
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337614085
Author: Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.1, Problem 36E
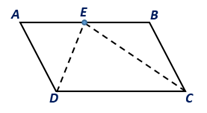
When the bisectors of two consecutive
parallelogram meet at a point on the remaining side,
what type of
| a) ∆DEC? | b) ∆ADE? | c) ∆BCE? |
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
the larger of two supplementary angles exceeds 7 times the smaller by 4°. Find the measure of the larger angle.
93
Y
y = f(x)
00
X
17
Chapter 4 Solutions
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Ch. 4.1 - ABCD is a parallelogram. a Using a ruler, compare...Ch. 4.1 - ABCD is a parallelogram. a Using a ruler, compare...Ch. 4.1 - MNPQ is a parallelogram. Suppose that MQ=5, MN=8,...Ch. 4.1 - MNPQ is a parallelogram. Suppose that MQ=12.7,...Ch. 4.1 - For Exercises 5 to 8, MNPQ is a parallelogram with...Ch. 4.1 - For Exercises 5 to 8, MNPQ is a parallelogram with...Ch. 4.1 - For Exercises 5 to 8, MNPQ is a parallelogram with...Ch. 4.1 - For Exercises 5 to 8, MNPQ is a parallelogram with...Ch. 4.1 - Given that AB=3x+2, BC=4x+1, and CD=5x-2, find the...Ch. 4.1 - Given that mA=2x+3, and mC=3x-27, find the measure...
Ch. 4.1 - Given that mA=2x+3, and mB=3x-23, find the measure...Ch. 4.1 - Given that mA=2x5, and mB=x2, find the measure of...Ch. 4.1 - Given that mA=2x3, and mC=x2+20, find the measure...Ch. 4.1 - Given that mA=2x+y, mB=2x+3y-20, and mC=3x-y+16,...Ch. 4.1 - Assuming that mBmA in , which diagonal AC-orBD-...Ch. 4.1 - Suppose that diagonals AC-andBD- of are drawn and...Ch. 4.1 - In Exercises 17 and 18, consider with VX- RS- and...Ch. 4.1 - In Exercises 17 and 18, consider with VX- RS- and...Ch. 4.1 - In Exercises 19 to 22, classify each statement as...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 20ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 4.1 - In quadrilateral RSTV, the midpoints of...Ch. 4.1 - In quadrilateral ABCD, the midpoints of opposite...Ch. 4.1 - Quadrilateral ABCD has AB-DC- and AD-BC-. Using...Ch. 4.1 - Quadrilateral RSTV has RS-TV- and RS-TV-. Using...Ch. 4.1 - In Exercises 27-30, use the definition of a...Ch. 4.1 - In Exercises 27-30, use the definition of a...Ch. 4.1 - In Exercises 27 to 30, use the definition of a...Ch. 4.1 - In Exercises 27-30, use the definition of a...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 31ECh. 4.1 - In Exercises 31 to 34, write a formal proof of...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 33ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 34ECh. 4.1 - The bisectors of two consecutive angles of HJKL...Ch. 4.1 - When the bisectors of two consecutive angles of a...Ch. 4.1 - Draw parallelogram RSTV with mR=700 and mS=1100....Ch. 4.1 - Draw parallelogram RSTV so that the diagonals have...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 39ECh. 4.1 - In quadrilaterals ABCD and EFGH, AB-DC-, EF-HG-,...Ch. 4.1 - The following problem is based on the...Ch. 4.1 - In the drawing for Exercise 41, the bearing...Ch. 4.1 - Two streets meet to form an obtuse angle at point...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 44ECh. 4.1 - Prob. 45ECh. 4.1 - Prove: In a parallelogram, the sum of the squares...Ch. 4.2 - Note: Exercises preceded by an asterisk are of a...Ch. 4.2 - a As shown, must RSTV be a parallelogram? b With...Ch. 4.2 - In the drawing, suppose that WY and XZ bisect each...Ch. 4.2 - In the drawing, suppose that ZX is the...Ch. 4.2 - A carpenter lays out boards of lengths 8 ft, 8 ft,...Ch. 4.2 - A carpenter joins four boards of lengths 6 ft, 6...Ch. 4.2 - In parallelogram ABCD not shown, AB=8, mB=110, and...Ch. 4.2 - In quadrilateral WXYZ, the measures of selected...Ch. 4.2 - In ABC, M and N are midpoints of AC and BC,...Ch. 4.2 - In ABC, M and N are midpoints of AC and BC,...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercises 11 to14 , assume that X, Y , and Z...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercises 11 to 14, assume that X, Y, and Z are...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 13ECh. 4.2 - In Exercises 11 to 14, assume that X, Y, and Z are...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 15ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 16ECh. 4.2 - For compactness, the drop-down wheels of a...Ch. 4.2 - For compactness, the drop-down legs of an ironing...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercises 19 to 24, complete each proof. Given:...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercises 19 to 24, complete each proof. Given:...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercises 19 to24 , complete each proof. Given:...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercise 19 to24, complete each proof. Given:...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercise 19 to24, complete each proof. Given:...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercise 19 to24, complete each proof. Given:...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 25ECh. 4.2 - In Exercises 25 to 28, write a formal proof of...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 27ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 28ECh. 4.2 - In Exercises 29 to 31, M and Nare the midpoints of...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercises 29 to 31, M and Nare the midpoints of...Ch. 4.2 - In Exercises 29 to 31, M and Nare the midpoints of...