
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134156415
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.6, Problem 17CYU
What type of membrane lines the thoracic walls and covers the lungs, and what is it called?
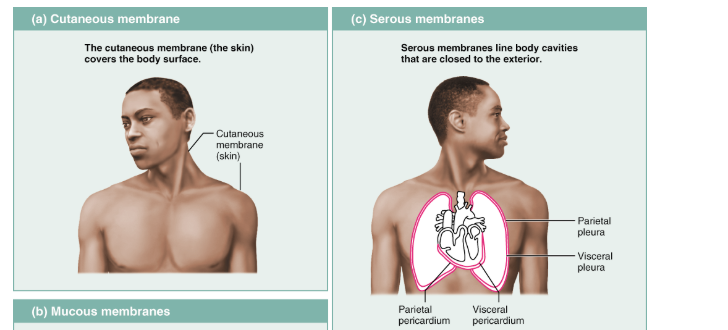
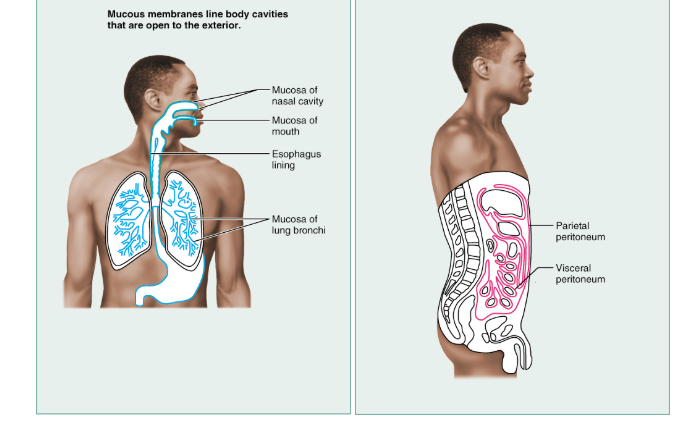
Figure 4.11 Classes of membranes.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Biology grade 10 study guide
I would like to see a professional answer to this so I can compare it with my own and identify any points I may have missed
what key characteristics would you look for when identifying microbes?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 1CYUCh. 4.1 - Prob. 2CYUCh. 4.2 - Epithelial tissue is the only tissue type that has...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4CYUCh. 4.2 - Stratified epithelia are built for protection or...Ch. 4.2 - Some epithelia are pseudostratified. What does...Ch. 4.2 - Where is transitional epithelium found and what is...Ch. 4.3 - What are four functions of connective tissue?Ch. 4.3 - What are the three types of fibers found in...Ch. 4.3 - Which connective tissue has a soft weblike matrix...
Ch. 4.3 - What type of connective tissue is damaged when you...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 12CYUCh. 4.4 - You are looking at muscle tissue through the...Ch. 4.4 - Which muscle type(s) is voluntary? Which is...Ch. 4.5 - How does the extended length of a neurons...Ch. 4.6 - What type of membrane consists of epithelium and...Ch. 4.6 - What type of membrane lines the thoracic walls and...Ch. 4.6 - MAKING CONNECTIONS The two layers of serous...Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 19CYUCh. 4.7 - Why does a deep injury to the skin result in...Ch. 4 - Use the key to classify each of the following...Ch. 4 - An epithelium that has several layers, with an...Ch. 4 - Match the epithelial types named in column B with...Ch. 4 - The gland type that secretes products such as...Ch. 4 - The membrane which lines body cavities that open...Ch. 4 - Scar tissue is a variety of (a) epithelium, (b)...Ch. 4 - Define tissue.Ch. 4 - Name four important functions of epithelial tissue...Ch. 4 - Describe the criteria used to classify covering...Ch. 4 - Prob. 10SAQCh. 4 - Provide examples from the body that illustrate...Ch. 4 - Name the primary cell type in connective tissue...Ch. 4 - Name the two major components of matrix and, if...Ch. 4 - Matrix is extracellular. How does the matrix get...Ch. 4 - Name the specific connective tissue type found in...Ch. 4 - What is the function of macrophages?Ch. 4 - Differentiate between the roles of neurons and the...Ch. 4 - Compare and contrast skeletal, cardiac, and smooth...Ch. 4 - Describe the process of tissue repair, making sure...Ch. 4 - In what ways are adipose tissue and bone similar?...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If you had an unknown microbe, what steps would you take to determine what type of microbe (e.g., fungi, bacteria, virus) it is? Are there particular characteristics you would search for? Explain.arrow_forwardavorite Contact avorite Contact favorite Contact ୫ Recant Contacts Keypad Messages Pairing ง 107.5 NE Controls Media Apps Radio Nav Phone SCREEN OFF Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help newconnect.mheducation.com M Sign in... S The Im... QFri May 9 9:23 PM w The Im... My first.... Topic: Mi Kimberl M Yeast F Connection lost! You are not connected to internet Sigh in... Sign in... The Im... S Workin... The Im. INTRODUCTION LABORATORY SIMULATION Tube 1 Fructose) esc - X Tube 2 (Glucose) Tube 3 (Sucrose) Tube 4 (Starch) Tube 5 (Water) CO₂ Bubble Height (mm) How to Measure 92 3 5 6 METHODS RESET #3 W E 80 A S D 9 02 1 2 3 5 2 MY NOTES LAB DATA SHOW LABELS % 5 T M dtv 96 J: ப 27 כ 00 alt A DII FB G H J K PHASE 4: Measure gas bubble Complete the following steps: Select ruler and place next to tube 1. Measure starting height of gas bubble in respirometer 1. Record in Lab Data Repeat measurement for tubes 2-5 by selecting ruler and move next to each tube. Record each in Lab Data…arrow_forwardCh.23 How is Salmonella able to cross from the intestines into the blood? A. it is so small that it can squeeze between intestinal cells B. it secretes a toxin that induces its uptake into intestinal epithelial cells C. it secretes enzymes that create perforations in the intestine D. it can get into the blood only if the bacteria are deposited directly there, that is, through a puncture — Which virus is associated with liver cancer? A. hepatitis A B. hepatitis B C. hepatitis C D. both hepatitis B and C — explain your answer thoroughlyarrow_forward
