
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-TEXT
9th Edition
ISBN: 2810014920922
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.9, Problem 4.89P
The steel bar has the dimensions shown. Determine the maximum axial force P that can be applied so as not to exceed an allowable tensile stress of σallow = 150 MPa.
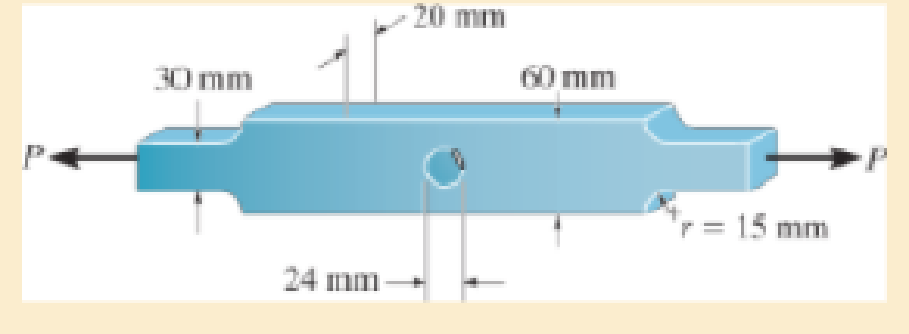
Prob. 4–89
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need drawing solution,draw each one by one no Ai
Qu. 17 Compute linear density values for [100] for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm''.
. Round off the
answer to three significant figures.
Qu. 18 Compute linear density value for [111] direction for silver (Ag). Express your answer in nm'. Round off the answer to three significant figures.
Qu. 19 Compute planar density value for (100) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm?.
Round off the answer to two significant figures.
Qu. 20 Compute planar density value for (110) plane for chromium (Cr). Express your answer in nm ≥ to four significant figures.
show all work please in material engineering
3-142
Chapter 4 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-TEXT
Ch. 4.2 - In each case, determine the internal normal force...Ch. 4.2 - Determine the internal normal force between...Ch. 4.2 - The post weighs 8kN/m. Determine the internal...Ch. 4.2 - The rod is subjected to an external axial force of...Ch. 4.2 - The rigid beam supports the load of 60 kN....Ch. 4.2 - The 20-mm-diameter A-36 steel rod is subjected to...Ch. 4.2 - Segments AB and CD of the assembly are solid...Ch. 4.2 - The 30-mm-diameter A992 steel rod is subjected to...Ch. 4.2 - If the 20-mm-diameter rod is made of A-36 steel...Ch. 4.2 - The 20-mm-diameter 2014-T6 aluminum rod is...
Ch. 4.2 - The 20-mm-diameter 2014-T6 aluminum rod is...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.1PCh. 4.2 - The copper shaft is subjected to the axial loads...Ch. 4.2 - The composite shaft, consisting of aluminum,...Ch. 4.2 - The composite shaft, consisting of aluminum,...Ch. 4.2 - 4-5. The assembly consists of a steel rod CB and...Ch. 4.2 - 4-6. The bar has a cross-sectional area of 3 in2,...Ch. 4.2 - 4–7. If P1 = 50 kip and P2 = 150 kip, determine...Ch. 4.2 - *4-8. If the vertical displacements of end A of...Ch. 4.2 - The assembly consists of two 10-mm diameter red...Ch. 4.2 - The assembly consists of two 10-mm diameter red...Ch. 4.2 - The load is supported by the four 304 stainless...Ch. 4.2 - The load is supported by the four 304 stainless...Ch. 4.2 - The rigid bar is supported by the pin-connected...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.14PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.15PCh. 4.2 - *4-16. The hanger consists of three 2014-T6...Ch. 4.2 - 4-17. The hanger consists of three 2014-T6...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.18PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.19PCh. 4.2 - The assembly consists of three titanium...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.21PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.22PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.23PCh. 4.2 - Determine the relative displacement of one end of...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.25PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.26PCh. 4.2 - 4-27. The circular bar has a variable radius of r...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.28PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.29PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.30PCh. 4.5 - 4-31. The concrete column is reinforced using four...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.32PCh. 4.5 - 4-33. The steel pipe is filled with concrete and...Ch. 4.5 - If column AB is made from high strength precast...Ch. 4.5 - If column AB is made from high strength precast...Ch. 4.5 - Determine the support reactions at the rigid...Ch. 4.5 - If the supports at A and C are flexible and have a...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.38PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.39PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.40PCh. 4.5 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod AC is reinforced with the...Ch. 4.5 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod AC is reinforced with the...Ch. 4.5 - The assembly consists of two red brass C83400...Ch. 4.5 - *4-44. The assembly consists of two red brass...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.45PCh. 4.5 - If the gap between C and the rigid wall at D is...Ch. 4.5 - The support consists of a solid red brass C83400...Ch. 4.5 - If there are n fibers, each having a...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.49PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.50PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.51PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.52PCh. 4.5 - 4-53. Each of the three A-36 steel wires has the...Ch. 4.5 - 4-54. The 200-kg load is suspended from three A-36...Ch. 4.5 - The three suspender bars are made of A992 steel...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.56PCh. 4.5 - 4-57. The rigid bar is originally horizontal and...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.58PCh. 4.5 - 4-59. Two identical rods AB and CD each have a...Ch. 4.5 - *4-60. The assembly consists of two posts AD and...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.61PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.62PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.63PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.64PCh. 4.5 - 4-65. Initially the A-36 bolt shank fits snugly...