
Concept explainers
1.
Journalize
1.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and
Record the adjusting entries of Company FP.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Store supplies expense (1) | 6,000 | ||
| Store supplies | 6,000 | |||
| (To record store supplies expense) | ||||
| b. | Insurance expenses | 2,800 | ||
| Prepaid expenses | 2,800 | |||
| (To record prepaid selling expenses) | ||||
| c. | 3,000 | |||
| 3,000 | ||||
| (To record depreciation expenses) | ||||
| d. | Cost of goods sold | 2,700 | ||
| Merchandise inventory (2) | 2,700 | |||
| (To record the inventory shrinkage) |
Table (1)
a. To record store supplies expense:
- Store supplies expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit office supplies expense with $6,000.
- Store supplies are an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office supplies with $6,000.
b. To record prepaid insurance expenses:
- Insurance expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $2,800.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $2,800.
c. To record depreciation expenses:
- Depreciation expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $3,000.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $3,000.
d. To record the shrinkage of inventory:
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and they are increased. Thus, it is debited with $2,700.
- Inventory is an asset account, and they are increased. Hence, debit the inventory returns estimated account by $2,700.
Working Note:
Compute the Store supplies expense.
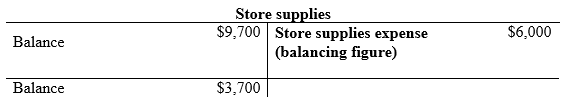 (1)
(1)
Compute the shrinkage of inventory.
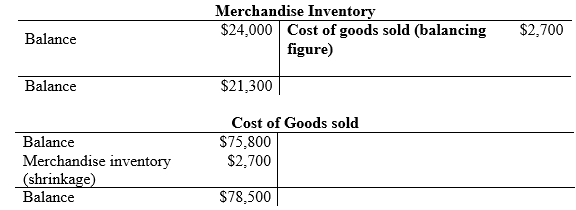 (2)
(2)
2.
Prepare the multi- step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Sales | $227,100 | |
| Less: Sales discounts | $1,000 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | $5,000 | ($6,000) |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold (2) | ($78,500) | |
| Gross profit | $142,600 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Selling expenses | ||
| Depreciation expense—Store equipment | $3,000 | |
| Sales salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Selling space | $13,000 | |
| Store supplies expense (1) | $6,000 | |
| Advertising expense | $17,800 | |
| Total selling expenses | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expenses | ||
| Insurance expense | $2,800 | |
| Office salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Office space | $13,000 | |
| Total general and administrative expenses | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($118,600) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015 is $24,000.
3.
Prepare the single-step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold (2) | $78,500 | |
| Selling expenses (Refer Table (2)) | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expense (Refer Table (2)) | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($197,100) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015 is $24,000.
4.
Compute
4.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the
Acid test ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Gross margin ratio: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross margin ratio. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses.
Formula:
Compute current ratio, acid test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP.
| Computation of ratios | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Cash | $7,400 |
| Merchandise inventory (2) | $21,300 |
| Store supplies (1) | $3,700 |
| Prepaid insurance | $3,800 |
| Total current assets (A) | $36,200 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $18,000 |
| Current ratio | 2.01 |
| Quick assets (Cash) (C) | $7,400 |
| Current liabilities (D) | $18,000 |
| Acid-test ratio | 0.41 |
| Net Sales (E) | $221,100 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (2) | ($78,500) |
| Gross margin (F) | $142,600 |
| Gross margin ratio | 0.64 or 64% |
Table (4)
The current ratio, acid- test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP is 2.01, 0.41 and 0.64 or 64% respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FUNDAMENTALS W/CO
- I need help with this general accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forwardAccounting 12 Could an expert provide a brief summary highlighting one unique feature of the app, recommend it to Sadie—who wants to avoid payroll hassles—and suggest it as she plans to hire employees to extend her dog grooming salon hours? Thank you,arrow_forward
- Required information Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]Reba Dixon is a fifth-grade school teacher who earned a salary of $38,000 in 2021. She is 45 years old and has been divorced for four years. She receives $1,200 of alimony payments each month from her former husband (divorced in 2016). Reba also rents out a small apartment building. This year Reba received $50,000 of rental payments from tenants and she incurred $19,500 of expenses associated with the rental.Reba and her daughter Heather (20 years old at the end of the year) moved to Georgia in January of this year. Reba provides more than one-half of Heather’s support. They had been living in Colorado for the past 15 years, but ever since her divorce, Reba has been wanting to move back to Georgia to be closer to her family. Luckily, last December, a teaching position opened up and Reba and Heather decided to make the move. Reba paid a moving company $2,010 to move their…arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forward
- Please provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forwardRequired information Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]Reba Dixon is a fifth-grade school teacher who earned a salary of $38,000 in 2021. She is 45 years old and has been divorced for four years. She receives $1,200 of alimony payments each month from her former husband (divorced in 2016). Reba also rents out a small apartment building. This year Reba received $50,000 of rental payments from tenants and she incurred $19,500 of expenses associated with the rental.Reba and her daughter Heather (20 years old at the end of the year) moved to Georgia in January of this year. Reba provides more than one-half of Heather’s support. They had been living in Colorado for the past 15 years, but ever since her divorce, Reba has been wanting to move back to Georgia to be closer to her family. Luckily, last December, a teaching position opened up and Reba and Heather decided to make the move. Reba paid a moving company $2,010 to move their…arrow_forwardAccounting 12 Could an expert provide a brief summary highlighting one unique feature of the app, recommend it to Sadie—who wants to avoid payroll hassles—and suggest it as she plans to hire employees to extend her dog grooming salon hours?arrow_forward
- Tally & Co. incurred a pretax operating loss of $100,000 in its first year of operations for both financial reporting and income tax purposes. However, it expects to be profitable in the future. Its expected future income tax rate is 25%.arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





