
Concept explainers
Explain how connective tissues differ from epithelial tissues in structure and function.
To review:
The difference between connective tissues and epithelial tissues, based on their structure and function.
Introduction:
Tissues are a group of cells that have a specific function. In a living organism, tissues are of four types, namely, epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue. The function and structure of these tissues vary from each other.
Explanation of Solution
The difference between connective tissues and epithelial tissues is given in the following table:
| Connective tissue | Epithelial tissue |
| This group of tissues connects different tissues with each other. | Epithelial tissue is the most abundant tissue as it covers the cavities and the surface of the body. |
| They have an extracellular matrix (ECM) where cells are scattered. Fibers and ground substances, are important structural parts of ECM. | The cells are arranged in a sheet-like manner with little ECM. There are no blood vessels in epithelial tissues. |
| Connective tissues are classified into proper connective tissue and specialized connective tissue. | Based on the tissue layer, epithelial tissues can be classified into simple and stratified. Simple epithelia have a single layer, whereas stratified epithelia have more than one layer. |
| Specialized connective tissues are cartilage, bone, and blood. Proper connective tissues are again classified into loose connective tissues, dense connective tissues, reticular tissues, and adipose tissues. | They are seen in three different principal shapes, namely, squamous, columnar, and cuboidal. |
| Blood is an example of a connective tissue. It transports nutrients and oxygen to various organs. Connective tissues provide support to our skeletal system. An example of a connective tissue that provides support is cartilage and dense connective tissue. | Epithelial tissues act as a barrier against mechanical and thermal injury. The best example is skin. |
The diagrams showing the structures of different types of connective and epithelial tissues are shown below:

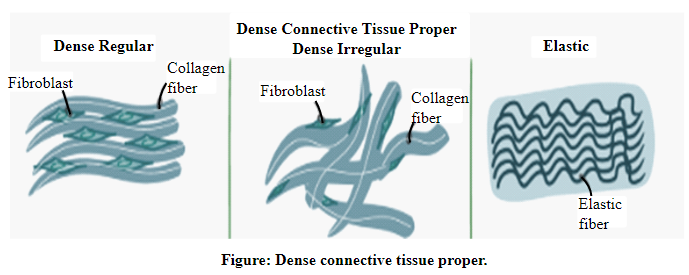
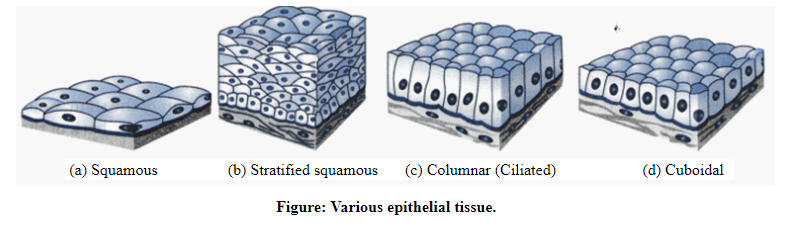
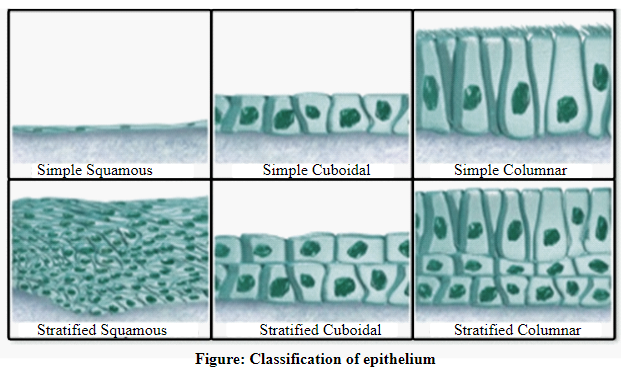
Thus, it can be concluded that the two tissue classifications, namely, epitheliumand connective tissues, play a major role in the defense mechanism of the body. Based on their composition, they can also be further classified into different types.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology Plus Mastering A&P with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (2nd Edition) (What's New in Anatomy & Physiology)
- 18. Watch this short youtube video about SARS CoV-2 replication. SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle (Summer 2020) - YouTube.19. What is the name of the receptor that SARS CoV-2 uses to enter cells? Which human cells express this receptor? 20. Name a few of the proteins that the SARS CoV-2 mRNA codes for. 21. What is the role of the golgi apparatus related to SARS CoV-2arrow_forwardState the five functions of Globular Proteins, and give an example of a protein for each function.arrow_forwardDiagram of check cell under low power and high powerarrow_forward
- a couple in which the father has the a blood type and the mother has the o blood type produce an offspring with the o blood type, how does this happen? how could two functionally O parents produce an offspring that has the a blood type?arrow_forwardWhat is the opening indicated by the pointer? (leaf x.s.) stomate guard cell lenticel intercellular space none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue? (stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem ○ phloem none of thesearrow_forward
- Where did this structure originate from? (Salix branch root) epidermis cortex endodermis pericycle vascular cylinderarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





