
Concept explainers
From Recording Transactions to Preparing Accrual and Deferral Adjustments and Reporting Results on the
RunHeavy Corporation (RHC) is a corporation that manages a local rock band. RHC was formed with an investment of $ 10,000 cash, paid in by the leader of the band on January 3 in exchange for common stock. On January 4, RHC purchased music equipment by paying $2,000 cash and signing an $8,000 promissory note payable in three years. On January 5, RHC booked the band for six concert events, at a price of $2,500 each. Of the six events, four were completed between January 10 and 20. On January 22, cash was collected for three of the four events. The other two bookings were for February concerts, but on January 24, RHC collected half of the $2,500 fee for one of them. On January 27, RHC paid $3,140 cash for the band’s travel-related costs. On January 28, RHC paid its band members a total of $2,400 cash for salaries and wages for the first three events. As of January 31, the band members hadn’t yet been paid wages for the fourth event completed in January, but they would be paid in February at the same rate as for the first three events. As of January 31, RHC has not yet recorded the $ 100 of monthly
Required:
- 1. Prepare
journal entries to record the transactions and adjustments needed on each of the dates indicated above. - 2.
Post the journal entries from requirement 1 to T-accounts, calculate ending balances, and prepare an adjustedtrial balance . - 3. Prepare a classified balance sheet and income statement as of and for the month ended January 31.
1.
To prepare: The journal entries for the given transactions and to prepare the adjusting entries that are needed on each of the dates.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Prepare the journal entries:
Journal entry for issuance of common stock:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 3 | Cash (A+) | 10,000 | |
| Common stock (SE+) | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of common stock to investors) |
Table (1)
- Cash is an asset. There is an increase in the asset. Hence, debit cash account with $10,000.
- Common stock is a component of stock holders’ equity. There is an increase in the common stock which increases the stock holders’ equity. Hence, credit common stock with $10,000.
Journal entry for purchase of equipment:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 4 | Equipment (A+) | 10,000 | |
| Notes payable (L+) | 8,000 | ||
| Cash (A–) | 2,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of equipment partly for cash and partly by signing a note ) |
Table (2)
- Equipment is an asset. There is an increase in the asset. Hence, debit equipment with $10,000.
- Notes payable is a liability. There is an increase in the liability. Hence, credit notes payable with $8,000.
- Cash is an asset. There is a decrease in the asset. Hence, credit cash account with $2,000.
January ,5:
RHC booked the band for six concert events. As the booking represents only the mere exchange of promises, there is no need of recording the journal entry for that transaction. Hence, no entry is recorded.
Journal entry for providing services on account:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 10-20 |
Accounts receivable (A+) |
10,000 |
|
| Service revenue(R+) (SE+) | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the service made on account) |
Table (3)
- Accounts receivable is an asset. There is an increase in the asset. Hence, debit accounts receivable with $10,000.
- Service revenue is a revenue account which is a component of stock holders’ equity. There is an increase in the revenue account which increases the stockholders’ equity. Hence credit stockholders’ equity with $10,000.
Journal entry for receiving cash for the service provided:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 22 | Cash (A+) | 7,500 | |
| Accounts receivable (A-) | 7,500 | ||
| (To record the cash receipt for the service performed on account) |
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset. There is an increase in the asset. Hence, debit cash account with $7,500.
- Accounts receivable is an asset. There is a decrease in the asset. Hence, credit accounts receivable with $7,500.
Working note:
Journal entry for unearned revenue:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 24 | Cash (A+) | 1,250 | |
| Unearned revenue (L+) | 1,250 | ||
| (To record the cash receipt for the service performed on account) |
Table (5)
- Cash is an asset. There is an increase in the asset. Hence, debit cash account with $1,250.
- Unearned revenue is a liability. There is an increase in the liability. Hence, credit unearned revenue with $1,250.
Working note:
Journal entry for travel expenses:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 27 | Travel expense (E+) (SE-) | 3,140 | |
| Cash (A-) | 3,140 | ||
| (To record the payment made for travel expense) |
Table (6)
- Travel expense is an expense account which is a component of stock holders’ equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreases the stockholders’ equity. Hence, debit travel expense with $3,140.
- Cash is an asset. There is a decrease in the asset. Hence, credit cash account with $3,140.
Journal entry for salaries and wages expense:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 28 | Salaries and wages expense (E+) (SE-) | 2,400 | |
| Cash (A-) | 2,400 | ||
| (To record the salaries and wages expense) |
Table (7)
- Salaries and wages expense is an expense account which is a component of stock holders’ equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreases the stockholders’ equity. Hence, debit salaries and wages expense with $2,400.
- Cash is an asset. There is a decrease in the asset. Hence, credit cash account with $2,400.
Adjusting entry for salaries and wages payable:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 31 | Salaries and wages expense (E+) (SE-) | 800 | |
| Salaries and wages payable (L+) | 800 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry salaries and wages expense) |
Table (8)
- Salaries and wages expense is an expense account which is a component of stock holders’ equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreases the stockholders’ equity. Hence, debit salaries and wages expense with $800.
- Salaries and wages payable is a liability. There is an increase in the liability. Hence, credit, salaries and wages payable with $800.
Working note:
Adjusting entry for accumulated depreciation on equipment:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 31 | Depreciation expense (E+) (SE-) | 100 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Equipment (xA+) (A-) | 100 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry salaries and accumulated depreciation) |
Table (9)
- Depreciation expense is an expense account which is a component of stockholders’ equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreases the stockholders’ equity. Hence, debit depreciation expense with $100.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. There is an increase in the contra-asset which decreases the asset account. Hence, credit accumulated depreciation with $100.
Adjusting entry for interest expense:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 31 | Interest expense (E+) (SE-) | 60 | |
| Interest payable (L+) | 60 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for interest expense) |
Table (10)
- Interest expense is an expense account which is a component of stock holders’ equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreases the stockholders’ equity. Hence, debit interest expense with $60.
- Interest payable is a liability. There is an increase in the liability. Hence, credit, interest payable with $60.
Adjusting entry for income tax expense:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January, 31 | Income tax expense (E+) (SE-)(2) | 525 | |
| Income tax payable (L+) | 525 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for income tax expense) |
Table (11)
- Income tax expense is an expense account which is a component of stock holders’ equity. There is an increase in the expense account which decreases the stockholders’ equity. Hence, debit interest expense with $60.
- Income tax payable is a liability. There is an increase in the liability. Hence, credit, interest payable with $60.
2.
To prepare: The T-Accounts for the journal entries to calculate the ending balance and prepare an adjusted trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal entries are posted to this account. It is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.
The components of the T-account are as follows:
- The title of the account
- The left or debit side
- The right or credit side
Prepare the T-account:
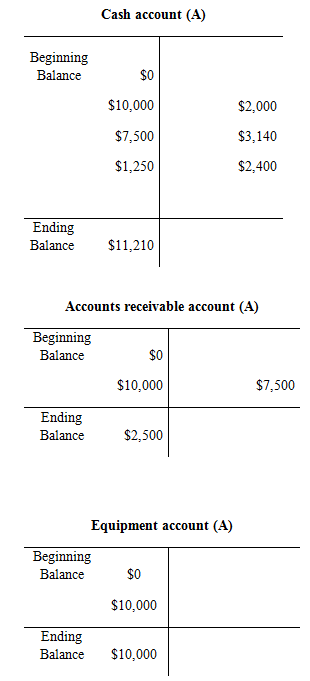
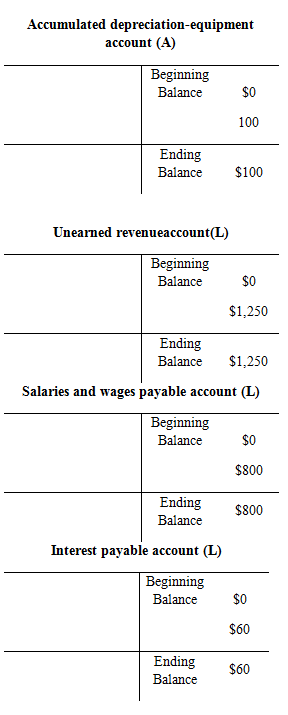
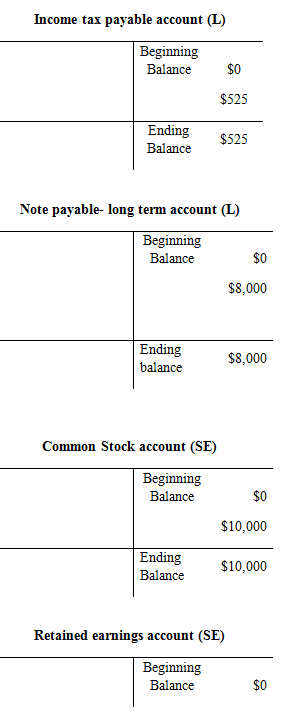
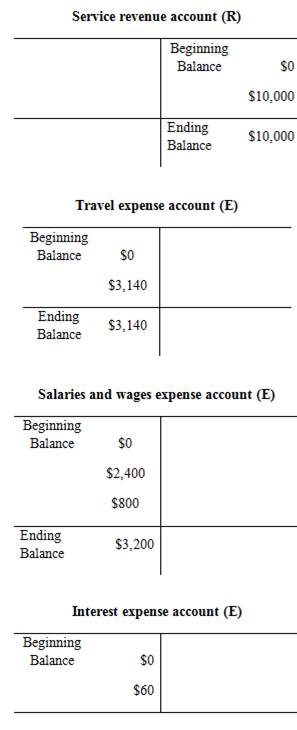
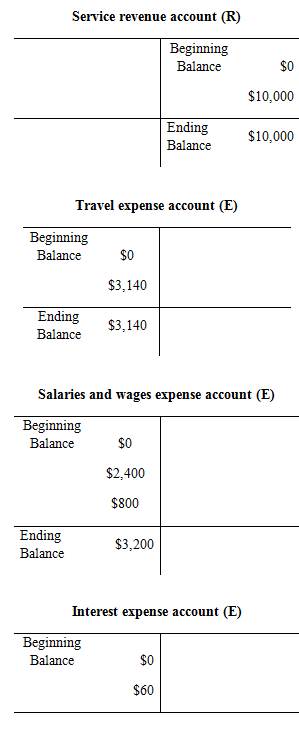
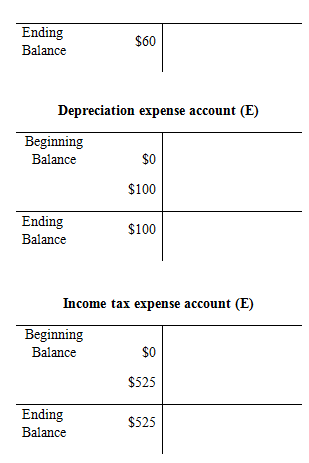
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance:
| Corporation RH | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| As on 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Debits ($) | Credits ($) |
| Cash | 11,210 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 2,500 | |
| Equipment | 10,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation-equipment | 100 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 1,250 | |
| Salaries and Wages payable | 800 | |
| Interest Payable | 60 | |
| Income Tax Payable | 525 | |
| Note Payable (long–term) | 8,000 | |
| Common Stock | 10,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 0 | |
| Service Revenue | 10,000 | |
| Travel Expense | 3,140 | |
| Salaries and Wages expense | 3,200 | |
| Interest Expense | 60 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 100 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 525 | |
| Total | 30,735 | 30,735 |
Table (12)
The debit column and credit column of the adjusted trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $30,735.
3.
To prepare: An income statement as on 31st January, and classified balance sheet.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues.
Prepare the income statement as on 31st January.
| Corporation RH | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Month Ended January 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Service Revenue | 10,000 | |
| Total Revenue | 10,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Salaries and Wages expense | 3,200 | |
| Travel Expenses | 3,140 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 100 | |
| Interest Expense | 60 | |
| Income Tax Expense(2) | 525 | |
| Total Expenses | 7,025 | |
| Net income | 2,975 | |
Table (13)
Working note:
Calculate the income before income tax:
Calculate the income tax expense:
Thus the income statement of Corporation R is prepared and it shows the net income of $2,975.
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Prepare the classified balance sheet as on 31st January:
| Corporation RH | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As on 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Assets | ||
| Current Assets: | ||
| Cash | 11,210 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 2,500 | |
| Total Current Assets | 13,710 | |
| Non-Current assets: | ||
| Equipment | 10,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation–Equipment | (100) | |
| Equipment, net of Accumulated Depreciation | 9,900 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $23,610 | |
| Liabilities and stockholders’ equity | ||
| Current Liabilities: | ||
| Unearned Revenue | 1,250 | |
| Salaries and Wages Payable | 800 | |
| Interest Payable | 60 | |
| Income Tax Payable | 525 | |
| Total Current Liabilities | 2,635 | |
| Non-Current liabilities: | ||
| Note Payable (long–term) | 8,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | 10,635 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity: | ||
| Common Stock | 10,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 2,975 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 12,975 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | 23,610 | |
Table (14)
Thus, the classified balance sheet of Corporation RHC is prepared and the total assets and liabilities showing equal balance of $23,610.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Financial Accounting
- Which account is a contra-asset?A. Accounts PayableB. Accumulated DepreciationC. Notes ReceivableD. Prepaid Rentneedarrow_forwardIf cash is received before services are provided, what is the journal entry?A. Debit Revenue, Credit CashB. Debit Unearned Revenue, Credit CashC. Debit Cash, Credit Unearned RevenueD. Debit Accounts Receivable, Credit RevenueCorrectarrow_forwardIf cash is received before services are provided, what is the journal entry?A. Debit Revenue, Credit CashB. Debit Unearned Revenue, Credit CashC. Debit Cash, Credit Unearned RevenueD. Debit Accounts Receivable, Credit Revenuecorrectarrow_forward
- GAP Corp. is a calendar year S corporation with three shareholders. George and Anna each own 49 percent of the stock. Peter owns 2 percent of the stock. The corporation was formed on January 2, Year 1, and has been an S corporation since its inception. Using the exhibits, prepare a schedule of GAP's income, gain, loss, and deduction items for Year 2. In column B, enter the amount for federal income tax purposes. In column C, enter the amount included in GAP's Form 1120S ordinary business income (OBI) or loss. In column D, enter the amount included on GAP's Schedule K as a taxable or deductible separately stated item. Each item may have amounts entered in ordinary business income, separately stated items, or both. Enter income and gain amounts as positive numbers. Enter losses and deductions as negative numbers. If the amount is zero, enter a zero (0). A B C D 1 Income, Gain, Loss, and Deduction Items Amount for Federal Income Tax Purposes Ordinary Business Income…arrow_forwardIf cash is received before services are provided, what is the journal entry?A. Debit Revenue, Credit CashB. Debit Unearned Revenue, Credit CashC. Debit Cash, Credit Unearned RevenueD. Debit Accounts Receivable, Credit Revenue need helparrow_forwardDennis Green and Peter Olinto are equal partners in Foxy Partnership. Peter is an active general partner. Dennis is a limited partner and is not involved in the operations of the business. Foxy Partnership's Year 2 financial statements are provided in the exhibits. Using the information provided, enter the appropriate amounts to be reported on page 1 of Foxy Partnership's income tax return in the table below. Enter all amounts as positive whole values. If a response is zero, enter a zero (0). A B 1 Gross receipts or sales 2 Cost of goods sold 3 Salaries and wages 4 Guaranteed payments to partners 5 Repairs and maintenance 6 Bad debts 7 Rent 8 Depreciation 9 Other deductions 10 Ordinary business income (loss)arrow_forward
- Dennis Green and Peter Olinto are equal partners in Foxy PartneDennis Green and Peter Olinto are equal partners in Foxy Partnership. Peter is an active general partner. Dennis is a limited partner and is not involved in the operations of the business. Foxy Partnership's Year 2 financial statements are provided in the exhibits. Using the information provided, enter the appropriate amounts to be reported on page 1 of Foxy Partnership's income tax return in the table below. Enter all amounts as positive whole values. If a response is zero, enter a zero (0). 2. Cost of goods sold 3. Salaries and wages 4. Guaranteed payments to partners 5. Repairs and maintenance 6. Bad debts 7. Rent 8. Depreciation 9. Other deductions 10. Ordinary business income (loss)arrow_forwardIf a business pays off a loan, which of the following will occur?A. Assets and liabilities increaseB. Assets and liabilities decreaseC. Only liabilities increaseD. Equity decreasesarrow_forwardWhich financial statement lists revenues and expenses?A. Balance SheetB. Cash Flow StatementC. Income StatementD. Retained Earnings Statementneedarrow_forward
- No chatgpt! Which financial statement lists revenues and expenses?A. Balance SheetB. Cash Flow StatementC. Income StatementD. Retained Earnings Statementarrow_forwardWhich financial statement lists revenues and expenses?A. Balance SheetB. Cash Flow StatementC. Income StatementD. Retained Earnings StatementNo Aiarrow_forwardWhich financial statement lists revenues and expenses?A. Balance SheetB. Cash Flow StatementC. Income StatementD. Retained Earnings Statementarrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