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.66PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.67PCh. 4.6 - The C83400-red-brass rod AB and 2014-T6- aluminum...Ch. 4.6 - The assembly has the diameters and material...Ch. 4.6 - The rod is made of A992 steel and has a diameter...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 4.71PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.72PCh. 4.6 - The pipe is made of A992 steel and is connected to...Ch. 4.6 - The bronze C86100 pipe has an inner radius of 0.5...Ch. 4.6 - The 40-ft-long A-36 steel rails on a train track...Ch. 4.6 - The device is used to measure a change in...Ch. 4.6 - The bar has a cross-sectional area A, length L,...Ch. 4.6 - When the temperature is at 30C, the A-36 steel...Ch. 4.6 - When the temperature is at 30C, the A-36 steel...Ch. 4.6 - When the temperature is at 30C, the A-36 steel...Ch. 4.6 - The 50-mm-diameter cylinder is made from Am...Ch. 4.6 - The 50-mm-diameter cylinder is made from Am...Ch. 4.6 - The wires AB and AC are made of steel, and wire AD...Ch. 4.6 - The cylinder CD of the assembly is heated from T1...Ch. 4.6 - The cylinder CD of the assembly is heated from T1=...Ch. 4.6 - The metal strap has a thickness t and width w and...Ch. 4.9 - Determine the maximum normal stress developed in...Ch. 4.9 - If the allowable normal stress for the bar is...Ch. 4.9 - The steel bar has the dimensions shown. Determine...Ch. 4.9 - 4-90. Determine the maximum axial force P that can...Ch. 4.9 - Determine the maximum axial force P that can be...Ch. 4.9 - Determine the maximum normal stress developed in...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 4.93PCh. 4.9 - 4-94. The resulting stress distribution along...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 4.95PCh. 4.9 - *4-96. The 10-mm-diameter shank of the steel bolt...Ch. 4.9 - The weight is suspended from steel and aluminum...Ch. 4.9 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 0.5 in2 and...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 4.99PCh. 4.9 - *4-100. The rigid beam is supported by a pin at A...Ch. 4.9 - The rigid lever arm is supported by two A-36 steel...Ch. 4.9 - The rigid lever arm is supported by two A-36 steel...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 4.103PCh. 4.9 - The rigid beam is supported by three 25-mm...Ch. 4.9 - The rigid beam is supported by three 25-mm...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 4.106PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.107PCh. 4.9 - The rigid beam is supported by the three posts A,...Ch. 4.9 - The rigid beam is supported by the three posts A,...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 4.110PCh. 4.9 - The bar having a diameter of 2 in. is fixed...Ch. 4.9 - Determine the elongation of the bar in Prob.4108...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 4.113PCh. 4 - The assembly consists of two A992 steel bolts AB...Ch. 4 - The assembly shown consists of two A992 steel...Ch. 4 - The rods each have the same 25-mm diameter and...Ch. 4 - Two A992 steel pipes, each having a...Ch. 4 - The force P is applied to the bar, which is made...Ch. 4 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 0.5 in....Ch. 4 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 0.5 in....Ch. 4 - The rigid link is supported by a pin at A and two...Ch. 4 - The joint is made from three A992 steel plates...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need solutionsarrow_forward3-137arrow_forwardLarge wind turbines with a power capacity of 8 MW and blade span diameters of over 160 m areavailable for electric power generation. Consider a wind turbine with a blade span diameter of 120m installed at a site subjected to steady winds at 8.25 m/s. Taking the overall efficiency of thewind turbine to be 33 percent and the air density to be 1.25 kg/m3, determine the electric powergenerated by this wind turbine. Also, assuming steady winds of 8.25 m/s during a 24-h period,determine the amount of electric energy and the revenue generated per day for a unit price of$0.08/kWh for electricity.arrow_forward
- The basic barometer can be used to measure the height of a building. If the barometric readingsat the top and at the bottom of a building are 672 and 696 mmHg, respectively, determine theheight of the building. Take the densities of air and mercury to be 1.18 kg/m3 and 13,600 kg/m3,respectivelyarrow_forwardA 7.25-hp (shaft) pump is used to raise water to an elevation of 17 m. If the mechanical efficiencyof the pump is 84 percent, determine the maximum volume flow rate of water.arrow_forwardConsider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown below. If the specific gravity ofone fluid is 13.8, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolutepressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 95 kPaarrow_forward
- A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. Disregard the 70 m in the picture. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I'm having trouble getting the correct y component of acceleration. all the other answers are correct. thank you!arrow_forwardFigure: 06_P041 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing a Prentice Hall 2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also a pin at F. 400 mm 15° 20 mm A 15° 15 D B 30 mm² 80 mm 20 mm 400 mm Figure: 06_P090 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall 15° 100 N 100 N 15°arrow_forwardA telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license