
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781260159080
Author: Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 44, Problem F44.14A
FIGURE 44.14 identity the features indicated on this anterior view of a frontal section of a human heart model using the terms provided (Note: The pulmonary valve is not shown on the portion of the model photographed)
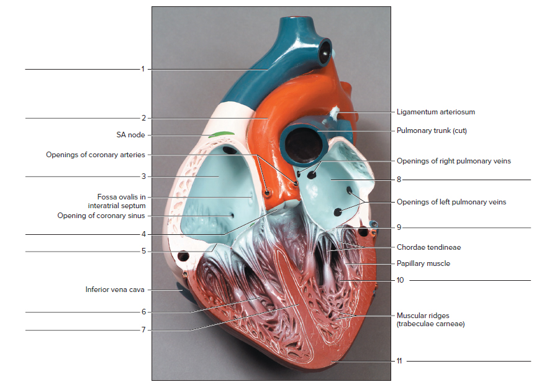
Terms:
Aorta Left atrium
Right ventricle
Aortic valve
Left ventricle
Superior vena cava
Apex of heart
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
Interventricularseptum
Right atrium
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Structure of the Heart
Use this table as a checklist for your study of the heart. Do not forget to fill in the function column.
Structure
Right atrium
Computer
Simulation Function(s)
Sheep
Human
Left atrium
Right ventricle
ロ
Left ventricle
Interventricular sulcus
Anterior interventricular artery
ロ
Great cardiac vein
Small cardiac vein
Right coronary artery
Circumflex artery
Left coronary artery
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
Superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Interventricular septum
Myocardium
ロ
Epicardium
Parietal pericardium
Pericardial space
Fibrous pericardium
ロ
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
Chordae tendineae
Papillary muscle
ロ
Aortic semilunar valve
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
323
Drag the steps below and place them in the order of blood flow through the heart.
First:
Second:
Third:
Fourth:
Fifth:
Sixth:
Seventh:
Eighth:
Ninth:
Tenth:
Flows through right atrial ventricular valve (tricuspid)
Blood back flowing in aorta toward heart enters coronary circulation
Flowing into the right atrium
Out the aortic semilunar valve into the aorta
Back to heart through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium
Into the right ventricle
Into the left ventricle
Left atrium through left atrial ventricular valve (BICUSPID OR MITRAL)
Out the pulmonary semilunar valve through the pulmonary arteries to lungs
To the body through the aortic branches
NOTES
and the left side serving the systemic circuit. In Figure 16-15, complete
the schematic showing the blood flow to and from the heart (the starting
points are given to you). Use a blue pen or pencil to denote the direction of
deoxygenated blood and a red pen or pencil for oxygenated blood flow.
Include the names of the major vessels, chambers, and valves involved,
based on the following list:
lung capillary beds
body capillary beds
right ventricle
left ventricle
bicuspid valve
superior vena cava
tricuspid valve
inferior vena cava
pulmonary semilunar valve
pulmonary trunk
aortic semilunar valve
R. and L. pulmonary arteries
R. and L. pulmonary veins
aorta
Pulmonary Circulation
Systemic Circulation
Right atrium
Left atrium
URA--YCK
HAT
Lungs
Body
Figure 16-15. Schematic of circulation
Chapter 44 Solutions
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Ch. 44 - The ________is the inferior end of the heart that...Ch. 44 - Oxygen-rich blood is located in the a. left-side...Ch. 44 - The two superior heart chambers are the a. left...Ch. 44 - Which of the following is an atrioventricular (AV)...Ch. 44 - The __________ lines the heart chambers. a....Ch. 44 - Which heart valve has two cusp s instead of three...Ch. 44 - Chordae tendineae connect the cusps of the AV...Ch. 44 - The systemic circuit delivers blood to the lungs...Ch. 44 - The right and left coronary arteries containing...Ch. 44 - FIGURE 44.13 Identity the features on this...
