
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Chair conformations of structure (1) and (2) have to be drawn for six-membered rings; the lowest energy conformations for the compound have to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Drawing Axial and Equatorial substituents:
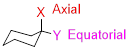
Each carbon in cyclohexane can bear two substituents. One group is said to occupy an axial position, which is parallel to a vertical axis passing through the center of the ring. the other group is said to occupy an equatorial position, which is positioned approximately along the equator of the ring.
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Newman projections: The new conformations of compounds can be drawn and analyzed by Newman projections. A Newman projection visualizes different conformations of Carbon-carbon
The angle between two hydrogens of a Newman projection is called as dihedral angle or torsional angle. This dihedral angle changes as the C-C bond rotates. Two conformations with special attentions are staggered and eclipsed conformation. Staggered conformation is the lowest in energy and the eclipsed conformation is the highest in energy.
For example,

Anti-conformation: The conformation with a dihedral angle of

The two methyl groups achieve maximum separation from each other. In other, methyl groups are closer to each other; their electron clouds are repelling each other, causing an increase in energy. This unfavorable interaction is called gauche interaction.
Conversion of chair conformation into Newman projection:
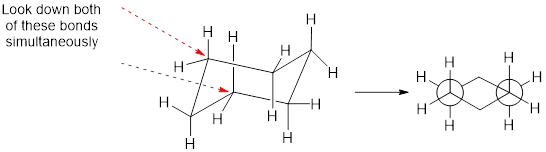
Ring flipping between Newman projections:
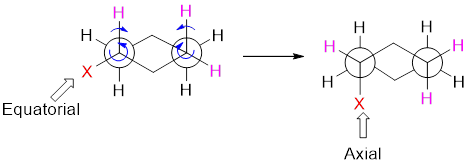
Ring flipping is a conformational change that is accomplished only through a rotation of all C-C single bonds. On ring flipping between two chair conformation equatorial changes into axial and vice-versa.
(b)
Interpretation:
The larger heat of combustion out of the given compounds has to be identified and explained.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of organic compounds:
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Drawing Axial and Equatorial substituents:
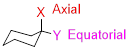
Each carbon in cyclohexane can bear two substituents. One group is said to occupy an axial position, which is parallel to a vertical axis passing through the center of the ring. the other group is said to occupy an equatorial position, which is positioned approximately along the equator of the ring.
Conformations: Rotation about C-C single bonds allows a compound to adopt a variety of possible three-dimensional shapes.
Newman projections: The new conformations of compounds can be drawn and analyzed by Newman projections. A Newman projection visualizes different conformations of Carbon-carbon chemical bond from front to back with the front carbon represented as a black dot and the back represented as a circle.
The angle between two hydrogens of a Newman projection is called as dihedral angle or torsional angle. This dihedral angle changes as the C-C bond rotates. Two conformations with special attentions are staggered and eclipsed conformation. Staggered conformation is the lowest in energy and the eclipsed conformation is the highest in energy.
For example,

Anti-conformation: The conformation with a dihedral angle of

The two methyl groups achieve maximum separation from each other. In other, methyl groups are closer to each other; their electron clouds are repelling each other, causing an increase in energy. This unfavorable interaction is called gauche interaction.
Conversion of chair conformation into Newman projection:

Ring flipping between Newman projections:

Ring flipping is a conformational change that is accomplished only through a rotation of all C-C single bonds. On ring flipping between two chair conformation equatorial changes into axial and vice-versa.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
- Describe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardState two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





