
Concept explainers
a.
To determine:
Internal Rate of Return (IRR):
IRR is the rate at which the future cash inflows will be equal to the initial
a.
Answer to Problem 10QP
Solution:
Compute the IRR.
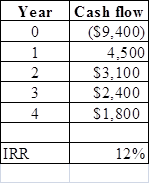
Explanation of Solution
- The excel spreadsheet is used to calculate the internal
rate of return . - The IRR function is used to compute the internal rate of return.
Hence, internal rate of return is 12%.
b.
To explain: Whether Person X should accept this offer or not on 10% discount rate.
b.
Answer to Problem 10QP
Solution:
Person X should accept this offer on 10% discount rate.
Explanation of Solution
One should accept this offer because internal rate of return is 12% which is higher than the discount rate of 10%. It means that the current project will fetch profit for the company.
Hence, Person X should accept this project.
c.
To explain: Whether one should accept this offer or not on 20% discount rate.
c.
Answer to Problem 10QP
Solution:
Person X should not accept this offer on 20% discount rate.
Explanation of Solution
Person X should not accept this offer because internal rate of return is 12% which is lower than the discount rate of 20%. It means that the current project will not be able to earn even what is initially invested in the project.
Hence, Person X should not accept this project.
d.
To determine: NPV at 10% and 20% discount rate.
Net present value refers to the present value of all the future cash flow that is adjusted according to the
d.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the NPV.
For discount rate of 10%:
Given,
C0 is $9,400.
CF1 is $4,500.
CF2 is $3,100.
CF3 is $2,400.
CF4 is $1,800.
r is 10%.
Solution:
Formula to compute NPV,
Where,
- C0 is initial investment.
- CF1 is
cash inflow in first year. - CF2 is cash inflow in second year.
- CF3 is cash inflow in third year.
- CF4 is cash inflow in fourth year.
- r is discount rate.
Substitute, $9,400 for C0, $4,500 for CF1, $3,100 for CF2, $2,400 for CF3,$1,800 for CF4 and 10% for r.
The NPV for discount rate of 10% is $285.47.
For discount rate of 20%:
Given,
C0 is $9,400.
CF1 is $4,500.
CF2 is $3,100.
CF3 is $2,400.
CF4 is $1,800.
r is 20%.
Formula to compute NPV,
Where,
- C0 is initial investment.
- CF1 is cash inflow in first year.
- CF2 is cash inflow in second year.
- CF3 is cash inflow in third year.
- CF4 is cash inflow in fourth year.
- r is discount rate.
Substitute, $9,400 for C0, $4,500 for CF1, $3,100 for CF2, $2,400 for CF3,$1,800 for CF4 and 20% for r.
The NPV for discount rate of 20% is −$1,240.27.
Hence, NPV for discount rate of 10% and 20% is $285.47 and -$1,240.27 respectively.
e.
To explain: Whether NPV rule is consistent with IRR rule or not.
e.
Answer to Problem 10QP
Solution:
Yes, NPV rule is consistent with the internal rate of return method.
Explanation of Solution
NPV rule is consistent with IRR because according to both the methods, project with 10% discount rate is accepted and project with 20% discount rate should be discarded. It is because project is giving positive return only when 10% discount rate is used otherwise it is giving negative returns and it is consistent because, only once the signs of the cash flows changes.
Hence, NPV is consistent with the IRR rule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
UPENN: LOOSE LEAF CORP.FIN W/CONNECT
- AP Associates needs to raise $35 million. The investment banking firm of Squeaks, Emmie, andChippy will handle the transaction.a. If stock is used, 1,800,000 shares will be sold to the public at $21.30 per share. The corporation willreceive a net price of $20 per share. What is the percentage underwriting spread per share?b. If bonds are utilized, slightly over 37,500 bonds will be sold to the public at $1,000 per bond. Thecorporation will receive a net price of $980 per bond. What is the percentage of underwritingspread per bond? (Relate the dollar spread to the public price.)c. Which alternative has the larger percentage of spread?arrow_forwardGracie’s Dog Vests currently has 5,200,000 shares of stock outstanding and will report earnings of$8.8 million in the current year. The company is considering the issuance of 1,500,000 additionalshares that will net $28 per share to the corporation.a. What is the immediate dilution potential for this new stock issue?b. Assume that Grace’s Dog Vests can earn 8 percent on the proceeds of the stock issue in time toinclude them in the current year’s results. Calculate earnings per share. Should the new issuebe undertaken based on earnings per share?arrow_forwardYou plan to contribute seven payments of $2,000 a year, with the first payment made today (beginning of year 0) and the final payment made at the beginning of year 6, earning 11% annually. How much will you have after 6 years? a. $12,000 b.$21,718 c.$19,567 d.$3,741arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





