
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.5.12P
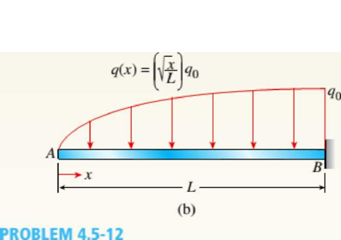
Draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams for a cantilever beam AB acted upon by two different load cases.
- A distributed load with linear variation and maximum intensity q0(see figure part a).
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
this is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = -4, Ay = -12,Az = 32.5, Bx= 34, Bz = 5, By = 0 but how?
This is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = Az = 0, Ay = 2000, TDE = 4750, Cx = 2000, Cy = 2000, Cz = -800 but how?
this is an old practice exam, the answer is Fmin = 290.5lb but how
Chapter 4 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 4 - Calculate the shear force V and bending moment...Ch. 4 - Determine the shear force V and bending moment M...Ch. 4 - Determine the shear force V and bending moment M...Ch. 4 - Calculate the shear force V and bending moment M...Ch. 4 - Consider the beam with an overhang shown in the...Ch. 4 - The beam ABC shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 4 - The beam ABCD shown in the figure has overhangs at...Ch. 4 - At a full d raw, an archer applies a pull of 130 N...Ch. 4 - A curved bar ABC is subjected to loads in the form...Ch. 4 - Under cruising conditions, the distributed load...
Ch. 4 - A beam ABCD with a vertical arm CE is supported as...Ch. 4 - A simply supported beam AB supports a trapezoid...Ch. 4 - Beam ABCD represents a reinforced-concrete...Ch. 4 - Find shear (V) and moment (M) at x = 3L/4 for the...Ch. 4 - Find expressions for shear force V and moment M at...Ch. 4 - Find expressions for shear force V and moment Mat...Ch. 4 - Find expressions for shear force V and moment Mat...Ch. 4 - Find expressions for shear force V and moment M at...Ch. 4 - Find expressions for shear force V and moment M at...Ch. 4 - Find expressions for shear force V and moment M at...Ch. 4 - A cable with force P is attached to a frame at A...Ch. 4 - Find expressions for shear force V and moment M at...Ch. 4 - A cable with force P is attached to a frame at D...Ch. 4 - Frame ABCD carries two concentrated loads (2P at T...Ch. 4 - Frame ABC has a moment release just left of joint...Ch. 4 - The simply supported beam ABCD is loaded by a...Ch. 4 - The centrifuge shown in the figure rotates in a...Ch. 4 - Draw the shear-Force and bending-moment diagrams...Ch. 4 - A simple beam AB is subjected to a counter...Ch. 4 - Draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams...Ch. 4 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure is...Ch. 4 - Cantilever beam AB carries an upward uniform load...Ch. 4 - The simple beam AB shown in the figure is...Ch. 4 - A simple beam AB subjected to couples M1and 3M2...Ch. 4 - A simply supported beam ABC is loaded by a...Ch. 4 - A simply supported beam ABC is loaded at the end...Ch. 4 - A beam ABC is simply supported at A and B and has...Ch. 4 - Beam ABCD is simply supported at B and C and has...Ch. 4 - Draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams...Ch. 4 - The simple beam AB supports a triangular load of...Ch. 4 - The beam AB shown in the figure supports a uniform...Ch. 4 - A cantilever beam AB supports a couple and a...Ch. 4 - The cantilever beam A B shown in the figure is...Ch. 4 - Beam ABC has simple supports at .A and B. an...Ch. 4 - Beam ABC with an overhang at one end supports a...Ch. 4 - Consider the two beams shown in the figures. Which...Ch. 4 - The three beams in the figure have the same...Ch. 4 - The beam ABC shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 4 - A simple beam AB is loaded by two segments of...Ch. 4 - Two beams (see figure) are loaded the same and...Ch. 4 - The beam A BCD shown in the figure has overhangs...Ch. 4 - A beam ABCD with a vertical arm CE is supported as...Ch. 4 - Beams ABC and CD are supported at A,C, and D and...Ch. 4 - The simple beam ACE shown in the figure is...Ch. 4 - A beam with simple supports is subjected to a...Ch. 4 - A beam of length L is designed to support a...Ch. 4 - The compound beam ABCDE shown in the figure...Ch. 4 - Draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams...Ch. 4 - The shear-force diagram for a simple beam is shown...Ch. 4 - The shear-force diagram for a beam is shown in the...Ch. 4 - A compound beam (see figure) has an internal...Ch. 4 - A compound beam (see figure) has an shear release...Ch. 4 - A simple beam AB supports two connected wheel...Ch. 4 - The inclined beam represents a ladder with the...Ch. 4 - Beam ABC is supported by a tie rod CD as shown....Ch. 4 - A plane frame (see figure) consists of column AB...Ch. 4 - The plane frame shown in the figure is part of an...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This is an exam review question. The answer is Pmin = 622.9 lb but whyarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2 = 6mm, and for w3 is h3 =6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm S 133 mm 140 mm Please solve the question above I solved the question but I'm sure the answer is wrong the link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1w5UD2EPDiaKSx3W33aj Rv0olChuXtrQx/view?usp=sharingarrow_forward
- Q2: (15 Marks) A water-LiBr vapor absorption system incorporates a heat exchanger as shown in the figure. The temperatures of the evaporator, the absorber, the condenser, and the generator are 10°C, 25°C, 40°C, and 100°C respectively. The strong liquid leaving the pump is heated to 50°C in the heat exchanger. The refrigerant flow rate through the condenser is 0.12 kg/s. Calculate (i) the heat rejected in the absorber, and (ii) the COP of the cycle. Yo 8 XE-V lo 9 Pc 7 condenser 5 Qgen PG 100 Qabs Pe evaporator PRV 6 PA 10 3 generator heat exchanger 2 pump 185 absorberarrow_forwardQ5:(? Design the duct system of the figure below by using the balanced pressure method. The velocity in the duct attached to the AHU must not exceed 5m/s. The pressure loss for each diffuser is equal to 10Pa. 100CFM 100CFM 100CFM ☑ ☑ 40m AHU -16m- 8m- -12m- 57m 250CFM 40m -14m- 26m 36m ☑ 250CFMarrow_forwardA mass of ideal gas in a closed piston-cylinder system expands from 427 °C and 16 bar following the process law, pv1.36 = Constant (p times v to the power of 1.36 equals to a constant). For the gas, initial : final pressure ratio is 4:1 and the initial gas volume is 0.14 m³. The specific heat of the gas at constant pressure, Cp = 0.987 kJ/kg-K and the specific gas constant, R = 0.267 kJ/kg.K. Determine the change in total internal energy in the gas during the expansion. Enter your numerical answer in the answer box below in KILO JOULES (not in Joules) but do not enter the units. (There is no expected number of decimal points or significant figures).arrow_forward
- my ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending momentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C-FEVzI8oe8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bending Stress; Author: moodlemech;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9QIqewkE6xM;License: Standard Youtube License