
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
Thus, this saturated molecule has 8 additional hydrogen atoms as compared to the given molecular formula. IHD for the given molecular formula is calculated by dividing that number of additional hydrogen atoms by 2. Thus, IHD is
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(b)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
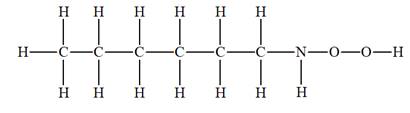
It takes a total of 15 hydrogen atoms to saturate each carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen in this compound. Thus, this saturated molecule has 10 additional hydrogen atoms as compared to the given molecular formula. IHD for the given molecular formula is calculated by dividing that number of additional hydrogen atoms by 2. Thus IHD is
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(c)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
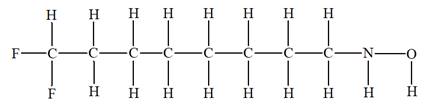
It takes a total of
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(d)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
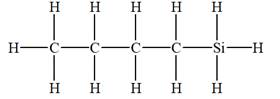
It takes a total of
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(f)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
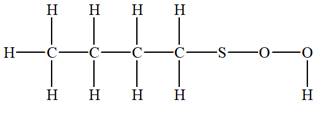
It takes a total of
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
- Question 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
- 2,2-Dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Indicate the products obtained.arrow_forwardAdd conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformationADS fint anditions 百 Abl res condinese NC ง Add on condtions 1.0 B H,N.arrow_forward3. Provide all the steps and reagents for this synthesis. OHarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



