
Concept explainers
Rank the following ions in order of increasing number of unpaired electrons: Tr3+, Fe2+, V3+, Cu+, Mn4+.
Interpretation: It should be ranked the given set of ions in increasing order of number of unpaired electrons.
Concept Introduction:
- Aufbau Principle tells that the orbital with the lower energy is filled with electrons first and then the filling of higher energy orbital follows. By using this, valence orbital diagram can be draw for any atoms or ions.
- Electronic configuration is the arrangement of the electrons of atoms in the orbital. The electronic configurations are writing for atoms and ions, in accordance with Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s rule.
- According to Pauli Exclusion Principle, no two electrons having the same spin can occupy the same orbital.
- According to Hund’s rule, the orbital in the subshell is filled singly by one electron before the same orbital is doubly filled. When the orbital is singly filled, all the electrons have same spin. In a doubly filled orbital, there are two electrons with opposite spin.
To determine the increasing order of unpaired electrons present in the given set of ions.
Answer to Problem 4.79QP
Ions in increasing order of unpaired electrons,
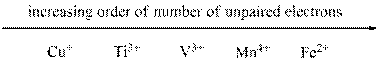
Explanation of Solution
Electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram of
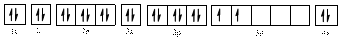
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
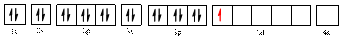
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there is one unpaired electron and which is highlighted in red colour.
Electronic configuration of
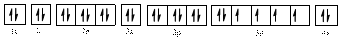
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
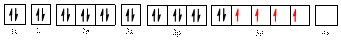
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there are four unpaired electrons that are highlighted in red colour.
Electronic configuration of
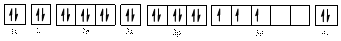
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
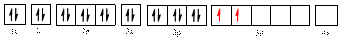
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there are two unpaired electrons, that are highlighted in red colour.
Electronic configuration of
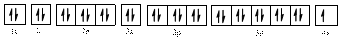
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
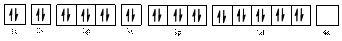
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this we can find that there are no unpaired electrons present.
Electronic configuration of
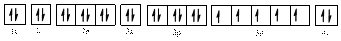
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
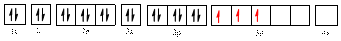
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there are three unpaired electrons present and the same is highlighted in red colour.
Given ions were ranked in increasing order of unpaired electron as follows,
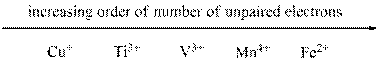
From the number of unpaired electrons for each of the given ions found out in the previous steps we can arrange them in increasing order of number of unpaired electrons as shown above.
The given sets of ions were ranked in increasing order of number of unpaired electrons.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:ATOMS FIRST-2 YEAR CONNECT
- Briefly state the electrocapillary equation for ideally polarized electrodes.arrow_forwardWhat is surface excess according to the Gibbs model?arrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forward
- The molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forwardGiven the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





