
Interpretation:
The two factors behind the polar nature of water are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A solution is a combination of two parts: solute and solvent. The solute is the substance that is present in small quantity and solvent is the substance in which solute is dissolved. Water is considered as one of the active solvents.
A polar molecule is a molecule in which there is an unequal distribution of electron density between the bonds present in the molecule. A polar molecule has partial charges on the atoms of the molecule. The general representation of the polar molecule is:
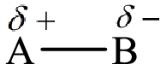
Here, B is more electronegative than A.
Answer to Problem 4.1P
The two factors behind the polar nature of water are:
1. Unequal distribution of electrons in the
2. Bent structure of water molecule.
Explanation of Solution
A water molecule has a bent structure with oxygen atom present as central atom and hydrogen atoms are present as side atom. The structure of the water molecule is,
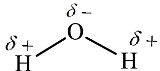
In the
Unequal distribution of electrons in the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
CHEM 212:CHEMISTSRY V 2
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forwardDE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: + H₂O H* ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic products of the reaction below and draw them on right side of the arrow. If there will be no significant reaction, check the box below the drawing area instead. C Cl CH, OH There will be no significant reaction. + pyridine G Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? H R+ H2O Δ OH 0= CH3-CH-O-CH3 + CH3-C-OH Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. dyarrow_forward
- You are trying to determine whether the following organic reaction can be done in a single synthesis step. If so, add any missing reagents or conditions in the drawing area below. If it isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step, check the box below the drawing area instead. Note for advanced students: if you have a choice of reagents to add, you should choose the least reactive and most economical reagents possible. Cl It isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step. + T OHarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: CH3 O CH3-CH-C-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 + H₂OH+ Η ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forward€ CH3-CH-C-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Predict the products of this organic reaction: CH3 O Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. No reaction ✓ Garrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





