
Iguana Decline In 1987, Martin Wikelski began a long-term study of marine iguanas in the Galápagos Islands. He marked iguanas on two islands—Genovesa and Santa Fe—and collected data on how their body size, survival, and reproductive rates varied over time. He found that because iguanas eat algae and have no predators, deaths usually result from food shortages, disease, or old age. In January 2001, an oil tanker ran aground and leaked a small amount of oil into the waters near Santa Fe. FIGURE 44.3 shows the number of marked iguanas that Wikelski and his team counted in their study populations just before the spill and about a year later.
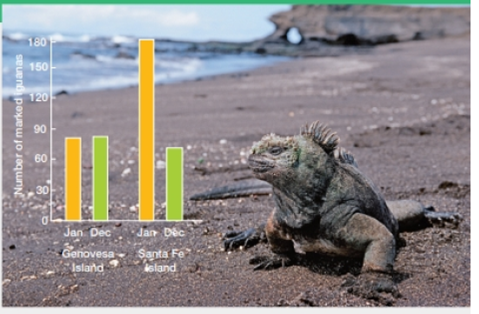
FIGURE 44.3 Shifting numbers of marked marine iguanas on two Galápagos islands. An oil spill occurred near Santa Fe just after the January 2001 census (orange bars). A second census was carried out in December 2001 (green bars).
Which island had more marked iguanas at the time of the first census?
To examine: The Island that has a greater population size of marine during the first census study.
Concept introduction: Marine iguanas are kind of reptiles but unique among the modern lizards. They feed on algae and large species find its food source on the tidal region as they live in rocky shores. These are currently considered as threatened species due to the poaching, negative effects of introduced species, loss, and fragmentation of habitat. Many NGO’s and program researchers have taken part in protecting these species by creating artificial nesting sites.
Explanation of Solution
The research group of Person M conducted the long- term study of marine iguanas in Galapagos Islands. The study on the population of marine iguanas was done on island Gen and island SF in the year 2001. This study tells about their body size, survival, and the reproductive rate over the period of time. During this year, the oil spill occurred near the island SF and led to the loss of marine iguanas species. They observed the population of marked marine iguanas on two islands over the period of a year by conducting two surveys.
Refer Fig. 44.3, “Shifting numbers of marked marine iguanas on two Galapagos islands” in the textbook. The graphical representation shows the number of marked iguanas in island Gen and island SF. Marked iguanas are identified on both islands. The island that had greater number of marked marine iguana population at the time of the first census is island SF.
Compared to island Gen, island SF has more marked marine iguanas during the first census study.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 44 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- please draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forwardplease answer all question below with the following answer choice, thank you!arrow_forward
- please draw in the answeres, thank youarrow_forwardA) What is being shown here?B) What is indicated by the RED arrow?C) What is indicated by the BLUE arrow?arrow_forwardPlease identify the curve shown below. What does this curve represent? Please identify A, B, C, D, and E (the orange oval). What is occurring in these regions?arrow_forward
- Please identify the test shown here. 1) What is the test? 2) What does the test indicate? How is it performed? What is CX? 3) Why might the test be performed in a clinical setting? GEN CZ CX CPZ PTZ CACarrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using fermentation of a 50 mM glucose solution?arrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration of a 7 mM glucose solution?arrow_forward
- Determine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration to degrade one small protein molecule into 12 molecules of malic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Malic acid is an intermediate in the Krebs cycle. Assume there is no other carbon source and no acetyl-CoA.arrow_forwardIdentify each of the major endocrine glandsarrow_forwardCome up with a few questions and answers for umbrella species, keystone species, redunant species, and aquatic keystone speciesarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





