
Concept explainers
Every second counts You must get from a point P on the straight shore of a lake to a stranded swimmer who is 50 m from a point Q on the shore that is 50 m from you (see figure). If you can swim at a speed of 2 m/s and run at a speed of 4 m/s, at what point along the shore, x meters from Q, should you stop running and start swimming if you want to reach the swimmer in the minimum time?
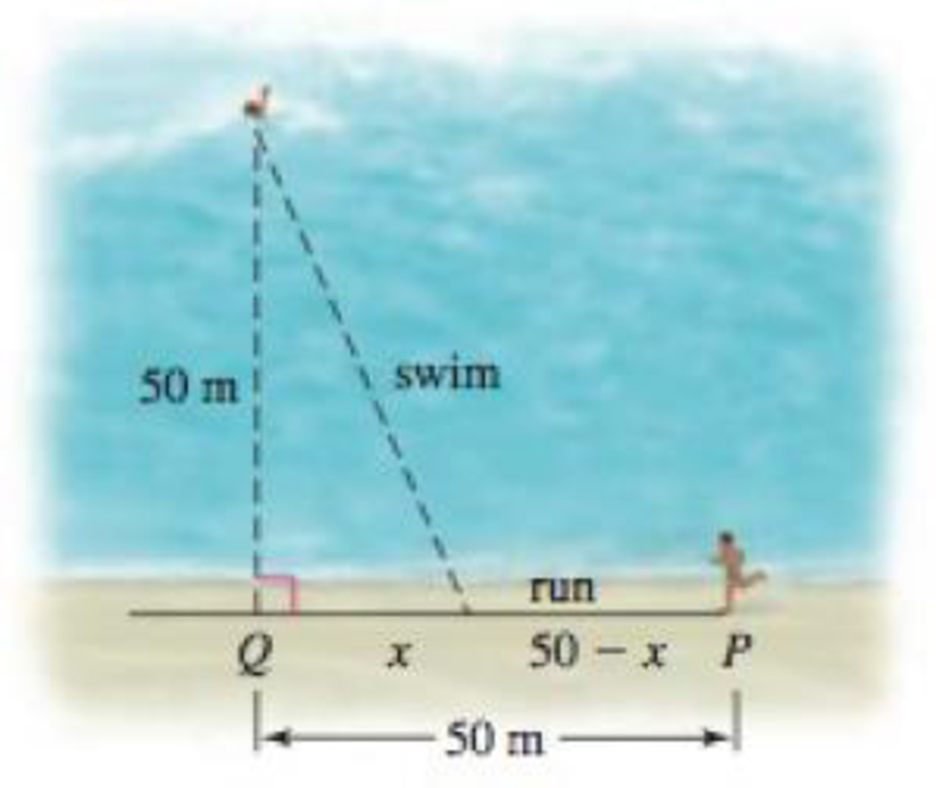
- a. Find the function T that gives the travel time as a function of x, where 0 ≤ x ≤ 50.
- b. Find the critical point of T on (0, 50).
- c. Evaluate T at the critical point and the endpoints (x = 0 and x = 50) to verify that the critical point corresponds to an absolute minimum. What is the minimum travel time?
- d. Graph the function T to check your work.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Early Transcendentals Plus MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (2nd Edition) (Briggs/Cochran/Gillett Calculus 2e)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- Question 2 Let F be a solenoidal vector field, suppose V × F = (-8xy + 12z², −9x² + 4y² + 9z², 6y²), and let (P,Q,R) = V²F(.725, —.283, 1.73). Then the value of sin(2P) + sin(3Q) + sin(4R) is -2.024 1.391 0.186 -0.994 -2.053 -0.647 -0.588 -1.851 1 ptsarrow_forward1 pts Let F and G be vector fields such that ▼ × F(0, 0, 0) = (0.76, -9.78, 3.29), G(0, 0, 0) = (−3.99, 6.15, 2.94), and G is irrotational. Then sin(5V (F × G)) at (0, 0, 0) is Question 1 -0.246 0.072 -0.934 0.478 -0.914 -0.855 0.710 0.262 .arrow_forwardanswerarrow_forward
- 1. Given the vector field F(x, y, z) = -zi, verify the relation 1 VF(0,0,0) lim +0+ volume inside S ff F• Nds S. where S, is the surface enclosing a cube centred at the origin and having edges of length 2€. Then, determine if the origin is sink or source.arrow_forwardLet a = (-4, 5, 4) and 6 = (1,0, -1). Find the angle between the vector 1) The exact angle is cos 2) The approximation in radians isarrow_forwardFind the (exact) direction cosines and (rounded to 1 decimal place) direction angles of = (3,7,6)arrow_forward
- Let a = (-1, -2, -3) and 6 = (-4, 0, 1). Find the component of b onto a.arrow_forwardForces of 9 pounds and 15 pounds act on each other with an angle of 72°. The magnitude of the resultant force The resultant force has an angle of pounds. * with the 9 pound force. The resultant force has an angle of with the 15 pound force. It is best to calculate each angle separately and check by seeing if they add to 72°.arrow_forward= Let (6,2,-5) and = (5,4, -6). Compute the following: บี.บี. บี. นี = 2 −4(u. v) = (-4). v= ū. (-40) (ū. v) v =arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage





