
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134683416
Author: Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.1, Problem 28E
Identifying
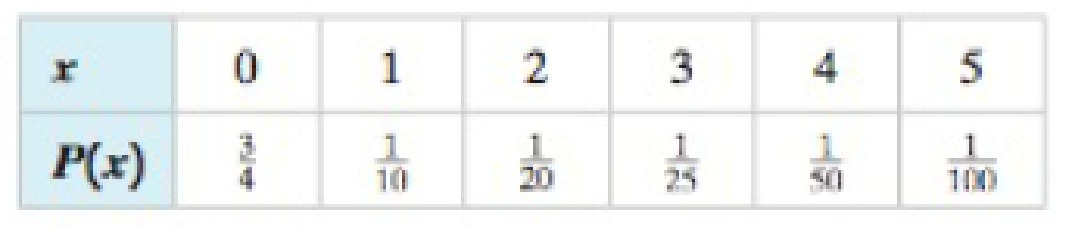
28. 
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
please find the answers for the yellows boxes using the information and the picture below
A marketing agency wants to determine whether different advertising platforms generate significantly different levels of customer engagement. The agency measures the average number of daily clicks on ads for three platforms: Social Media, Search Engines, and Email Campaigns. The agency collects data on daily clicks for each platform over a 10-day period and wants to test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean number of daily clicks among these platforms. Conduct ANOVA test.
You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: also please provide a step by on getting the answers in excel
Null hypothesis,
Alternative hypothesis,
Show answer (output table/summary table), and
Conclusion based on the P value.
A company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers
Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800?
Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve)
Provide answers in the yellow cells
Chapter 4 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Ch. 4.1 - Determine whether each random variable x is...Ch. 4.1 - A company tracks the number of sales new employees...Ch. 4.1 - Verify that the distribution you constructed in...Ch. 4.1 - Determine whether each distribution is a...Ch. 4.1 - Find the mean of the probability distribution you...Ch. 4.1 - Find the variance and standard deviation of the...Ch. 4.1 - At a raffle, 2000 tickets are sold at 5 each for...Ch. 4.1 - What is a random variable? Give an example of a...Ch. 4.1 - What is a discrete probability distribution? What...Ch. 4.1 - Is the expected value of the probability...
Ch. 4.1 - What does the mean of a probability distribution...Ch. 4.1 - True or False? In Exercises 58, determine whether...Ch. 4.1 - True or False? In Exercises 58, determine whether...Ch. 4.1 - True or False? In Exercises 58, determine whether...Ch. 4.1 - True or False? In Exercises 58, determine whether...Ch. 4.1 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 912, determine...Ch. 4.1 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 912, determine...Ch. 4.1 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 912, determine...Ch. 4.1 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 912, determine...Ch. 4.1 - Discrete Variables and Continuous Variables In...Ch. 4.1 - Discrete Variables and Continuous Variables In...Ch. 4.1 - Discrete Variables and Continuous Variables In...Ch. 4.1 - Discrete Variables and Continuous Variables In...Ch. 4.1 - Discrete Variables and Continuous Variables In...Ch. 4.1 - Discrete Variables and Continuous Variables In...Ch. 4.1 - Constructing and Graphing Discrete Probability...Ch. 4.1 - Constructing and Graphing Discrete Probability...Ch. 4.1 - Finding Probabilities Use the probability...Ch. 4.1 - Finding Probabilities Use the probability...Ch. 4.1 - Unusual Events In Exercise 19, would it be unusual...Ch. 4.1 - Unusual Events In Exercise 20, would it be unusual...Ch. 4.1 - Determining a Missing Probability In Exercises 25...Ch. 4.1 - Determining a Missing Probability In Exercises 25...Ch. 4.1 - Identifying Probability Distributions In Exercises...Ch. 4.1 - Identifying Probability Distributions In Exercises...Ch. 4.1 - Finding the Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation...Ch. 4.1 - Baseball The number of games played in each World...Ch. 4.1 - Finding the Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation...Ch. 4.1 - Finding the Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation...Ch. 4.1 - Hurricanes The histogram shows the distribution of...Ch. 4.1 - Reviewer Ratings The histogram shows the reviewer...Ch. 4.1 - Writing The expected value of an accountants...Ch. 4.1 - Writing In a game of chance, what is the...Ch. 4.1 - Finding an Expected Value In Exercises 37and 38,...Ch. 4.1 - A high school basketball team is selling 10 raffle...Ch. 4.1 - Linear Transformation of a Random Variable In...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 40ECh. 4.1 - What is the average sum of their scores? What is...Ch. 4.1 - What is the standard deviation of the difference...Ch. 4.2 - Determine whether the experiment is a binomial...Ch. 4.2 - A card is selected from a standard deck and...Ch. 4.2 - A survey found that 52% of U.S. adults associate...Ch. 4.2 - The survey in Example 5 found that 27% of U.S....Ch. 4.2 - About 5% of workers (ages 16 years and older) in...Ch. 4.2 - A recent study found that 28% of U.S. adults read...Ch. 4.2 - In San Francisco, California, about 44% of the...Ch. 4.2 - In a binomial experiment, what does it mean to say...Ch. 4.2 - In a binomial experiment with n trials, what does...Ch. 4.2 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 35, the histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 35, the histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 35, the histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 68, the histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 68, the histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Graphical Analysis In Exercises 68, the histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Identify the unusual values of x in each histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Identify the unusual values of x in each histogram...Ch. 4.2 - Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation In...Ch. 4.2 - Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation In...Ch. 4.2 - Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation In...Ch. 4.2 - Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation In...Ch. 4.2 - Identifying and Understanding Binomial Experiments...Ch. 4.2 - Identifying and Understanding Binomial Experiments...Ch. 4.2 - Identifying and Understanding Binomial Experiments...Ch. 4.2 - Identifying and Understanding Binomial Experiments...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Finding Binomial Probabilities In Exercises 1926,...Ch. 4.2 - Constructing and Graphing Binomial Distributions...Ch. 4.2 - Constructing and Graphing Binomial Distributions...Ch. 4.2 - Constructing and Graphing Binomial Distributions...Ch. 4.2 - Constructing and Graphing Binomial Distributions...Ch. 4.2 - Finding and Interpreting Mean, Variance, and...Ch. 4.2 - Finding and Interpreting Mean, Variance, and...Ch. 4.2 - Finding and Interpreting Mean, Variance, and...Ch. 4.2 - Finding and Interpreting Mean, Variance, and...Ch. 4.2 - Finding and Interpreting Mean, Variance, and...Ch. 4.2 - Finding and Interpreting Mean, Variance, and...Ch. 4.2 - Genetics According to a theory in genetics, when...Ch. 4.2 - Genetics Another proposed theory in genetics gives...Ch. 4.2 - Manufacturing An assembly line produces 10,000...