
Loose Leaf for Fundamental Accounting Principles
23rd Edition
ISBN: 9781259687709
Author: John J Wild, Ken Shaw Accounting Professor, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4E
Exercise 4-4
Completing a work sheet
Pl
The following data are taken from the unadjusted
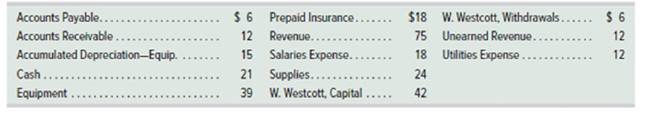
1. Use the data above to prepare a work sheet. Enter the accounts in proper order and enter their balances in the correct Debit or Credit column.
2. Use the following adjustment information to complete the work sheet.
a.
b. Accrued salaries, $6
C. The $12 of unearned revenue has been earned
d. Supplies available at December 31, 2017, $15
e. Expired insurance, $15
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.
4 MCQ
Ovid Holdings acquired Twilight Enterprises on January 1, 2019 for $8,200,000, and recorded goodwill of $1,500,000 as a result of that purchase. At December 31, 2019, the Twilight Enterprises Division had a fair value of $7,300,000. The net identifiable assets of the Division (excluding goodwill) had a fair value of $6,400,000 at that time. What amount of loss on impairment of goodwill should Ovid Holdings record in 2019? a) $0 b) $600,000 c) $900,000 d) $1,500,000
Chapter 4 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Fundamental Accounting Principles
Ch. 4 - Prob. 1DQCh. 4 - Prob. 2DQCh. 4 - Prob. 3DQCh. 4 - Prob. 4DQCh. 4 - Prob. 5DQCh. 4 - Prob. 6DQCh. 4 - 7. Why are the debit and credit entries in the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 8DQCh. 4 - Prob. 9DQCh. 4 - Prob. 10DQ
Ch. 4 - Prob. 11DQCh. 4 - 12. How do reversing entries simplify...Ch. 4 - If a company recorded accrued salaries expense of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 14DQCh. 4 - Prob. 15DQCh. 4 - Prob. 16DQCh. 4 - Prob. 17DQCh. 4 - Prob. 1QSCh. 4 - Prob. 2QSCh. 4 - Prob. 3QSCh. 4 - Prob. 4QSCh. 4 - Prob. 5QSCh. 4 - Prob. 6QSCh. 4 - Prob. 7QSCh. 4 - Prob. 8QSCh. 4 - Prob. 9QSCh. 4 - Prob. 10QSCh. 4 - Prob. 11QSCh. 4 - Prob. 12QSCh. 4 - Exercise 4-1
Extending adjusted account balances...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2ECh. 4 - Prob. 3ECh. 4 - Exercise 4-4 Completing a work sheet Pl The...Ch. 4 - Exercise 4-5 Determining effects of closing...Ch. 4 - Prob. 6ECh. 4 - Exercise 4-7 Preparing a work sheet and recording...Ch. 4 - Prob. 8ECh. 4 - Prob. 9ECh. 4 - Prob. 10ECh. 4 - Prob. 11ECh. 4 - Prob. 12ECh. 4 - Exercise 4-13 Computing the current ratio A1 Use...Ch. 4 - Prob. 14ECh. 4 - Prob. 15ECh. 4 - Prob. 16ECh. 4 - Prob. 17ECh. 4 - Problem 4-1A Applying the accounting cycle C1 C2...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2APSACh. 4 - Prob. 3APSACh. 4 - Prob. 4APSACh. 4 - Problem 4-5A Preparing trial balances, closing...Ch. 4 - Prob. 6APSACh. 4 - Prob. 1BPSBCh. 4 - Prob. 2BPSBCh. 4 - Prob. 3BPSBCh. 4 - Prob. 4BPSBCh. 4 - Prob. 5BPSBCh. 4 - Prob. 6BPSBCh. 4 - Business Solutions P2 P3 (This serial problem...Ch. 4 - Prob. 1GLPCh. 4 - Prob. 2GLPCh. 4 - Prob. 3GLPCh. 4 - Prob. 4GLPCh. 4 - Prob. 5GLPCh. 4 - Prob. 1BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 2BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 3BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 4BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 5BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 6BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 7BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 8BTNCh. 4 - Prob. 9BTN
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forward
- Oyama Manufacturing's performance report shows that its employees worked 120 hours, but their pay card report indicates that they worked 132 hours. What is the variance percentage?arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forwardIt's days' sales uncollected equals:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning  College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub


Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn Journal
Accounting
ISBN:9781337679503
Author:Gilbertson
Publisher:Cengage

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305088436
Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305654174
Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Accounting
ISBN:9781337280570
Author:Scott, Cathy J.
Publisher:South-Western College Pub
The accounting cycle; Author: Alanis Business academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XTspj8CtzPk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY