
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given set of compounds the IUPAC should be determined.
Concept introduction:
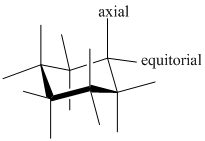
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:
- Newman projection: Newman projection of molecule is one type of representations for the
alkanes , where the projection visualization from one carbon to another carbon. In this Newman projection, front carbon which represented with dot is called proximal and the back carbon which represented with circle is called distal.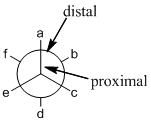
The most stable conformation in the Newman projection is the one which has least steric hindrance among all conformations.
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given set of compounds the IUPAC should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:

- Newman projection: Newman projection of molecule is one type of representations for the alkanes, where the projection visualization from one carbon to another carbon. In this Newman projection, front carbon which represented with dot is called proximal and the back carbon which represented with circle is called distal.

The most stable conformation in the Newman projection is the one which has least steric hindrance among all conformations.
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given set of compounds the IUPAC should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:

- Newman projection: Newman projection of molecule is one type of representations for the alkanes, where the projection visualization from one carbon to another carbon. In this Newman projection, front carbon which represented with dot is called proximal and the back carbon which represented with circle is called distal.

The most stable conformation in the Newman projection is the one which has least steric hindrance among all conformations.
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given set of compounds the IUPAC should be determined.
Concept introduction:
- Chair conformer: chair conformer is a stable conformer for cyclohexane compound. In this chair conformer two positions are important for substitutions one is equatorial and other one axial position. Axial positions are parallel to the axis of ring while equatorial positions are perpendicular to the axis of the ring.
Example:

- Newman projection: Newman projection of molecule is one type of representations for the alkanes, where the projection visualization from one carbon to another carbon. In this Newman projection, front carbon which represented with dot is called proximal and the back carbon which represented with circle is called distal.

The most stable conformation in the Newman projection is the one which has least steric hindrance among all conformations.
Systematic Name: It is a standardized name given for a chemical compound in systematic manner. Any organic molecule can be named by using IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry) rules. IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkyl group and carboxy, amino, cyano etc…
Suffix represents the substituent present in the molecule. It can be any alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton present in the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo.
Common Name: It is quiet opposite to systematic name which is used for branched groups.
Chirality: It refers to a Carbon atom in a molecule that contains four different substituents.
Enantiomers: they are chiral molecules whose mirror images are not superimposable.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Binder Ready Version
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