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 1ACh. 4.2 - Prob. 2ACh. 4.2 - For the election in Exercise 1, simulate selecting...Ch. 4.2 - 1. Construct a probability distribution for the...Ch. 4.2 - 2. Construct binomial probability distributions...Ch. 4.2 - 3. Compare your distributions from Exercise 1 and...Ch. 4.2 - 4. During the 2016 regular season, Kris Bryant of...Ch. 4.3 - The study in Example 1 found that the smartphones...Ch. 4.3 - What is the probability that more than four...Ch. 4.3 - Two thousand brown trout are introduced into a...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 14, find the indicated probability...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 2ECh. 4.3 - In Exercises 14, find the indicated probability...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 4.3 - In Exercises 58, find the indicated probability...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 4.3 - In Exercises 58, find the indicated probability...Ch. 4.3 - In Exercises 58, find the indicated probability...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 9ECh. 4.3 - In your own words, describe the difference between...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 11ECh. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In...Ch. 4.3 - Comparing Binomial and Poisson Distributions An...Ch. 4.3 - Hypergeometric Distribution Binomial experiments...Ch. 4.3 - Geometric Distribution: Mean and Variance In...Ch. 4.3 - Geometric Distribution: Mean and Variance In...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 31ECh. 4.3 - Geometric Distribution: Mean and Variance In...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 13, assume the fire department...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 13, assume the fire department...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 13, assume the fire department...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 1 and 2, determine whether the random...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 1 and 2, determine whether the random...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 3 and 4, (a) construct a probability...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 3 and 4, (a) construct a probability...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 5 and 6, determine whether the...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 5 and 6, determine whether the...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 7 and 8, (a) find the mean, variance,...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 7 and 8, (a) find the mean, variance,...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 9 and 10, find the expected net gain...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 9 and 10, find the expected net gain...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 11 and 12, determine whether the...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 11 and 12, determine whether the...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 1316, find the indicated binomial...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 1316, find the indicated binomial...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 1316, find the indicated binomial...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 1316, find the indicated binomial...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 17 and 18, (a) construct a binomial...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 17 and 18, (a) construct a binomial...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 19 and 20, find the mean, variance,...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 19 and 20, find the mean, variance,...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 2126, find the indicated...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.3.22RECh. 4 - In Exercises 2126, find the indicated...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.3.24RECh. 4 - Prob. 4.3.25RECh. 4 - In Exercises 2126, find the indicated...Ch. 4 - Determine whether the random variable x is...Ch. 4 - The table lists the number of wireless devices per...Ch. 4 - Prob. 3CQCh. 4 - The five-year success rate of kidney transplant...Ch. 4 - An online magazine finds that the mean number of...Ch. 4 - Basketball player Dwight Howard makes a free throw...Ch. 4 - Which event(s) in Exercise 6 can be considered...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 13find the indicated probabilities...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 13, find the indicated probabilities...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 13find the indicated probabilities...Ch. 4 - Determine whether the distribution is a...Ch. 4 - The table shows the ages of students in a freshman...Ch. 4 - Seventy-seven percent of U.S. college students pay...Ch. 4 - The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention...Ch. 4 - The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention...Ch. 4 - Suspicious Samples? A lab worker tells you that...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 17, consider a grocery store that can...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 17, consider a grocery store that can...Ch. 4 - Prob. 3TCh. 4 - Prob. 4TCh. 4 - Prob. 5TCh. 4 - In Exercises 17, consider a grocery store that can...Ch. 4 - In Exercises 17, consider a grocery store that can...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Business Discussarrow_forwardThe following data represent total ventilation measured in liters of air per minute per square meter of body area for two independent (and randomly chosen) samples. Analyze these data using the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis testarrow_forwardeach column represents before & after measurements on the same individual. Analyze with the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis test for a paired design.arrow_forward
- Should you be confident in applying your regression equation to estimate the heart rate of a python at 35°C? Why or why not?arrow_forwardGiven your fitted regression line, what would be the residual for snake #5 (10 C)?arrow_forwardCalculate the 95% confidence interval around your estimate of r using Fisher’s z-transformation. In your final answer, make sure to back-transform to the original units.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw HillAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw HillAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage
Mod-01 Lec-01 Discrete probability distributions (Part 1); Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6x1pL9Yov1k;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Discrete Probability Distributions; Author: Learn Something;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9U4UelWLFs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Probability Distribution Functions (PMF, PDF, CDF); Author: zedstatistics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YXLVjCKVP7U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Discrete Distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Hypergeometric | Statistics for Data Science; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHhyy4JMigg;License: Standard Youtube License