
Concept explainers
(a)
The angle
(a)
Answer to Problem 4.90P
The angle
Explanation of Solution
The free-body diagram corresponding to the arrangement in Fig. P4.89 is given in Figure 1. The reaction at
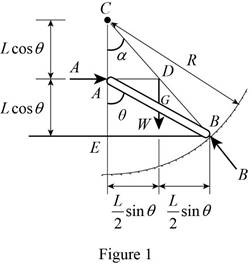
Write the expression for the distances
Write the expression for the distances
Write the expression of Pythagoras theorem in the triangle
Conclusion:
Use equation (I) and (II) in (III).
Use equation (IV), (V) and (VII) in (VI).
Simplify equation (VIII).
The expression for the equilibrium condition of the rod is,
Given that the length of the rod is
Substitute
Therefore, the angle
(b)
The reaction at
(b)
Answer to Problem 4.90P
The reaction at
Explanation of Solution
The free-body diagram corresponding to the arrangement is given in Figure 1.
Write the expression for computing the angle
Use equation (IV) and (VII) in (X).
At the equilibrium condition, a force triangle can be drawn using
Conclusion:
Substitute
The force triangle using
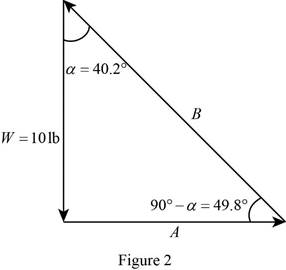
Write the trigonometric relation for determining
Write the trigonometric relation for det4ermoini ng
Substitute
and,
The reaction at
Therefore, the reaction at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
- Hydrodynamic Lubrication Theory Q1: Convert this equations into Python by 1- ah ap a h³ ap 1..ah = ax 12μ ax ay 12μ ay 2 ax Where P=P(x, y) is the oil film pressure. 2- 3μU (L² ε sin P= C²R (1+ cos 0)³ Q2: prove that |h(0) = C(1+ cos 0) ?arrow_forward### To make a conclusion for a report of an experiment on rockets, in which the openrocket software was used for the construction and modeling of two rockets: one one-stage and one two-stage. First rocket (single-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 200 m/s and a maximum height of 1000 m The second rocket (two-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 250 m/s and a maximum height of 1800 m To make a simplified conclusion, taking into account the efficiency of the software in the study of rocketsarrow_forwardWhat is the difference between saturated liquid and compressed liquid? What is the difference between the critical point and the triple pointarrow_forward
- What is quality? Does it have any meaning in the superheated vapour region? What is the difference between saturated vapor and superheated vapour? What is the difference between saturated liquid and compressed liquid? What is the difference between the critical point and the triple point?arrow_forwardHomework#5arrow_forwardDescribe the principle operation of PEMFC, and role of membrane electrode assembly (MEA).arrow_forward
- Homework#5arrow_forwardUsing graphical methods, draw the pressure angle at the position shown in (a) and (b). e |------- R = Cam Base Radius e = Follower Offset ẞ₁ = Section Duration 1 B₁ = Section Duration 2 ẞ₂ = Section Duration 3 В2 B₁ Follower Position ww R ẞ3 (a) Reference Radial (b)arrow_forwardThe figure below illustrates a graph that has a variable load torque and constant drive torque. Each cycle lasts three revolutions (6л radians). Torque (N-m) 600 550 400 1 200 TD= 225 N-m 2 + -T₁ 3 4 1 + 0 In addition, the rotation speed is @o steady-state conditions, determine 1. the average power required, 2πT 4π 5πT 6п Ꮎ = 180° rpm = 18.85 rad/sec, Imachine 125 kg-m². Assuming 2. the maximum and minimum rotational speeds throughout a cycle, 3. the mass of a 0.6-meter-diameter solid disc flywheel to produce Cs = 0.025.arrow_forward
- An elastic cord is stretched between 2 points A and B located 2y = 0.8 m apart in the horizontal plane. When stretched directly between A and B, the tension is P₂ = 40 N. The cord is then stretched as shown until its midpoint C has moved through x = 0.3 m to C', and a force of F = 240 N is required to hold the cord at C'. A pellet (m = 0.1 kg) is placed at C' and the cord is released. Find the speed of the pellet as it passes through C.arrow_forwardA 6305 ball bearing is subjected to a steady 5000-N radial load and a 2000-N thrust load and uses a very clean lubricant throughout its life. If the inner race angular velocity is 500rpm find (a) The equivalent radial load (b) The L10 life (c) The L50 lifearrow_forwardSlove this the question plearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





