
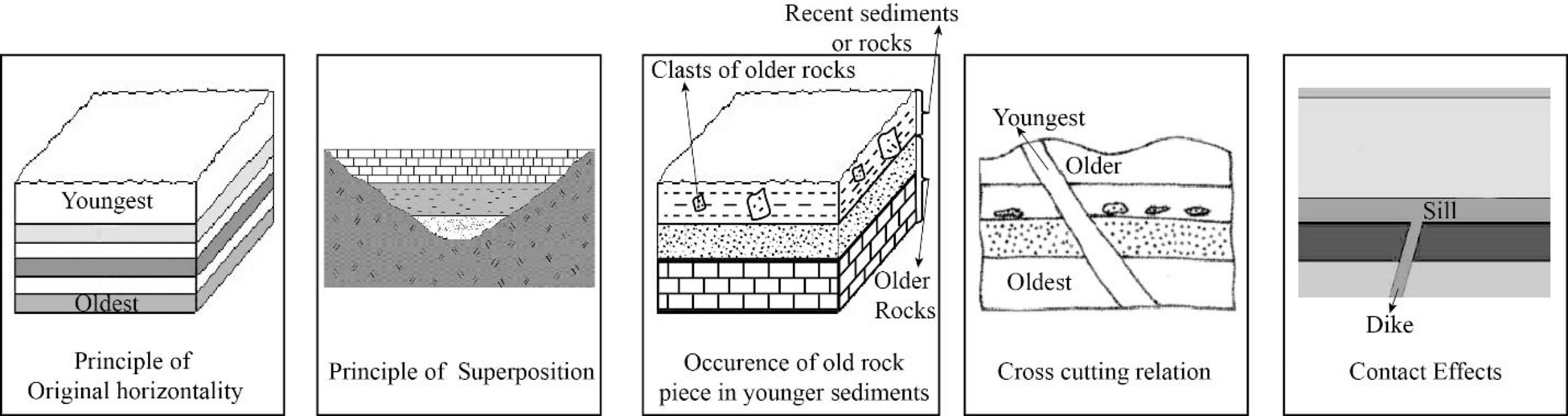
The five principles of relative dating and provide an example for each principle with the help of a sketch.
Answer to Problem 1BYL
Explanation of Solution
The geologic history of an area can be determined by determining the age of geologic units, features, and events. The first step that can be used to determine the age of a rock relative to one another is the method of relative dating. Geoscientists are assigning actual numbers in thousands to billions of years using analytical laboratory methods or isotopic dating to this relative chronology. To compare the ages of different rock layers and to correlate one rock unit relative to one another, fossils are also used. The five main principles of relative dating include the original horizontality, principle of superposition, cross-cutting relation, the occurrence of an older rock piece in younger sediment or rock, and contact effects.
The deposition of most sediments and volcanic units occurred in a more or less horizontal pattern. The principle used to denote this process is known as principle of original horizontality. When the layers are no longer horizontal, it indicates the occurrence of some events after the formation of that layers. The special environments, such as the face of a sand dune or the undersea slopes of a delta are the few exceptions to the principle.
The principle of superposition states that when the deposition of a sediment layer occurs, it overlies the older rocks or sediments. In a sequence of horizontal sedimentary layer sequence, the oldest layer is on the bottom and the youngest layer is at the top.
The third principle of relative dating describes that a younger sediment or rock can contain pieces of an older rock. It indicates that during the formation of a rock or sedimentary deposit, pieces or clasts of older rocks are incorporated into it.
Principle of cross cutting relation states that the rocks are crosscut by fracture. Therefore, the rocks existed there before the formation of fractures. Mainly, there are two types of fractures. They are joints and faults. The slight pulling apart movement of the rock results in the formation of joints and faults are formed along which rocks on opposite side have moved up and down, side to side or as combination.
When magma erupts on to the surface or solidifies at depth, it comes into contact with the pre-existing rock. In both, this setting involves the baking of magma with adjacent rock or chemical alteration of nearby rocks due to the effects of fluids from the magma. Those type of changes that occurred following the eruption or solidification of magma are termed as contact effects.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Exploring Earth Science
- Use the Portage, Montana, topographic map in Figure 8.6 (on page 136) and the stereogram in Figure 8.7 (on page 137) to complete the following. 1. Compare the stereogram in Figure 8.7 to the map in Figure 8.6. Then, on the topographic map, outline the area shown in the photo. 2. Is the terrain in Section 14, located on the west side of this map, relatively flat or hilly? Explain. 3. Label the areas that topographically resemble Section 14 on the topographic map as "upland." 4. Describe the topography in the lower half of Section 17, located three sections east of section 14. 5. Section 17 contains a portion of the valley occupied by the Missouri River. Approximately what percentage of the area shown on the map is stream valley (similar to the lower half of Section 17) and what percentage is upland? 6. Which of the following best describes the shape of the Missouri River Valley along the line labeled D.-D': wide valley with a floodplain or steep-sided V-shaped valley with no floodplain?…arrow_forwardPlease upload your one to two-page summary about what you learned from the 55-minute Magnetic Storm documentary. H) The Universe Magnetic Storm Threat.... Η The Liver MWgnete storm Threat. Watch later Share HISTORY H Watch on YouTubearrow_forwardUse the textbook and the internet to complete the following work covering all of the previous material. It will help with a deeper understanding of the material before taking Midterm #1 too. Choose the best bold word/s option for each one given below. Please write out in complete sentences your answers and upload your file. 1. The Earth is a/an open or closed system as far as energy is concerned and a/an open or closed as far as "rocky" material (10 points). 2. Divergent boundaries experience tensional, compressional, or shearing forces creating normal, reverse, or strike-slip faults (10 points). 3. Convergent experience tensional, compressional, or shearing forces creating normal, reverse, or strike-slip faults (10 points). 4. Transform boundaries experience tensional, compressional, or shearing forces creating normal, reverse, or strike-slip faults (10 points). 5. The Himalayas an example of a convergent, divergent, or transform boundary (5 points). 6. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge an…arrow_forward
- Discussion Question: Solar Energy, Seasons, and the Atmospherearrow_forward1. Does urbanization increase or decrease the peak streamflow? 2. What is the effect of urbanization on lag time (the span between when rainfall occurred and when peak stream discharge occurred)? 3. Does total runoff occur over a longer or shorter time span after an area has been urbanized? 4. Based on what you have learned from the hydrographs in Figure 8.4, explain why urban areas often experience more flash-flooding than do rural areas during intense rainfalls.arrow_forwardLabel the drawing in Figure 8.2 with the letters that correspond to the following terms: Runoff Evaporation Infiltration Precipitation Groundwater Reservoirarrow_forward
- Use Figure 8.1 as a reference to complete the following: 1. Globally, from which source does more water evaporate into the atmosphere: oceans or land? 2. Approximately what percentage of the total water evaporated into the atmosphere comes from the oceans?Percentage from oceans = Ocean evaporation/Total evaporation × 100% = _____ % 3. Notice in Figure 8.1 that more water evaporates from the oceans than is returned directly by precipitation. If sea level is not dropping, identify a source of water for the oceans in addition to precipitation. 4. Worldwide, about how much of the precipitation that falls on the land becomes runoff: 35, 55, or 75 percent? 5. Much of the water that falls on land does not immediately return to the ocean via runoff. Instead, it is temporarily stored in reservoirs such as lakes. In some mountainous and polar regions, what features serve as reservoirs to temporarily store water?arrow_forwardWhy did the Shiveluch erruption occur?arrow_forwardBackground/Synopsis You are working for the administrative or government apparatus of a city. Good credentials have resulted in you working in this position. The top echelon of the city government changed a few years ago, but they did not replace many staff. Nonetheless, the situation is such that the city is led by a corrupt mayor who has realized dded that elections are approaching. Opinion polls suggest that a significant part of the electorate has the environment as a major concern. Close associates of the mayor organized a focus group and chose to investigate several initiatives which they felt might be possible to conduct in a relatively short amount of time. Jual pro Metho The administration wants several projects examined. You have been tasked with conducting a cost benefit analysis on the construction of permeable pavements. The idea put forth is to replace A2_Call city alleyways with permeable pavements as a means to better manage water resources. Group -07- You are asked to…arrow_forward
- Provide two paragraphs on your thoughts of the African dust and its impact on the environment. Please write in first personarrow_forwardAnswer the last question only. "Make a prediction where the next island in the Hawaiian island will form mark the location on the map"arrow_forwardDiscussion Question: Glacial (or Ice) and Periglacial Landscapes A+ The Ice and Glaciers chapter focuses on the Cryosphere, the ice on our planet. I always find it interesting to consider the Earth's Hydrologic Cycle, our water in all of the different phases: solid ice, liquid water, and water vapor (a gas). In place number one for the majority of the World's water, we have the oceans. In place number two, we have ice. Neither one is available to us for drinking water at this point. Amazingly enough, in place number three is groundwater before lakes and streams. Water has led to many problems in the history of California, the United States, and even the world. Nevada Idaho B) at Flats el Mone Lake Arizona Severe Dry Lake (c) Mono Lake, tufa towersarrow_forward
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





