
Concept explainers
(25–30 min.)
Underwood is eager to impress his new employer, and he knows that in 2017. Anderson’s upper management is under pressure to show a profit in a challenging competitive environment because they are hoping to be acquired by a large private equity firm sometime in 2018. At the end of 2016, Underwood decides to adjust the manufacturing overhead rate to 160% of direct labor cost. He explains to the company president that, because overhead was underallocated in 2016, this adjustment is necessary. Cost information for 2017 follows:
| Direct materials control, 1/1/2017 | 25,000 |
| Direct materials purchased, 2017 | 650,000 |
| Direct materials added to production, 2017 | 630,000 |
| Work in process control, 1/1/2017 | 280,000 |
| Direct manufacturing labor, 2017 | 880,000 |
| Cost of goods manufactured, 2017 | 2,900,000 |
| Finished goods control, 1/1/2017 | 320,000 |
| Finished goods control, 12/31/2017 | 290,000 |
| Manufacturing overhead costs, 2017 | 1,300,000 |
Anderson’s revenue for 2017 was $5,550,000, and the company’s selling and administrative expenses were $2,720,000.
- 1. Insert the given information in the T-accounts below. Calculate the following amounts to complete the T-accounts:
Required
- a. Direct materials control, 12/31/2017
- b. Manufacturing overhead allocated, 2017
- c. Cost of goods sold, 2017
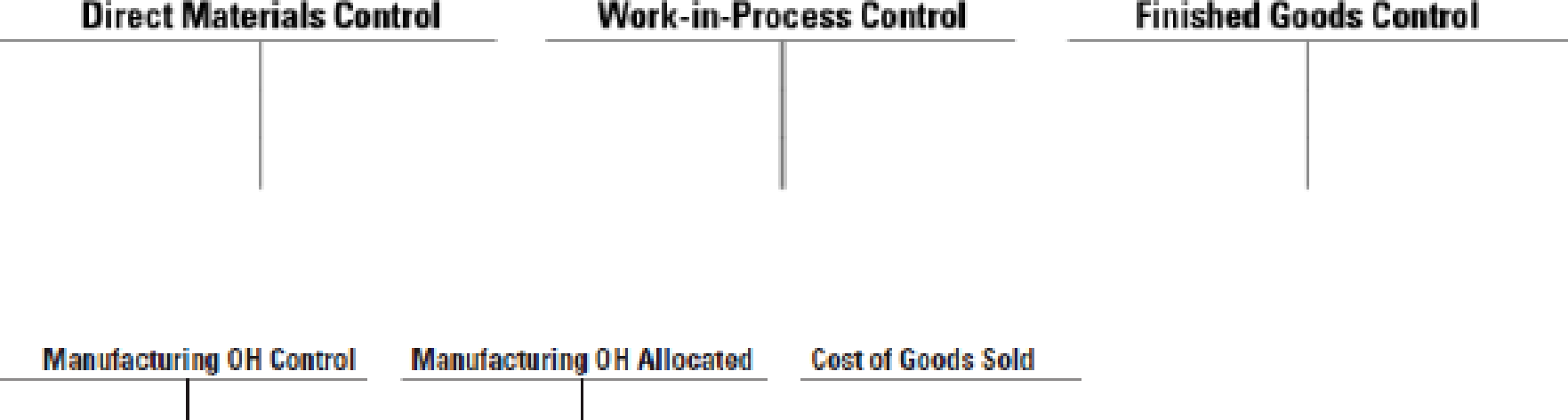
- 2. Calculate the amount of under- or overallocated manufacturing overhead.
- 3. Calculate Anderson’s net operating income under the following:
- a. Under- or overallocated manufacturing overhead is written off to cost of goods sold.
- b. Under- or overallocated manufacturing overhead is prorated based on the ending balances in work in process, finished goods, and cost of goods sold.
- 4. Underwood chooses option 3a above, stating that the amount is immaterial. Comment on the ethical implications of his choice. Do you think that there were any ethical issues when he established the manufacturing overhead rate for 2017 back in late 2016? Refer to the IMA Statement of Ethical Professional Practice.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 4 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Operations Management
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Essentials of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
- Financial Accounting Questionarrow_forwardFlorida Kitchens produces high-end cooking ranges. The costs to manufacture and market the ranges at the company’s volume of 3,000 units per quarter are shown in the following table: Unit manufacturing costs Variable costs $ 1,440 Fixed overhead 720 Total unit manufacturing costs $ 2,160 Unit nonmanufacturing costs Variable 360 Fixed 840 Total unit nonmanufacturing costs 1,200 Total unit costs $ 3,360 The company has the capacity to produce 3,000 units per quarter and always operates at full capacity. The ranges sell for $4,000 per unit. Required: a. Florida Kitchens receives a proposal from an outside contractor, Burns Electric, who will manufacture 1,200 of the 3,000 ranges per quarter and ship them directly to Florida’s customers as orders are received from the sales office at Florida. Florida would provide the materials for the ranges, but Burns would assemble, box, and ship the ranges. The variable manufacturing costs would be…arrow_forwardCan you please solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

