
(a)
Interpretation: The mechanism for monochlorination with the help of iodobenzene dichloride should be proposed.
Concept introduction: The monochlorination performed with ultraviolet light proceeds via radical chain mechanism. Chlorine transforms
The mechanism for monochlorination comprises of three stages illustrated as follows:
Step1- Initiation via homolytic cleavage of
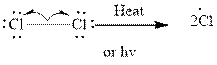
Step2-: Propagation: In first of the propagation steps,
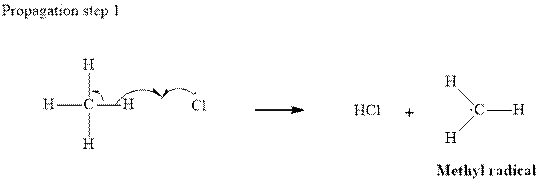
In subsequent propagation step chloromethyl radical abstracts
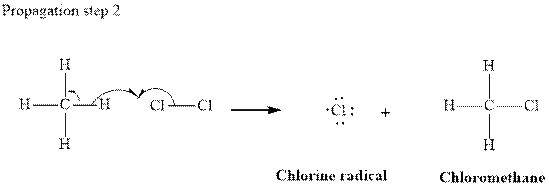
Step3: Termination: Radicals generated in propagation steps get quenched upon combination with one another. Thus termination steps are essentially the radical− radical combination illustrated as follows:
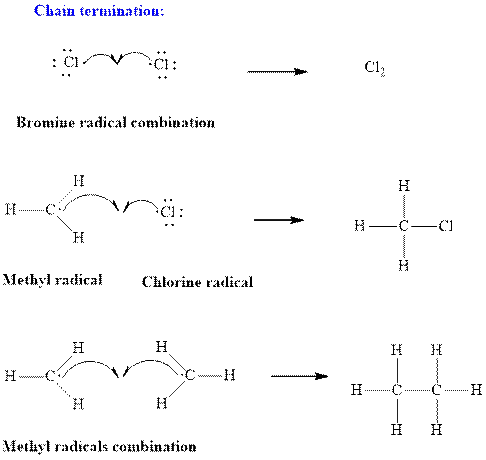
(b)
Interpretation: The three major sites of monochlorination present over steroidsshould be predicted.
Concept introduction: The monochlorination performed with ultraviolet light proceeds via radical chain mechanism. Chlorine transforms
The mechanism for monochlorination comprises of three stages illustrated as follows:
Initiation via homolytic cleavage of
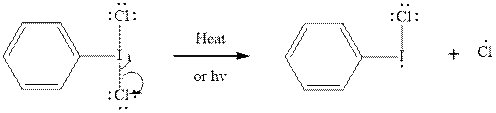
Step2-: Propagation: In first of the propagation steps

In subsequent propagation step alkyl radical abstracts
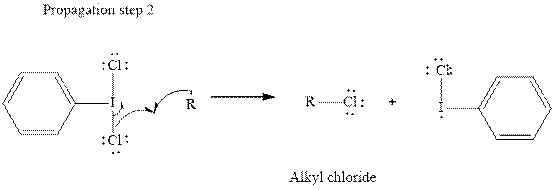
Step3: Termination: Radicals generated in propagation steps get quenched upon combination with one another. Thus termination steps are essentially the radical− radical combination illustrated as follows:
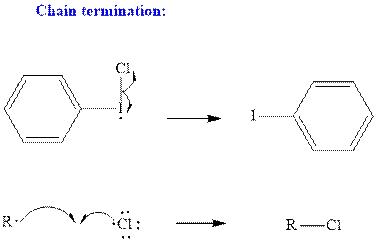
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK STUDY GUIDE/SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR OR
- V Determine whether the following molecule is a hemiacetal, acetal, or neither and select the appropriate box below. Also, highlight the hemiacetal or acetal carbon if there is one. Explanation O CH O Ohemiacetal Oacetal Oneither Check A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Cer 000 Ararrow_forward1. Using Online resources and chemical structures hand draw four different organic compounds (not those already shown in your handout) that are chiral, optically active (a pair of enantiomers will count as one). Pay attention to correct stereochemistry 2. Write or type a short paragraph to Discuss the stereochemical relationship between the four compounds.arrow_forward1. Using a Model set Build a model for the following compound [CHBRIF] 2. Build another model of the mirror image of your first molecule. 3. Place the two models next to each other and take a picture which shows the differences between the two models. 4. Determine the absolute stereochemistry R or S for the two models. 5. Write or type a paragraph to Discuss the stereochemical relationship between the two models of CHBгCIF. You must provide an explanation for your conclusions also provide a description for the colors used to representarrow_forward
- The specific rotation of a sample depends upon measured angle of rotation, the density of the sample, and the pathway length of the light. True Falsearrow_forwardConsider the molecule A,B, C and D shown below, (1 x 4) Br NH2 A OH Br 边 H B C D 1. Assign the R/S configuration to each chiral center and identify by circling all the chiral centers. 2. Draw an image for the enantiomer of each of the compounds A, B, C and D.arrow_forwardCould you crystallize one enantiomer of mandelic acid from a racemic mixture (using the typical achiral solvents found in our lab) without preparing a diastereomeric salt? Why or why not? No, because both enantiomers have the same solubility in achiral solvents. than the other. ооо Yes, because one enantiomer has a higher melting point No, because both enantiomers are liquids. Yes, because one enantiomer is more crystalline than the other.arrow_forward
- If the literature value of specific rotation for a chiral compound is -53.6°, what is the enantiomeric excess of a compound with a measured specific rotation of -40.5°?arrow_forwardThe process to determine the configuration, starts by placing the lowest priority substituent toward the back. If the substituents pointing forward decrease in priority in a clockwise order, the configuration is S. If the substituents decrease in priority in a counterclockwise order, the configuration is R. True Falsearrow_forwardIn the drawing area below, create a hemiacetal with 1 hydroxyl group, 1 methoxy group, and a total of 3 carbon atoms. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check Х PO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Predict the product of the reaction below (3 pts). hydrazine Ph H₂NNH2 KOH Write the mechanism for the above reaction using curved arrows to show electron movements. show all intermediates in the process (7 pts).arrow_forward↓ Feedback (8/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 2 attempts remaining N H3O+ 0 × Select to Draw + V Retryarrow_forward2. Calculate the branching ratio of the reaction of the methyl peroxy radical with either HO, NO 298K) (note: rate constant can be found in the tropospheric chemistry ppt CH,O,+NO-HCHO+HO, + NO, CH₂O+HO, CH₂00H +0₂ when the concentration of hydroperoxyl radical is DH01-1.5 x 10 molecules and the nitrogen oxide maxing ratio of 10 ppb when the concentration of hydroperoxyl radicalis [H0] +1.5x10 molecules cm" and the nitrogen oxide mixing ratio of 30 p Under which condition do you expect more formaldehyde to be produced and whyarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole




