
Concept explainers
(a)
The force that the table exerts on box A if box B weighs
Answer to Problem 61QAP
The force exerted by table on box A is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
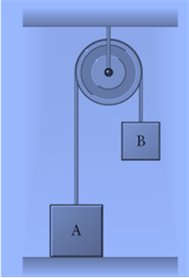
Box A weighs
Box B weighs
Pulley and rope are massless.
Formula Used:
Calculation:
The forces acting on Box A are the tension in the rope, the force due to gravity, and the force the table exerts on box A (also known as the normal force).
The tension in the rope is equal to the weight of box B when box B is at rest.
If the weight of box B is larger than the weight of box A, both boxes start to move-box A moves up, while box B moves down.
Free-body diagram of box A:
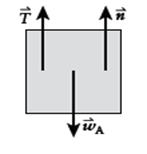
If box A remains at rest, then
If box B weighs
Conclusion:
The force that table exerts on box A if box B weighs
(b)
The force that the table exerts on box A if box B weighs
Answer to Problem 61QAP
The force exerted by table on box A is
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
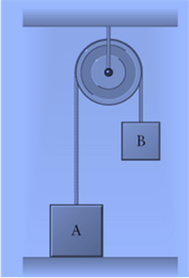
Box A weighs
Box B weighs
Pulley and rope are massless.
Formula Used:
Calculation:
The forces acting on Box A are the tension in the rope, the force due to gravity, and the force the table exerts on box A (also known as the normal force).
The tension in the rope is equal to the weight of box B when box B is at rest.
If the weight of box B is larger than the weight of box A, both boxes start to move-box A moves up, while box B moves down.
Free-body diagram of box A:
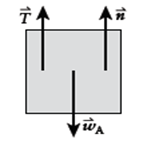
If box A remains at rest, then
If box B weighs
Conclusion:
The force that table exerts on box A if box B weighs
(c)
The force that the table exerts on box A if box B weighs
Answer to Problem 61QAP
The force that table exerts on box A if box B weighs
Explanation of Solution
Given:
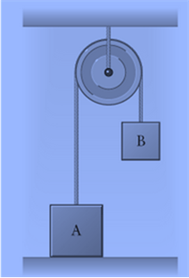
Box A weighs
Box B weighs
Pulley and rope are massless.
Formula Used:
Calculation:
The forces acting on Box A are the tension in the rope, the force due to gravity, and the force the table exerts on box A (also known as the normal force).
The tension in the rope is equal to the weight of box B when box B is at rest.
If the weight of box B is larger than the weight of box A, both boxes start to move-box A moves up, while box B moves down.
.
Free-body diagram of box A:
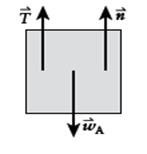
If box A remains at rest, then
If box B weighs more than box A, then we would expect box B to fall down and lift box A off
The table.
Since box A is no longer touching the table, the normal goes to
Conclusion:
The force that table exerts on box A if box B weighs
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS-ACHIEVE AC (1-TERM)
- How long will it take you to double your money if you invest it at a rate of 8% compounded annually?arrow_forwardOne hundred dollars is invested at 7.2% interest compounded annually. Determine how much the investment is worth after: a. I year b. 5 years c. 10 years d. 20 years e. Use your answers to parts (a)-(d) to estimate the doubling time for the investment.arrow_forward6) A farmer has 60 acres on which to plant oats or corn. Each acre of oats requires 100 lbs of fertilizer and 1 hour of labor. Each acre of corn requires 50 lbs of fertilizer and 2 hours of labor. The farmer has 5000 lbs of fertilizer and 100 hours available for labor. If the profit is $60 from each acre of oats and $100 from each acre of corn, what planting combination will produce the greatest total profit? a) Fill in the following chart to help organize the information given in the problem: Oats Labor Fertilizer Land Profit b) Write down the question of interest. Corn Available c) Define variables to answer the question of interest. Call these x and y. d) Write the objective function to answer the question of interest. e) List any constraints given in the problem.arrow_forward
- I need help with number 5.arrow_forward3) Use the following system of linear inequalities graphed below to answer the questions. a) Use the graph to write the symbolic form of the system of linear inequalities. b) Is (-4,2) a solution to the system? Explain. 5 -7 -5 -3 -2 0 2 3 4 $ 6 -2 -6 -7arrow_forward) Graph the feasible region subject to the following constraints. x + y ≤ 6 y ≤ 2x x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 P + xarrow_forward
- Solve the following system of equations: 50x+20y=1800 10x+3y=300arrow_forward> > > we are hiring Salesforce Admin Location: Remote Key Responsibilities: Administer Salesforce Sales & Revenue Cloud (CPQ & Billing) Configure workflows, validation rules & dashboards Automate processes using Flows & Process Builder Collaborate with Sales, Finance & Marketing teams Manage user roles & security Apply: Hr@forcecraver.comarrow_forwardAnswer this questionarrow_forward
- 1. vector projection. Assume, ER1001 and you know the following: ||||=4, 7=-0.5.7. For each of the following, explicitly compute the value. འབ (a) (b) (c) (d) answer. Explicitly compute ||y7||. Explain your answer. Explicitly compute the cosine similarity of and y. Explain your Explicitly compute (x, y). Explain your answer. Find the projection of onto y and the projection of onto .arrow_forward2. Answer the following questions using vectors u and v. --0-0-0 = find the the cosine similarity and the angle between u and v. འརྒྱ (a) (b) find the scalar projection of u onto v. (c) find the projection of u onto v. (d) (e) (f) find the scalar projection of onto u. find the projection of u onto u. find the projection of u onto and the projection of onto . (Hint: find the inner product and verify the orthogonality)arrow_forwardPlease type out answerarrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,


