
Mechanics of Materials
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605460
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education (US)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.5, Problem 33P
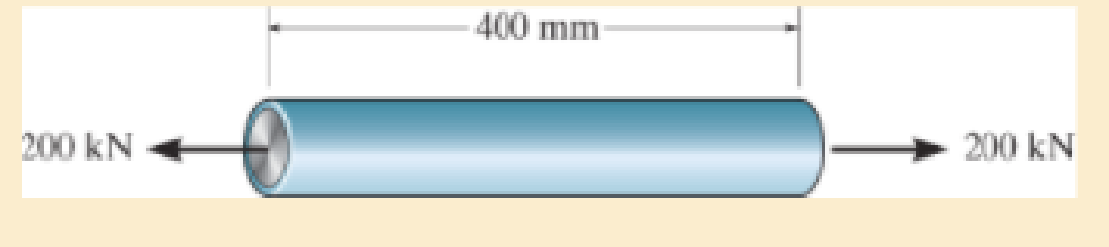
The A-36 steel pipe has a 6061-T6 aluminum core. It is subjected to a tensile force of 200 kN. Determine the average normal stress in the aluminum and the steel due to this loading. The pipe has an outer diameter of 80 mm and an inner diameter of 70 mm
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Chapter 4 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 4.2 - The 20-mm-diameter A-36 steel rod is subjected to...Ch. 4.2 - Segments AB and CD of the assembly are solid...Ch. 4.2 - The 30-mm-diameter A992 steel rod is subjected to...Ch. 4.2 - If the 20-mm-diameter rod is made of A-36 steel...Ch. 4.2 - The 20-mm-diameter 2014-T6 aluminum rod is...Ch. 4.2 - The 20-mm-diameter 2014-T6 aluminum rod is...Ch. 4.2 - The copper shaft is subjected to the axial loads...Ch. 4.2 - The A-36 steel rod is subjected to the loading...Ch. 4.2 - The A-36 steel rod is subjected to the loading...Ch. 4.2 - The A-36 steel drill shaft of an oil well extends...
Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 8PCh. 4.2 - The post is made of Douglas fir and has a diameter...Ch. 4.2 - The post is made of Douglas fir and has a diameter...Ch. 4.2 - The coupling rod is subjected to a force of 5 kip....Ch. 4.2 - The pipe is stuck in the ground so that when it is...Ch. 4.2 - The assembly consists of three titanium...Ch. 4.2 - The assembly consists of two rigid bars that are...Ch. 4.2 - The truss consists of three members, each made...Ch. 4.2 - Solve Prob. 426 when the load P acts vertically...Ch. 4.2 - The ball is truncated at its ends and is used to...Ch. 4.5 - The column is constructed from high-strength...Ch. 4.5 - The column is constructed from high-strength...Ch. 4.5 - The A-36 steel pipe has a 6061-T6 aluminum core....Ch. 4.5 - The 304 stainless steel post A has a diameter of...Ch. 4.5 - The 304 stainless steel post A is surrounded by a...Ch. 4.5 - The 10-mm-diameter steel bolt is surrounded by a...Ch. 4.5 - The rigid beam is supported by the three suspender...Ch. 4.5 - The bolt AB has a diameter of 20 mm and passes...Ch. 4.5 - If the gap between C and the rigid wall at D is...Ch. 4.5 - The support consists of a solid red brass C83400...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 55PCh. 4.5 - The three A-36 steel wires each have a diameter of...Ch. 4.5 - The A-36 steel wires AB and AD each have a...Ch. 4.5 - The assembly consists of two posts AB and CD each...Ch. 4.5 - The assembly consists of two posts AB and CD each...Ch. 4.5 - The assembly consists of two posts AB and CD each...Ch. 4.5 - The wheel is subjected to a force of 18 kN from...Ch. 4.6 - The C83400-red-brass rod AB and 2014-T6- aluminum...Ch. 4.6 - The assembly has the diameters and material...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 77PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 80PCh. 4.6 - The 50-mm-diameter cylinder is made from Am...Ch. 4.6 - The 50-mm-diameter cylinder is made from Am...Ch. 4.6 - The metal strap has a thickness t and width w and...Ch. 4.9 - Determine the maximum normal stress developed in...Ch. 4.9 - If the allowable normal stress for the bar is...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 89PCh. 4.9 - The A-36 steel plate has a thickness of 12 mm. If...Ch. 4.9 - Determine the maximum axial force P that can be...Ch. 4.9 - Determine the maximum normal stress developed in...Ch. 4.9 - The member is to be made from a steel plate that...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 96PCh. 4.9 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 0.5 in2 and...Ch. 4.9 - The distributed loading is applied to the rigid...Ch. 4.9 - The distributed loading is applied to the rigid...Ch. 4.9 - The rigid lever arm is supported by two A-36 steel...Ch. 4.9 - The rigid lever arm is supported by two A-36 steel...Ch. 4.9 - The wire BC has a diameter of 0.125 in. and the...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 104PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 106PCh. 4 - The assembly consists of two A992 steel bolts AB...Ch. 4 - The assembly shown consists of two A992 steel...Ch. 4 - The rods each have the same 25-mm diameter and...Ch. 4 - Two A992 steel pipes, each having a...Ch. 4 - The force P is applied to the bar, which is made...Ch. 4 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 0.5 in....Ch. 4 - The 2014-T6 aluminum rod has a diameter of 0.5 in....Ch. 4 - The rigid link is supported by a pin at A and two...Ch. 4 - The joint is made from three A992 steel plates...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- [Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forwardcan you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forward
- hi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forwardHi, can you please help me .Identify and justify suitable analytical techniques of the scenario below, bearing in mind the kinds of information being handled to reach a conclusion (methodology). A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of…arrow_forwardHi, can you please define and calculate the failure mode of the linkage that failed on the swing (images added) : A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of a caged-type seat. However, the location was within the play area not…arrow_forward
- Page 11-68. The rectangular plate shown is subjected to a uniaxial stress of 2000 psi. Compute the shear stress and the tensile developed on a plane forming an angle of 30° with the longitud axis of the member. (Hint: Assume a cross-sectional area of unity) 2000 psi 2000 psi hparrow_forward11-70. A shear stress (pure shear) of 5000 psi exists on an element. (a) Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses caused in the element due to this shear. (b) Sketch the element showing the planes on which the maximum tensile and compressive stresses act.arrow_forward11-20. An aluminum specimen of circular cross section, 0.50 in. in diameter, ruptured under a tensile load of 12,000 lb. The plane of failure was found to be at 48° with a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the specimen. (a) Compute the shear stress on the failure plane. (b) Compute the maximum tensile stress. (c) Compute the tensile stress on the failure plane. hparrow_forward
- A long flat steel bar 13 mm thick and 120 mm wide has semicircular grooves as shown and carries a tensile load of 50 kN Determine the maximum stress if plate r= 8mm r=21mm r=38mmarrow_forwardProblem 13: F₁ = A =250 N 30% Determine the moment of each of the three forces about point B. F₂ = 300 N 60° 2 m -3 m B 4 m F3=500 Narrow_forward3 kN 3 kN 1.8 kN/m 80 mm B 300 mm D an 1.5 m-1.5 m--1.5 m- PROBLEM 5.47 Using the method of Sec. 5.2, solve Prob. 5.16 PROBLEM 5.16 For the beam and loading shown, determine the maximum normal stress due to bending on a transverse section at C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license