Ch. 44 - FIGURE 44.14 identity the features indicated on...Ch. 44 - FIGURE 44.15 Label this frontal section of the...Ch. 44 - Prob. 2.1ACh. 44 - Compare the structure of the left atrioventricular...Ch. 44 - Prob. 3.2ACh. 44 - What is the functional significance of the...Ch. 44 - List the correct pathway through which blood must...Ch. 44 - Describe the general overall shape of the left and...Ch. 44 - What was the measured thickness of the left...Ch. 44 - Explain the functional significance of the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please list in order the chambers and valves blood passes through on its way through the heart. Identify whether blood has high or low oxygen content as it passes through each structure.Start with the vessel returning blood to the heart from the systemic circulation: ____________________ (superior structures) or _____________________ (inferior structures)↓____________________↓____________________↓____________________↓____________________↓Pulmonary trunk↓Left and right pulmonary arteries↓Lungs↓Vessels returning oxygenated blood to the heart = ______________________ ↓____________________↓____________________↓____________________↓Aorta (systemic circulation)arrow_forwardWhat is the tissue type for the following structures of the heart Fibrous pericardium Serous pericardium Myocardium Endocardium Right atrium right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Auricles Papillary muscles Fossa Ovalis Pectinate Muscles Chordae Tendinae Interventricular septum Tricuspid, pulmonary, Bicuspid, mitral, and Aortic semilunar valves pulmonary trunk Pulmonary artery Aorta Arteries Sinus/veinsarrow_forwardIn the figure below on the left, label the P, QRS and T waves. Describe what is happening in the heart in the P wave: Relate the P wave to the cardiac cycle:o Is the heart in systole or diastole?o Is the pressure high or low?o Where is blood flowing? Which valves are open? closed? o Which muscle fibers are contracting, if any?arrow_forward
- Identify whether the given statement is true or false -Left ventricle->Left atrium->Right ventricle->Right atrium is the correct sequence for blood entering the heart through the vena cavae and leaving through the aorta. -The sinoatrial node is situated in the wall of the interventricular septum. -Impulses through the conduction system of the heart follow the ordered path: SA node->conduction myofibers->AV bundle->AV node. -The heart is covered by the suprardium. -The “lub” sound of the heart is caused by closing of the semilunar valves. -To clearly hear the heart sound of the bicuspid valve, a stethoscope should be placed to the left of the sternum at the second intercostal space. -The left ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right wall in order to pump blood with a greater pressure. -When the atrioventricular bundle is completely interrupted the ventricles typically contract at 30 to 40 beats/min. -At late diastole, the atria and ventricles are relaxed…arrow_forwardName a structure that is on the ventural side of the heart located more laterally within the axial regionarrow_forwardThe four-chambered heart is a single organ but is sometimes described as a “double pump” because it functions more like two pumps than one. Explain why this is so, including the names of the heart structures involved. please helparrow_forward
- The diagrams show structures that comprise the external and internal regions of the heart. Label the components A to Larrow_forwardPlease explain blood flow through your body in a flow diagram format (do not put a picture of heart or write a paragraph). Start and end at the inferior/superior vena cava. (HINT: make sure you mention all the valves within the heart and where does blood go from deoxygenated to oxygenated and vice versa).arrow_forwardIdentify whether the following statement is either true or false. Left ventricle->Left atrium->Right ventricle->Right atrium is the correct sequence for blood entering the heart through the vena cavae and leaving through the aorta. The sinoatrial node is situated in the wall of the interventricular septum. Impulses through the conduction system of the heart follow the ordered path: SA node->conduction myofibers->AV bundle->AV node. To clearly hear the heart sound of the bicuspid valve, a stethoscope should be placed to the left of the sternum at the second intercostal space. At late diastole, the atria and ventricles are relaxed and the aortic semilunar valve is open. During ventricular contraction all the blood is forced out of the ventricles.arrow_forward
- The events of the cardiac cycle cause cyclical changes in left ventricular pressure and volume over time. Another way to represent these events is with a pressure-volume loop, as shown below. Drag the labels from the left into the appropriate boxes on the pressure- volume loop to demonstrate your understanding of the cardiac cycle. Aortic valve closure AV valve opening Systolic pressure Isovolumetric relaxation Isovolumetric contraction 120 Diastolic pressure Ventricular filling 80 End-diastolic volume Ventricular ejection 40 AV valve closure End-systolic volume Aortic valve opening 60 120 LV volume (mL) O McGraw-Hill Education Reset LV pressure (mm Hg)arrow_forwardDraw and Label the sheep’s heart in the external anterior and posterior views. Include the coronary arteries and cardiac veins. List the similarities and differences in the microanatomy of arteries and veins.arrow_forwardUse an arrow to indicate where DORV would occur on the flow chart (right ventricle to aorta and pulmonary trunk)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Respiratory System; Author: Amoeba Sisters;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v_j-LD2YEqg;License: Standard youtube license