
Concept explainers
Student Financial Aid In a recent year 8,073,000 male students and 10,980,000 female students were enrolled as undergraduates. Receiving aid were 60.6% of the male students and 65.2% of the female students. Of those receiving aid, 44.8% of the males got federal aid and 50.4% of the females got federal aid. Choose 1 student at random. (Hint: Make a tree diagram.) Find the
a. A male student without aid
b. A male student, given that the student has aid
c. A female student or a student who receives federal aid
Source: www.nces.gov
a.
To find: The probability that the student is a male student without aid.
Answer to Problem 19E
The probability that the student is a male student without aid is 0.167.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
There is one student is chosen at random. There are 8,073,000 male students and 10,980,000 female students in which aid were 60.6% of the male students and 65.2% of the female students. Of those receiving aid, 44.8% of the males got federal aid and 50.4% of the females got federal aid.
Calculation:
Multiplication rule for dependent events:
If the events A and B are dependent, the probability of occurring of event B is affected by event A, that is
Let event M denote that student is a male and WOA be denote that selecting student has without aids.
Here, there are 8,073,000 male students and 10,980,000 female students.
Also, the tree diagram is shown below:
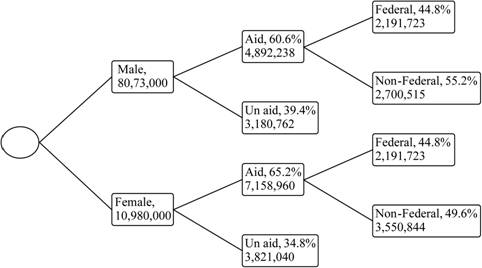
The frequency for the class is 8,073,000. Also, the total frequency is,
The formula for probability of event M is,
Substitute 8,073,000 for ‘Frequency for the class’ and 19,053,000 for ‘Total frequencies in the distribution’,
Thus, the probability that the student is a male is 0.424.
Also, from the tree diagram it is observed that the probability that the without aid in male students are 0.394.
By applying multiplication rule, the probability that the student is a male student without aid is,
Thus, the probability that the student is a male student without aid is 0.167.
b.
To find: The probability that the student is a male student, given that the student has aid.
Answer to Problem 19E
The probability that the student is a male student, given that the student has aid is 0.406.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Let event F denote that student is a female and WA be denote that selecting student has with aids.
From the part (a), it is observed that the probability that the student is a male student is 0.424then the probability that the student is a female student is 0.576
From, tree diagram it is observed that the probability that the students has aid in males is 0.606 and the probability that the students has aid in females is 0.652.
By applying multiplication rule, the probability that that the student has aid is,
The required probability is,
Then, the probability that the student is a male student and the student has aid is,
Then, the probability that the student is a male student, given that the student has aid is,
Thus, the probability that the student is a male student, given that the student has aid is 0.406.
c.
To find: The probability that the student is a female student or a student who receives federal aid.
Answer to Problem 19E
The probability that the student is a female student or a student who receives federal aid is 0.691.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Let event FA denote that student has federal aid.
From, part (b) it is observed that the student is a female student is 0.576. Also, from tree graph it is observed that the probability that the student has aid in males is 0.606 and in which federal aids are 0.448. Also, the probability that the student has aid in females is 0.652 and in which federal aids are 0.448.
By applying multiplication rule, the probability that the student has federal aid is,
Then, the probability that the student is a female student and the student has federal aid is,
Addition Rule:
The formula for probability of getting event F or event FA is,
Substitute 0.576 for
Thus, the probability that the student is a female student or a student who receives federal aid is 0.691
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
- 2PM Tue Mar 4 7 Dashboard Calendar To Do Notifications Inbox File Details a 25/SP-CIT-105-02 Statics for Technicians Q-7 Determine the resultant of the load system shown. Locate where the resultant intersects grade with respect to point A at the base of the structure. 40 N/m 2 m 1.5 m 50 N 100 N/m Fig.- Problem-7 4 m Gradearrow_forwardNsjsjsjarrow_forwardA smallish urn contains 16 small plastic bunnies - 9 of which are pink and 7 of which are white. 10 bunnies are drawn from the urn at random with replacement, and X is the number of pink bunnies that are drawn. (a) P(X=6)[Select] (b) P(X>7) ≈ [Select]arrow_forward
- A smallish urn contains 25 small plastic bunnies - 7 of which are pink and 18 of which are white. 10 bunnies are drawn from the urn at random with replacement, and X is the number of pink bunnies that are drawn. (a) P(X = 5)=[Select] (b) P(X<6) [Select]arrow_forwardElementary StatisticsBase on the same given data uploaded in module 4, will you conclude that the number of bathroom of houses is a significant factor for house sellprice? I your answer is affirmative, you need to explain how the number of bathroom influences the house price, using a post hoc procedure. (Please treat number of bathrooms as a categorical variable in this analysis)Base on the same given data, conduct an analysis for the variable sellprice to see if sale price is influenced by living area. Summarize your finding including all regular steps (learned in this module) for your method. Also, will you conclude that larger house corresponding to higher price (justify)?Each question need to include a spss or sas output. Instructions: You have to use SAS or SPSS to perform appropriate procedure: ANOVA or Regression based on the project data (provided in the module 4) and research question in the project file. Attach the computer output of all key steps (number) quoted in…arrow_forwardElementary StatsBase on the given data uploaded in module 4, change the variable sale price into two categories: abovethe mean price or not; and change the living area into two categories: above the median living area ornot ( your two group should have close number of houses in each group). Using the resulting variables,will you conclude that larger house corresponding to higher price?Note: Need computer output, Ho and Ha, P and decision. If p is small, you need to explain what type ofdependency (association) we have using an appropriate pair of percentages. Please include how to use the data in SPSS and interpretation of data.arrow_forward
- An environmental research team is studying the daily rainfall (in millimeters) in a region over 100 days. The data is grouped into the following histogram bins: Rainfall Range (mm) Frequency 0-9.9 15 10 19.9 25 20-29.9 30 30-39.9 20 ||40-49.9 10 a) If a random day is selected, what is the probability that the rainfall was at least 20 mm but less than 40 mm? b) Estimate the mean daily rainfall, assuming the rainfall in each bin is uniformly distributed and the midpoint of each bin represents the average rainfall for that range. c) Construct the cumulative frequency distribution and determine the rainfall level below which 75% of the days fall. d) Calculate the estimated variance and standard deviation of the daily rainfall based on the histogram data.arrow_forwardAn electronics company manufactures batches of n circuit boards. Before a batch is approved for shipment, m boards are randomly selected from the batch and tested. The batch is rejected if more than d boards in the sample are found to be faulty. a) A batch actually contains six faulty circuit boards. Find the probability that the batch is rejected when n = 20, m = 5, and d = 1. b) A batch actually contains nine faulty circuit boards. Find the probability that the batch is rejected when n = 30, m = 10, and d = 1.arrow_forwardTwenty-eight applicants interested in working for the Food Stamp program took an examination designed to measure their aptitude for social work. A stem-and-leaf plot of the 28 scores appears below, where the first column is the count per branch, the second column is the stem value, and the remaining digits are the leaves. a) List all the values. Count 1 Stems Leaves 4 6 1 4 6 567 9 3688 026799 9 8 145667788 7 9 1234788 b) Calculate the first quartile (Q1) and the third Quartile (Q3). c) Calculate the interquartile range. d) Construct a boxplot for this data.arrow_forward
- Pam, Rob and Sam get a cake that is one-third chocolate, one-third vanilla, and one-third strawberry as shown below. They wish to fairly divide the cake using the lone chooser method. Pam likes strawberry twice as much as chocolate or vanilla. Rob only likes chocolate. Sam, the chooser, likes vanilla and strawberry twice as much as chocolate. In the first division, Pam cuts the strawberry piece off and lets Rob choose his favorite piece. Based on that, Rob chooses the chocolate and vanilla parts. Note: All cuts made to the cake shown below are vertical.Which is a second division that Rob would make of his share of the cake?arrow_forwardThree players (one divider and two choosers) are going to divide a cake fairly using the lone divider method. The divider cuts the cake into three slices (s1, s2, and s3). If the choosers' declarations are Chooser 1: {s1 , s2} and Chooser 2: {s2 , s3}. Using the lone-divider method, how many different fair divisions of this cake are possible?arrow_forwardTheorem 2.6 (The Minkowski inequality) Let p≥1. Suppose that X and Y are random variables, such that E|X|P <∞ and E|Y P <00. Then X+YpX+Yparrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning




