
Compare traditional and ABC cost allocations at a pharmacy (Learning Objective 2)
Gracen Pharmacy, part of a large chain of pharmacies, fills a variety of prescriptions for customers. The complexity of prescriptions filled by Gracen varies widely; pharmacists can spend between five minutes and six hours on a prescription order. Traditionally, the pharmacy has allocated its
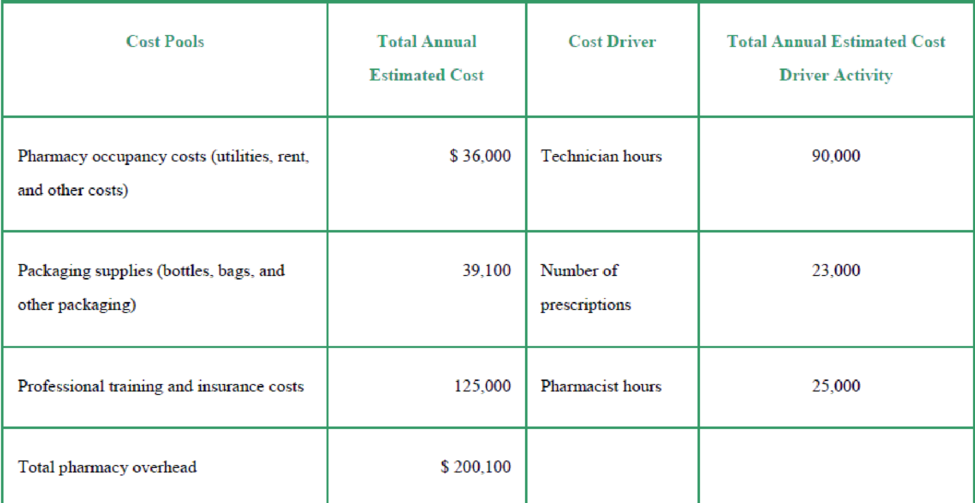
The pharmacy chain’s controller is exploring whether activity-based costing (ABC) may better allocate the pharmacy overhead costs to pharmacy orders. The controller has gathered the following information:

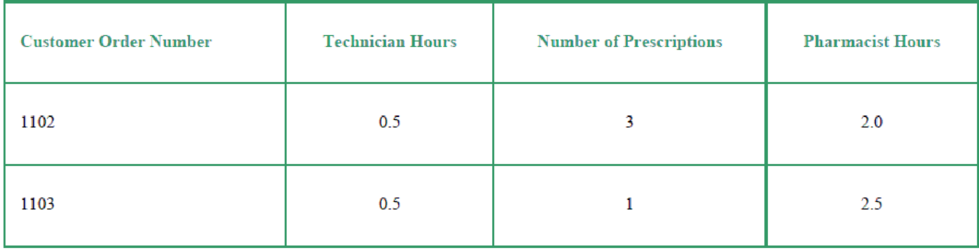
The clerk for Gracen Pharmacy has gathered the following information regarding two recent pharmacy orders:
Requirements
- 1. What is the traditional overhead rate based on the number of prescriptions?
- 2. How much pharmacy overhead would be allocated to customer order number 1102 if traditional overhead allocation based on the number of prescriptions is used?
- 1. How much pharmacy overhead would be allocated to customer order number 1103 if traditional overhead allocation based on the number of prescriptions is used?
- 2. What are the following cost pool allocation rates?
- a. Pharmacy occupancy costs
- b. Packing supplies
- c. Professional training and insurance costs
- 3. How much would be allocated to customer order number 1102 if activity-based costing (ABC) is used to allocate the pharmacy overhead costs?
- 4. How much would be allocated to customer order number 1103 if activity-based costing (ABC) is used to allocate the pharmacy overhead costs?
- 5. Which allocation method (traditional or activity-based costing) would produce a more accurate product cost? Explain your answer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING
- Glendale Manufacturing has a profit margin of 6%, a 40% dividend payout ratio, a total asset turnover of 1.5, and an equity multiplier of 1.6. What is the sustainable growth rate?Solve thisarrow_forwardDuring May, Schultz Company produced 12,000 units of a product called Premium. Premium has a standard materials cost of three pieces per unit at $6 per piece. The actual materials used consisted of 35,000 pieces at a cost of $175,000. Actual purchases of the materials amounted to 45,000 pieces at a cost of $225,000. Compute the two materials variances.arrow_forwardSolve this ?arrow_forward
- Which of the following choice is the correct status of manufacturing overhead at year end ?.arrow_forwardMadison Corporation began 2025 with $24,000 in stockholders' equity. Of this amount, $15,000 was in common stock, and there were no changes in the common stock account during 2025. At December 31, 2025, Madison had $28,000 in stockholders' equity. Madison paid out $9,000 in dividends during the year. How much was its net income in 2025? correct answerarrow_forwardMadison Corporation began 2025 with $24,000 in stockholders' equity. Of this amount, $15,000 was in common stock, and there were no changes in the common stock account during 2025. At December 31, 2025, Madison had $28,000 in stockholders' equity. Madison paid out $9,000 in dividends during the year. How much was its net income in 2025?arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