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 32ECh. 4.2 - For Exercises 32 to 35, consider kite ABCD with...Ch. 4.2 - For Exercises 32 to 35, consider kite ABCD with...Ch. 4.2 - For Exercises 32 to 35, consider kite ABCD with...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 36ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 37ECh. 4.2 - Prob. 38ECh. 4.2 - For regular octagon ABCDEFGH, a are quadrilateral...Ch. 4.2 - RSTV is a kite, with RSST and RVVT. If mSTV=40,...Ch. 4.2 - In concave kite ABCD, there is an interior angle...Ch. 4.2 - If the length of side AB for kite ABCD is 6 in.,...Ch. 4.2 - Prove that the segment that joins the midpoints of...Ch. 4.2 - Prove that when the midpoints of consecutive sides...Ch. 4.3 - Being as specific as possible, name the type of...Ch. 4.3 - Being as specific as possible, name the type of...Ch. 4.3 - Being as specific as possible, name the type of...Ch. 4.3 - Being as specific as possible, name the type of...Ch. 4.3 - If the diagonals of a parallelogram are...Ch. 4.3 - If the diagonals of a quadrilateral are...Ch. 4.3 - A line segment joins the midpoints of two opposite...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 8 to 10, use the properties of...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 8 to 10, use the properties of...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 8 to 10, use the properties of...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 11 to 14, consider MNPQ with...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 11 to 14, consider MNPQ with...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 11 to 14, consider MNPQ with...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 11 to 14, consider MNPQ with...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 15 to 18, consider rhombus ABCD with...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 15 to 18, consider rhombus ABCD with...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 15 to 18, consider rhombus ABCD with...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 15 to 18, consider rhombus ABCD with...Ch. 4.3 - Given: ABCD not shown with AB = 8 and BC = 6; M...Ch. 4.3 - Given: Rhombus RSTV not shown with diagonals...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 21ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 22ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 23ECh. 4.3 - For Exercises 21 t 24, let...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 25 and 26, supply the missing...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 25 and 26, supply the missing...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 27ECh. 4.3 - Which types of quadrilaterals is are necessarily...Ch. 4.3 - Find the perimeter of the cyclic quadrilateral...Ch. 4.3 - Find the perimeter of the square shown.Ch. 4.3 - Are quadrilaterals ABCD and EFGH congruent aif...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 32ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 33ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 34ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 35ECh. 4.3 - In Exercises 34 to 39, write a formal proof of...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 37ECh. 4.3 - Prob. 38ECh. 4.3 - In Exercises 34 to 39, write a formal proof of...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 40ECh. 4.3 - In Exercises 40 to 41, you will need to use the...Ch. 4.3 - a Argue that the midpoint of the hypotenuse of a...Ch. 4.3 - Two sets of rails railroad tracks are equally...Ch. 4.3 - In square ABCD not shown, point E lies on side DC....Ch. 4.3 - In square ABCD not shown, point E lies in the...Ch. 4.3 - The sides of square ABCD are trisected at the...Ch. 4.4 - Find the measures of the remaining angles of...Ch. 4.4 - Find the measures of the remaining angles of...Ch. 4.4 - What type of trapezoid a has congruent diagonals....Ch. 4.4 - What type quadrilateral is formed when the...Ch. 4.4 - Given isosceles trapezoid ABCD, Find. a AC, if BD...Ch. 4.4 - In trapezoid ABCD, MN is the median. Without...Ch. 4.4 - If HandJ are supplementary, what type of...Ch. 4.4 - If HandJ are supplementary in HJKL, are a KandL...Ch. 4.4 - For Exercises 9 and 10, consider isosceles...Ch. 4.4 - For Exercises 9 and 10, consider isosceles...Ch. 4.4 - In Exercises 11 to 16, the drawing shows trapezoid...Ch. 4.4 - In Exercises 11 to 16, the drawing shows trapezoid...Ch. 4.4 - In Exercises 11 to 16, the drawing shows trapezoid...Ch. 4.4 - In Exercises 11 to 16, the drawing shows trapezoid...Ch. 4.4 - In Exercises 11 to 16, the drawing shows trapezoid...Ch. 4.4 - In Exercises 11 to 16, the drawing shows trapezoid...Ch. 4.4 - Given: ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid. Prove: ABE...Ch. 4.4 - Given: Isosceles ABE with AEBE; also, D and C are...Ch. 4.4 - In isosceles trapezoid WXYZ with bases ZY and WX,...Ch. 4.4 - In trapezoid WXYZ with bases ZY and WX, ZY = 12,...Ch. 4.4 - In isosceles trapezoid MNPQ with MNQP, diagonal...Ch. 4.4 - In trapezoid RSTV, RVST,mSRV=90, and M and N are...Ch. 4.4 - Each vertical section of a suspension bridge is in...Ch. 4.4 - The state of Nevada approximates the shape of a...Ch. 4.4 - In the figure, abc and B is the midpoint of AC. If...Ch. 4.4 - In the figure, abc and B is the midpoint of AC. If...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 27ECh. 4.4 - HJKL and WXYZ are right trapezoids. Are these...Ch. 4.4 - In exercises 29 to 35, complete a formal proof....Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 30ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 31ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 32ECh. 4.4 - In exercises 29 to 35, complete a formal proof. If...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 34ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 35ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 36ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 37ECh. 4.4 - Given: ABDC mA=mB=56CEDA and CF bisects DCB Find:...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 39ECh. 4.4 - Prob. 40ECh. 4.4 - The vertical side wall of an in-ground pool that...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 42ECh. 4.4 - With MNQP and MQQP, MNPQ is a right trapezoid....Ch. 4.4 - With MNQP and MQ, MNPQ is a right trapezoid. Find...Ch. 4.4 - In trapezoid ABCD not shown, mA=x2+10, mB=x3+50...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 46ECh. 4.4 - Draw and then trisect AB. Use the construction...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 48ECh. 4.CR - Review Exercises State whether the statements in...Ch. 4.CR - Prob. 2CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 3CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 4CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 5CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 6CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 7CRCh. 4.CR - Review Exercises State whether the statements in...Ch. 4.CR - Prob. 9CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 10CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 11CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 12CRCh. 4.CR - Review Exercises Given: ABCD CD=2x+3 BC=5x-4...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises Given: ABCD mA=2x+6 mB=x+24 Find:...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises The diagonals of ABCD not shown...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises Given: MNOP mM=4x mO=2x+50 Find:...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises Using the information from Review...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises In quadrilateral ABCD, M is the...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises In isosceles trapezoid DEFG,...Ch. 4.CR - One base of a trapezoid has a length of 12.3 cm...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises In trapezoid MNOP, MN-PO- and R...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises In Review Exercises 22 to 24, M...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises In Review Exercises 22 to 24, M...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises In Review Exercises 22 to 24, M...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises Given: ABCD is a AF-CE- Prove:...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises Given: ABEF is a rectangle BCDE...Ch. 4.CR - Prob. 27CRCh. 4.CR - Prob. 28CRCh. 4.CR - Review Exercises Given: ABCD is a parallelogram...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises Given: TWX is an isosceles, with...Ch. 4.CR - Prob. 31CRCh. 4.CR - Review Exercises Draw rectangle ABCD with AB=5 and...Ch. 4.CR - Review Exercises Draw rectangle WXYZ with...Ch. 4.CR - Prob. 34CRCh. 4.CR - Review Exercises What type of quadrilateral is...Ch. 4.CT - Consider ABCD as shown. a How are A and C...Ch. 4.CT - In RSTV not shown, RS=5.3 cm and ST=4.1 cm. Find...Ch. 4.CT - In ABCD, AD=5 and DC=9. If the altitude from...Ch. 4.CT - In RSTV, mS=57. Which diagonal (VSorRT) would have...Ch. 4.CT - In RSTV, VT=3x1,TS=2x+1,andRS=4(x2). Find the...Ch. 4.CT - Complete each statement: a If a quadrilateral has...Ch. 4.CT - Complete each statement: a In RSTV, RW is the...Ch. 4.CT - In ABC, M is the midpoint of AB and N is the...Ch. 4.CT - In ABC, M is the midpoint of AB and N is the...Ch. 4.CT - In ABC, M is the midpoint of AB and N is the...Ch. 4.CT - In rectangle ABCD, AD=12 and DC=5. Find the length...Ch. 4.CT - In trapezoid RSTV, RSVT. a Which sides are the...Ch. 4.CT - In trapezoid RSTV, RSVT and MN is the median, Find...Ch. 4.CT - In trapezoid RSTV of Exercise 13, RSVT and MN is...Ch. 4.CT - Complete the proof of the following theorem: In a...Ch. 4.CT - Complete the proof of the following theorem: The...Ch. 4.CT - In Kite RSTV, RS=2x4,ST=x1,TV=y3andRV=y. Find the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, geometry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:9781285195698
Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:McDougal Littell
What are the Different Types of Triangles? | Don't Memorise; Author: Don't Memorise;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1k0G-Y41jRA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Law of Sines AAS, ASA, SSA Ambiguous Case; Author: Mario's Math Tutoring;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FPVGb-yWj3s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Introduction to Statistics..What are they? And, How Do I Know Which One to Choose?; Author: The Doctoral Journey;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HpyRybBEDQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Triangles | Mathematics Grade 5 | Periwinkle; Author: Periwinkle;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zneP1Q7IjgQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
What Are Descriptive Statistics And Inferential Statistics?; Author: Amour Learning;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MUyUaouisZE;License: Standard Youtube License