
Concept explainers
1.
Journalize
1.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and
Record the adjusting entries of Company N.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Store supplies expense (1) | 4,050 | ||
| Store supplies | 4,050 | |||
| (To record store supplies expense) | ||||
| b. | Insurance expenses | 1,400 | ||
| Prepaid expenses | 1,400 | |||
| (To record prepaid selling expenses) | ||||
| c. | 1,525 | |||
| 1,525 | ||||
| (To record depreciation expenses) | ||||
| d. | Cost of goods sold | 1,600 | ||
| Merchandise inventory (2) | 1,600 | |||
| (To record the inventory shrinkage) |
Table (1)
a. To record store supplies expense:
- Store supplies expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit office supplies expense with $4,050.
- Store supplies are an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office supplies with $4,050.
b. To record prepaid insurance expenses:
- Insurance expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $1,400.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $1,400.
c. To record depreciation expenses:
- Depreciation expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $1,525.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $1,525.
d. To record the shrinkage of inventory:
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and they are increased. Thus, it is debited with $1,600.
- Inventory is an asset account, and they are increased. Hence, debit the inventory returns estimated account by $1,600.
Working Note:
Compute the Store supplies expense.
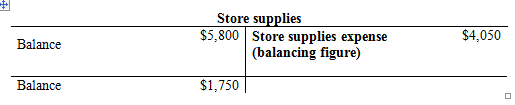 (1)
(1)
Compute the shrinkage of inventory.
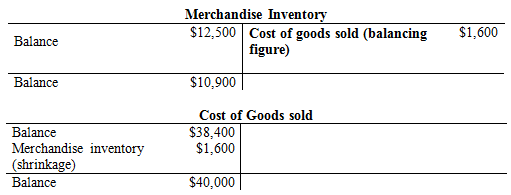 (2)
(2)
2.
Prepare the multi-step income statement of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare the income statement of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015.
| Company N | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Sales | $111,950 | |
| Less: Sales discounts | $2,000 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | $2,200 | ($4,200) |
| Net sales | $107,750 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold (2) | ($40,000) | |
| Gross profit | $67,750 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Selling expenses | ||
| Depreciation expense—Store equipment | $1,525 | |
| Sales salaries expense | $17,500 | |
| Rent expense—Selling space | $7,500 | |
| Store supplies expense (1) | $4,050 | |
| Advertising expense | $9,800 | |
| Total selling expenses | $40,375 | |
| General and administrative expenses | ||
| Insurance expense | $1,400 | |
| Office salaries expense | $17,500 | |
| Rent expense—Office space | $7,500 | |
| Total general and administrative expenses | $26,400 | |
| Total expenses | ($66,775) | |
| Net income | $975 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the net income of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015 is $975.
3.
Prepare the single-step income statement of Company N for the year ended December 31, 2015.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare the income statement of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015.
| Company N | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Net sales | $107,750 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold (2) | $40,000 | |
| Selling expenses (Refer Table (2)) | $40,375 | |
| General and administrative expense (Refer Table (2)) | $26,400 | |
| Total expenses | ($106,775) | |
| Net income | $975 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the net income of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015 is $975.
4.
Compute
4.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the
Acid test ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Gross margin ratio: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross margin ratio. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses.
Formula:
Compute current ratio, acid test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company N.
| Computation of ratios | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Cash | $1,000 |
| Merchandise inventory (2) | $10,900 |
| Store supplies (1) | $1,750 |
| Prepaid insurance | $1,000 |
| Total current assets (A) | $14,650 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $10,000 |
| Current ratio | 1.47 |
| Quick assets (Cash) (C) | $1,000 |
| Current liabilities (D) | $10,000 |
| Acid-test ratio | 0.10 |
| Net Sales (E) | $107,750 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (2) | ($40,000) |
| Gross margin (F) | $67,750 |
| Gross margin ratio | 0.63 or 63% |
Table (4)
The current ratio, acid- test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company N is 1.47, 0.10 and 0.63 or 63% respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FUNDAMENTALS W/CO
- Please Solve this Questionarrow_forwardTechtronic Inc., a manufacturing company, has just completed an order that Micro Solutions placed for 150 gadgets. The direct material, purchased parts, and direct labor costs for the Micro order are as follows: • Cost of direct materials: $54,000 • Cost of purchased parts: $30,000 • Direct labor hours: 300 hours • • Average direct labor pay rate: $18 per hour Overhead costs were applied at a plant wide overhead rate of 250 percent of direct labor dollars. Compute the total cost of the Micro order.arrow_forwardHello tutor please given General accounting question answer do fast and properly explain all answerarrow_forward
- Given below are the account balances for Redstone Corp: . Gross sales: $150,000 • Sales returns and allowances: $6,000 • Selling expenses: $15,000 • Cost of goods sold: $65,000 • Interest expense: $4,000 How much is the gross profit margin?arrow_forwardTechtronic Inc., a manufacturing company, has just completed an order that Micro Solutions placed for 150 gadgets. The direct material, purchased parts, and direct labor costs for the Micro order are as follows: • Cost of direct materials: $54,000 • Cost of purchased parts: $30,000 • Direct labor hours: 300 hours • • Average direct labor pay rate: $18 per hour Overhead costs were applied at a plant wide overhead rate of 250 percent of direct labor dollars. Compute the total cost of the Micro order.arrow_forwardBlueSky Corp has total debt of $250 million and 40 million shares outstanding with a market price of $5.50 per share. Calculate BlueSky's market debt-equity ratio. A) 1.52 B) 0.88 C) 1.14 D) 2.15arrow_forward
- Please need answer the general accounting question not use aiarrow_forwardGroot Co. (GC) sells $1,200,000 of 6-year, 10% bonds at par plus accrued interest. The bonds are dated January 1, 2026 but due to market conditions are not issued until May 1, 2026. Interest is payable on June 30 and December 31 each year. The market rate of interest at time of issue is the same as the stated rate. Required The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 2026. Assume that GC has adopted a policy of crediting accrued interest payable for the accrued interest on the date of sale. Payment of interest on June 30, 2026. Payment of interest on December 31, 2026.arrow_forward1. Define working capital and explain its importance in financial health and liquidity management. 2. Assess how the matching concept and accrual basis affect the reporting of current assets and liabilities. 3. Using a hypothetical balance sheet (you may create one), identify at least 5 current assets and 5 current liabilities and analyze how changes in these elements affect liquidity ratios. 4. Recommend at least two strategies VinGrenDom Ltd. can implement to optimize working capital.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