- Ch.21 What causes patients infected with the yellow fever virus to turn yellow (jaundice)? A. low blood pressure and anemia B. excess leukocytes C. alteration of skin pigments D. liver damage in final stage of disease — What is the advantage for malarial parasites to grow and replicate in red blood cells? A. able to spread quickly B. able to avoid immune detection C. low oxygen environment for growth D. cooler area of the body for growth — Which microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum — explain your answer thoroughlyarrow_forwardCh.22 Streptococcus pneumoniae has a capsule to protect it from killing by alveolar macrophages, which kill bacteria by… A. cytokines B. antibodies C. complement D. phagocytosis — What fact about the influenza virus allows the dramatic antigenic shift that generates novel strains? A. very large size B. enveloped C. segmented genome D. over 100 genes — explain your answer thoroughlyarrow_forwardWhat is this?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology A-C components of the question are corresponding to attached image labeled 1. D component of the question is corresponding to attached image labeled 2. For a eukaryotic mRNA, the sequences is as follows where AUGrepresents the start codon, the yellow is the Kozak sequence and (XXX) just represents any codonfor an amino acid (no stop codons here). G-cap and polyA tail are not shown A. How long is the peptide produced?B. What is the function (a sentence) of the UAA highlighted in blue?C. If the sequence highlighted in blue were changed from UAA to UAG, how would that affecttranslation? D. (1) The sequence highlighted in yellow above is moved to a new position indicated below. Howwould that affect translation? (2) How long would be the protein produced from this new mRNA? Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Explain why the cell doesn’t need 61 tRNAs (one for each codon). Please help. Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology You discover a disease causing mutation (indicated by the arrow) that alters splicing of its mRNA. This mutation (a base substitution in the splicing sequence) eliminates a 3’ splice site resulting in the inclusion of the second intron (I2) in the final mRNA. We are going to pretend that this intron is short having only 15 nucleotides (most introns are much longer so this is just to make things simple) with the following sequence shown below in bold. The ( ) indicate the reading frames in the exons; the included intron 2 sequences are in bold. A. Would you expected this change to be harmful? ExplainB. If you were to do gene therapy to fix this problem, briefly explain what type of gene therapy youwould use to correct this. Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you Explain what is meant by the term “defective virus.” Explain how a defective virus is able to replicate.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain why changing the codon GGG to GGA should not be harmful. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardStage Percent Time in Hours Interphase .60 14.4 Prophase .20 4.8 Metaphase .10 2.4 Anaphase .06 1.44 Telophase .03 .72 Cytukinesis .01 .24 Can you summarize the results in the chart and explain which phases are faster and why the slower ones are slow?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning


Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Types of Human Body Tissue; Author: MooMooMath and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O0ZvbPak4ck;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY