
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
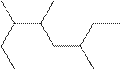
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
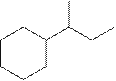
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
The compounds in which a series of atoms are connected to form a ring is known as cyclic compound whereas the compounds which are open chain compounds and whose atoms don't form a ring is known as acyclic compounds. The general molecular formula of a cyclic alkane is
Rules of naming cycloalkanes are:
- First, determine the cycloalkane present in the structure which is considered as a parent chain (maximum number of carbon atoms). If the acyclic alkane chain has more carbon atoms, then the alkyl chain is considered a parent chain.
- For a cyclic system, the number of carbon atoms must be identified as present in different paths connected with two bridgeheads.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group or cycloalkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number
- The alkyl groups or cycloalkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.

Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
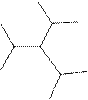
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(e)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
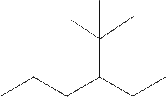
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(f)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
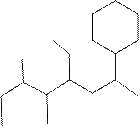
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(g)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
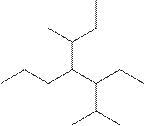
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(h)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
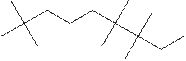
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(i)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.

Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(j)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
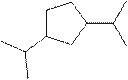
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
The compounds in which a series of atoms are connected to form a ring is known as cyclic compound whereas the compounds which are open chain compounds and whose atoms don't form a ring is known as acyclic compounds. The general molecular formula of a cyclic alkane is
Rules of naming cycloalkanes are:
- First, determine the cycloalkane present in the structure which is considered as a parent chain (maximum number of carbon atoms). If the acyclic alkane chain has more carbon atoms, then the alkyl chain is considered a parent chain.
- For a cyclic system, the number of carbon atoms must be identified as present in different paths connected with two bridgeheads.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group or cycloalkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups or cycloalkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(k)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
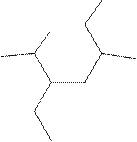
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM PRINT STUDY GDE & SSM
- + C8H16O2 (Fatty acid) + 11 02 → 8 CO2 a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? H2o CO₂ c. Which reactant is the electron donor? Futty acid d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? e. Which of the product is now reduced? f. Which of the products is now oxidized? 02 #20 102 8 H₂O g. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 2 h. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward→ Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + 1FAD + 1ADP 2CO2 + CoA + 3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? d. Which reactants are the electron acceptors? e. Which of the products are now reduced? f. Which product is now oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. OCH 3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) Br (Choose one) Explanation Check NO2 (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Aarrow_forward
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Assign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forwardRank each set of substituents using the Cahn-Ingold-Perlog sequence rules (priority) by numbering the highest priority substituent 1.arrow_forward

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT




