric fields of an infinite sheet...Ch. 5 - Describe the electric fields of an infinite...Ch. 5 - A negative charge is placed at center of a ring of...Ch. 5 - If a point charge is released fmm rest in a...Ch. 5 - Under what conditions, if any, will the trajectory...Ch. 5 - How would you experimentally distinguish an...Ch. 5 - A representation of an electric field shows 10...Ch. 5 - What is the ratio of the number of electlic field...Ch. 5 - What are the stable orientation(s) for a dipole in...Ch. 5 - Common static electricity involves charges ranging...Ch. 5 - If 1.801020 electrons move through a pocket...Ch. 5 - To stat a car engine, the car battery moves...Ch. 5 - A certain lightning bolt moves 40.0 C of charge....Ch. 5 - A 2.5-g copper penny is given a charge of 2.0109C...Ch. 5 - A 2.5-g copper penny is given a charge of 4.0109C...Ch. 5 - Suppose a speck of dust in an electrostatic...Ch. 5 - An amoeba has 1.001016 protons and a net charge of...Ch. 5 - A 50.0-g ball of copper has a net charge of 2.00C....Ch. 5 - What net charge would you place on a 100-g piece...Ch. 5 - How many coulombs of positive charge are there in...Ch. 5 - Two point particles with charges +3C and +5C are...Ch. 5 - Two charges +3C and +12C are fixed 1 m apart, with...Ch. 5 - In a salt crystal, the distance between adjacent...Ch. 5 - Protons in an atomic nucleus ale typically 1015 m...Ch. 5 - Suppose Earth and the Moon each carried a net...Ch. 5 - Point charges q1=50C and q2=25C are placed 1.0 m...Ch. 5 - Where must q3 of the preceding problem be placed...Ch. 5 - Two small balls, each of mass 5.0 g, are attached...Ch. 5 - Point charges q1=2.0C and q3=4.0C arelocated at...Ch. 5 - The net excess charge on two small spheres (small...Ch. 5 - Two small, identical conducting spheres repel each...Ch. 5 - A charge q=2.0C is placed at the point P shown...Ch. 5 - What is the net electric fore on the charge...Ch. 5 - Two fixed particles, each of charge 5.0106C , are...Ch. 5 - The charges q1=2.0107C, q2=4.0107C, and q3=1.0107C...Ch. 5 - What is the force on the charge q at the...Ch. 5 - Point charges q1=10C and q2=30C are fixed at...Ch. 5 - A particle of charge 2.0108C experiences an upward...Ch. 5 - On a typical clear day, the atmospheric electric...Ch. 5 - Consider an electron that is 1010 m from an alpha...Ch. 5 - Each the balls shown below carries a charge q and...Ch. 5 - What is the electric field at a point where the...Ch. 5 - A proton is suspended in the air by an electric...Ch. 5 - The electric field in a particular thundercloud is...Ch. 5 - A small piece of cork whose mass is 2.0 g is given...Ch. 5 - If the electric field is 100 N/C at a distance of...Ch. 5 - What is the electric field of a proton at the...Ch. 5 - (a) What is the electric field of an oxygen...Ch. 5 - Two point charges, q1=2.0107C and q2=6.0108C , are...Ch. 5 - Point charges q1=50C and q2=25C are placed 1.0 m...Ch. 5 - Can you arrange the two point charges q1=2.0106C...Ch. 5 - Point charges q1=q2=4.0106C are fixed on the...Ch. 5 - A thin conducting plate 1.0 m on the side is given...Ch. 5 - Calculate the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 5 - Two thin conducting plates, each 25.0 cm on a...Ch. 5 - The charge per unit length on the thin rod shown...Ch. 5 - The charge per unit length on thin semicircular...Ch. 5 - Two thin parallel conducting plates are placed 2.0...Ch. 5 - A thin conducing plate 2.0 m on a side is given a...Ch. 5 - A total charge q is distributed uniformly along a...Ch. 5 - Charge is distributed along the entire x-axis...Ch. 5 - Charge is distributed along the entire x-axis...Ch. 5 - A rod bent into the arc of a circle subtends an...Ch. 5 - A pluton moves in the electric field E=200iN/C ....Ch. 5 - An electron and a proton, each starting from rest,...Ch. 5 - A spherical water droplet of radius 25 m carries...Ch. 5 - A proton enters the uniform electric field...Ch. 5 - Shown below is a small sphere of mass 0.25 g that...Ch. 5 - Two infinite rods, each carrying a uniform charge...Ch. 5 - Positive charge is distributed with a uniform...Ch. 5 - From a distance of 10 cm, a proton is projected...Ch. 5 - A particle of mass m and charge q moves along a...Ch. 5 - Which of the following electric field lines are...Ch. 5 - In this exercise, you practice electric field...Ch. 5 - Draw the electric field for a system of three...Ch. 5 - Two charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign...Ch. 5 - Suppose the electric field of an isolated point...Ch. 5 - Consider the equal and opposite charges shown...Ch. 5 - (a) What is the dipole moment of the configuration...Ch. 5 - A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms...Ch. 5 - Point charges q1=2.0C and q1=4.0C are located at...Ch. 5 - What is the force on the 5.0C charge shown below?Ch. 5 - What is the force on the charge placed at the 2.0C...Ch. 5 - Four charged particles are positioned at the...Ch. 5 - A charge Q is fixed at the origin and a second...Ch. 5 - A charge q=2.0C is released from rest when it is...Ch. 5 - What is the electric field at the midpoint M of...Ch. 5 - Find the electric field at P for the charge...Ch. 5 - (a) What is the electric field at the...Ch. 5 - Point charges are placed at the four corner of a...Ch. 5 - Three charges are positioned at the cornets of a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 119APCh. 5 - A particle of charge q and mass m is placed at the...Ch. 5 - Charge is distributed uniformly along the entire...Ch. 5 - The circular are shown below carries a charge per...Ch. 5 - Calculate the electric field due to a uniformly...Ch. 5 - The charge unit length on the thin shown below is ...Ch. 5 - The charge per unit length on the thin rod shown...Ch. 5 - The charge per unit length on the thin...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The colour of the solution on adding chloride is to be explained. Concept Introduction : A reversible process i...
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
The mammalian trachea and esophagus both connect to the (A) pharynx. (B) stomach. (C) large intestine. (D) rect...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY