
Concept explainers
For Exercises 1-14,
a. Write the domain.
b. Write the range.
c. Find the x-intercept(s).
d. Find the y-intercept.
e. Determine the asymptotes if applicable.
f. Determine the intervals over which the function is increasing.
g. Determine the intervals over which the function is decreasing.
h. Match the function with its graph.
1.
(a)
To find the domainof the function
Answer to Problem 1PRE
The domain of function
Explanation of Solution
Given: The function
Formula Used:
The domain of a function is the set of input or argument values for which the function is real and defined.
Calculation:
The function has no undefined points nor domain constraints. So, the domain will be all real numbers.
Therefore, the domain is
Conclusion:
The domain of function
(b)
To find the range of the function
Answer to Problem 1PRE
The range of function
Explanation of Solution
Given: The function
Formula Used:
The range of a function is the set of values of the dependent variable for which a function is defined.
Calculation:
Here, the function
Conclusion:
The range of function
(c)
To find x-intercept of the function
Answer to Problem 1PRE
There is no x-intercept
Explanation of Solution
Given: Function -
Formula Used:
x-intercept is a point on the graph where
Calculation:
The y-intercept of a function is obtained at the point when
But,
So, there is no such value of x which gives
Conclusion:
Hence, there are no x-axis interception points.
(d)
To find the y-intercept of the function
Answer to Problem 1PRE
The y-intercept of function
Explanation of Solution
Given: Function -
Formula Used:
y-intercept is a point on the graph where
Calculation:
Function is given as
For y-intercept,
And
Thus, y-axis interception point is
Conclusion:
The y-intercept of function
(e)
To find Asymptotes (if applicable) of the function
Answer to Problem 1PRE
There are no asymptotes of the function
Explanation of Solution
Given: Function -
Formula Used:
If
Calculation:
Given function is
There are no asymptotes as polynomial functions of degree 1 or higher can’t have asymptotes.
Conclusion:
Hence, there is no asymptote for the function
(f)
To find intervals over which the function
Answer to Problem 1PRE
Function is not an increasing function.
Explanation of Solution
Given: Function -
Formula Used:
If
Calculation:
Derivative of
Thus, the function is not increasing.
Conclusion:
Hence, function is not an increasing function
(g)
To find intervals over which the function
Answer to Problem 1PRE
Function is not a decreasing function.
Explanation of Solution
Given: Function -
Formula Used:
If
Calculation:
Derivative of
Thus, the function is not decreasing.
Conclusion:
Hence, the function is not a decreasing function
(h)
To graph the function
Explanation of Solution
Given: Function -
Graph:
Given function is
When
When
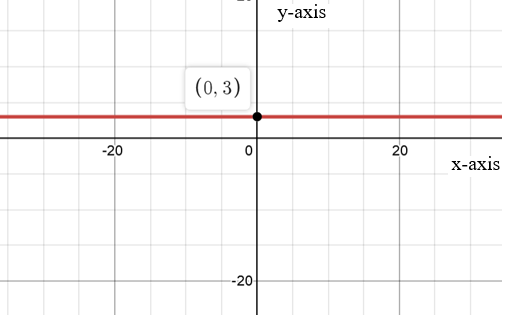
Thus, the graph is matched with the function
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
COLLEGE ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY(LL) FDS
- Solve the problems on the imagearrow_forwardAsked this question and got a wrong answer previously: Third, show that v3 = (−√3, −3, 3)⊤ is an eigenvector of M3 . Also here find the correspondingeigenvalue λ3 . Just from looking at M3 and its components, can you say something about the remaining twoeigenvalues? If so, what would you say?arrow_forwardDetermine whether the inverse of f(x)=x^4+2 is a function. Then, find the inverse.arrow_forward
- The 173 acellus.com StudentFunctions inter ooks 24-25/08 R Mastery Connect ac ?ClassiD-952638111# Introduction - Surface Area of Composite Figures 3 cm 3 cm 8 cm 8 cm Find the surface area of the composite figure. 2 SA = [?] cm² 7 cm REMEMBER! Exclude areas where complex shapes touch. 7 cm 12 cm 10 cm might ©2003-2025 International Academy of Science. All Rights Reserved. Enterarrow_forwardYou are given a plane Π in R3 defined by two vectors, p1 and p2, and a subspace W in R3 spanned by twovectors, w1 and w2. Your task is to project the plane Π onto the subspace W.First, answer the question of what the projection matrix is that projects onto the subspace W and how toapply it to find the desired projection. Second, approach the task in a different way by using the Gram-Schmidtmethod to find an orthonormal basis for subspace W, before then using the resulting basis vectors for theprojection. Last, compare the results obtained from both methodsarrow_forwardPlane II is spanned by the vectors: - (2) · P² - (4) P1=2 P21 3 Subspace W is spanned by the vectors: 2 W1 - (9) · 1 W2 1 = (³)arrow_forward
- show that v3 = (−√3, −3, 3)⊤ is an eigenvector of M3 . Also here find the correspondingeigenvalue λ3 . Just from looking at M3 and its components, can you say something about the remaining twoeigenvalues? If so, what would you say? find v42 so that v4 = ( 2/5, v42, 1)⊤ is an eigenvector of M4 with corresp. eigenvalue λ4 = 45arrow_forwardChapter 4 Quiz 2 As always, show your work. 1) FindΘgivencscΘ=1.045. 2) Find Θ given sec Θ = 4.213. 3) Find Θ given cot Θ = 0.579. Solve the following three right triangles. B 21.0 34.6° ca 52.5 4)c 26° 5) A b 6) B 84.0 a 42° barrow_forwardQ1: A: Let M and N be two subspace of finite dimension linear space X, show that if M = N then dim M = dim N but the converse need not to be true. B: Let A and B two balanced subsets of a linear space X, show that whether An B and AUB are balanced sets or nor. Q2: Answer only two A:Let M be a subset of a linear space X, show that M is a hyperplane of X iff there exists ƒ€ X'/{0} and a € F such that M = (x = x/f&x) = x}. fe B:Show that every two norms on finite dimension linear space are equivalent C: Let f be a linear function from a normed space X in to a normed space Y, show that continuous at x, E X iff for any sequence (x) in X converge to Xo then the sequence (f(x)) converge to (f(x)) in Y. Q3: A:Let M be a closed subspace of a normed space X, constract a linear space X/M as normed space B: Let A be a finite dimension subspace of a Banach space X, show that A is closed. C: Show that every finite dimension normed space is Banach space.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL





