
(a) Write an expression for a Riemann sum of a function f on an interval [a, b]. Explain the meaning of the notation that you use.
(b) If
(c) If f(x) takes on both positive and negative values, what is the geometric interpretation of a Riemann sum? Illustrate with a diagram.
(a)
To find: The expression for a Riemann sum of a function
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The expression for a Riemann sum of a function f is
Explanation of Solution
The Riemann sum of a function f is the method to find the total area underneath a curve.
The area under the curve dividedas n number of approximating rectangles. Hence the Riemann sum of a function f is the sum of the area of the all individual rectangles.
Here,
Thus, the expression for a Riemann sum of a function f is
b)
To define: The geometric interpretation of a Riemann sum with diagram.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Consider the condition for the function
Explanation:
The function
Sketch the curve
Show the curve as in Figure 1.
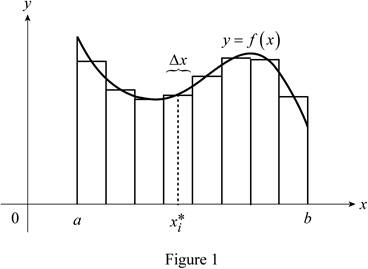
Refer to Figure 1
The function
Thus, the geometric interpretation of a Riemann sum of
c)
To define: The geometric interpretation of a Riemann sum, if the function
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The function
Explanation:
The function
Sketch the curve
Show the curve as in Figure 2.
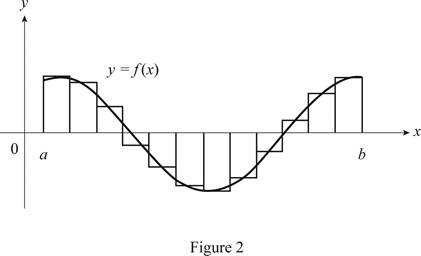
Refer figure 2,
The Riemann sum is the difference of areas of approximating rectangles above and below the x-axis
Therefore, the geometric interpretation of a Riemann sum is defined, if
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK SINGLE VARIABLE CALCULUS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
Elementary Algebra For College Students (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary and Intermediate Algebra: Concepts and Applications (7th Edition)
Intermediate Algebra (13th Edition)
- (10) (16 points) Let R>0. Consider the truncated sphere S given as x² + y² + (z = √15R)² = R², z ≥0. where F(x, y, z) = −yi + xj . (a) (8 points) Consider the vector field V (x, y, z) = (▼ × F)(x, y, z) Think of S as a hot-air balloon where the vector field V is the velocity vector field measuring the hot gasses escaping through the porous surface S. The flux of V across S gives the volume flow rate of the gasses through S. Calculate this flux. Hint: Parametrize the boundary OS. Then use Stokes' Theorem. (b) (8 points) Calculate the surface area of the balloon. To calculate the surface area, do the following: Translate the balloon surface S by the vector (-15)k. The translated surface, call it S+ is part of the sphere x² + y²+z² = R². Why do S and S+ have the same area? ⚫ Calculate the area of S+. What is the natural spherical parametrization of S+?arrow_forward(1) (8 points) Let c(t) = (et, et sint, et cost). Reparametrize c as a unit speed curve starting from the point (1,0,1).arrow_forward(9) (16 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (x² + y − 4)i + 3xyj + (2x2 +z²)k = - = (x²+y4,3xy, 2x2 + 2²). (a) (4 points) Calculate the divergence and curl of F. (b) (6 points) Find the flux of V x F across the surface S given by x² + y²+2² = 16, z ≥ 0. (c) (6 points) Find the flux of F across the boundary of the unit cube E = [0,1] × [0,1] x [0,1].arrow_forward
- (8) (12 points) (a) (8 points) Let C be the circle x² + y² = 4. Let F(x, y) = (2y + e²)i + (x + sin(y²))j. Evaluate the line integral JF. F.ds. Hint: First calculate V x F. (b) (4 points) Let S be the surface r² + y² + z² = 4, z ≤0. Calculate the flux integral √(V × F) F).dS. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardDetermine whether the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines can be used to find another measure of the triangle. a = 13, b = 15, C = 68° Law of Sines Law of Cosines Then solve the triangle. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) C = 15.7449 A = 49.9288 B = 62.0712 × Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward(4) (10 points) Evaluate √(x² + y² + z²)¹⁄² exp[}(x² + y² + z²)²] dV where D is the region defined by 1< x² + y²+ z² ≤4 and √√3(x² + y²) ≤ z. Note: exp(x² + y²+ 2²)²] means el (x²+ y²+=²)²]¸arrow_forward
- (2) (12 points) Let f(x,y) = x²e¯. (a) (4 points) Calculate Vf. (b) (4 points) Given x directional derivative 0, find the line of vectors u = D₁f(x, y) = 0. (u1, 2) such that the - (c) (4 points) Let u= (1+3√3). Show that Duƒ(1, 0) = ¦|▼ƒ(1,0)| . What is the angle between Vf(1,0) and the vector u? Explain.arrow_forwardFind the missing values by solving the parallelogram shown in the figure. (The lengths of the diagonals are given by c and d. Round your answers to two decimal places.) a b 29 39 66.50 C 17.40 d 0 54.0 126° a Ꮎ b darrow_forward(5) (10 points) Let D be the parallelogram in the xy-plane with vertices (0, 0), (1, 1), (1, 1), (0, -2). Let f(x,y) = xy/2. Use the linear change of variables T(u, v)=(u,u2v) = (x, y) 1 to calculate the integral f(x,y) dA= 0 ↓ The domain of T is a rectangle R. What is R? |ǝ(x, y) du dv. |ð(u, v)|arrow_forward
- 2 Anot ined sove in peaper PV+96252 Q3// Find the volume of the region between the cylinder z = y2 and the xy- plane that is bounded by the planes x=1, x=2,y=-2,andy=2. vertical rect a Q4// Draw and Evaluate Soxy-2sin (ny2)dydx D Lake tarrow_forwardDetermine whether the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines can be used to find another measure of the triangle. B 13 cm 97° Law of Sines Law of Cosines A 43° Then solve the triangle. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) b = x C = A = 40.00arrow_forwardFind the missing values by solving the parallelogram shown in the figure. (The lengths of the diagonals are given by c and d. Round your answers to two decimal places.) a 29 b 39 d Ꮎ 126° a Ꮎ b darrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning  Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning



