
Concept explainers
Label the structures in this diagram of an animal cell. Review the functions of each of these organelles.
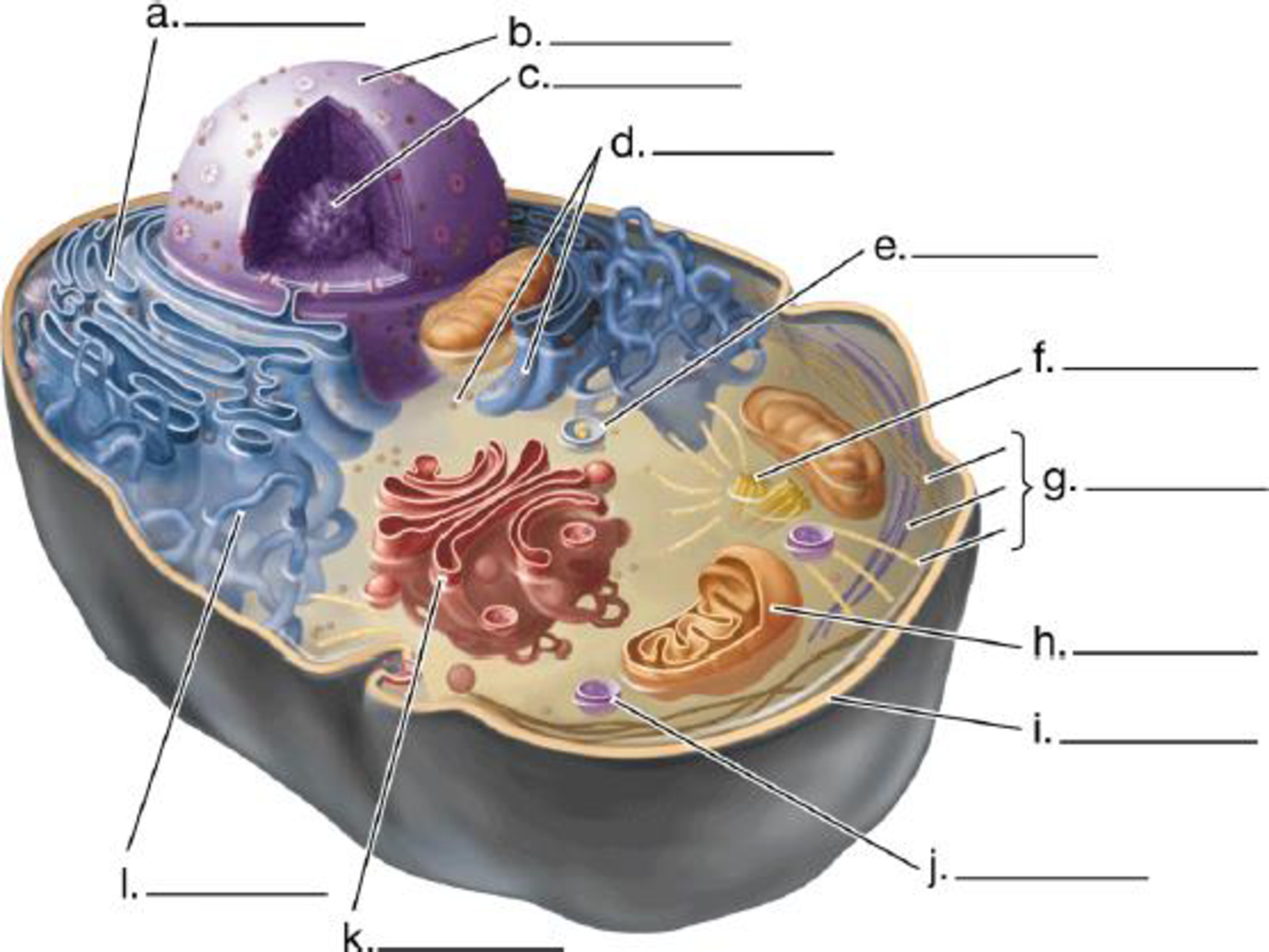
To review: The structures and functions of each of the organelles in the given animal cell.
Introduction:
A cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of living organisms. It is bounded by a cell membrane. Cells contain different organelles. Each organelle has its own specific features and functions. Each cellular organelle possesses different structural peculiarities.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
Fig. 1 shows various structural organelles of an animal cell.
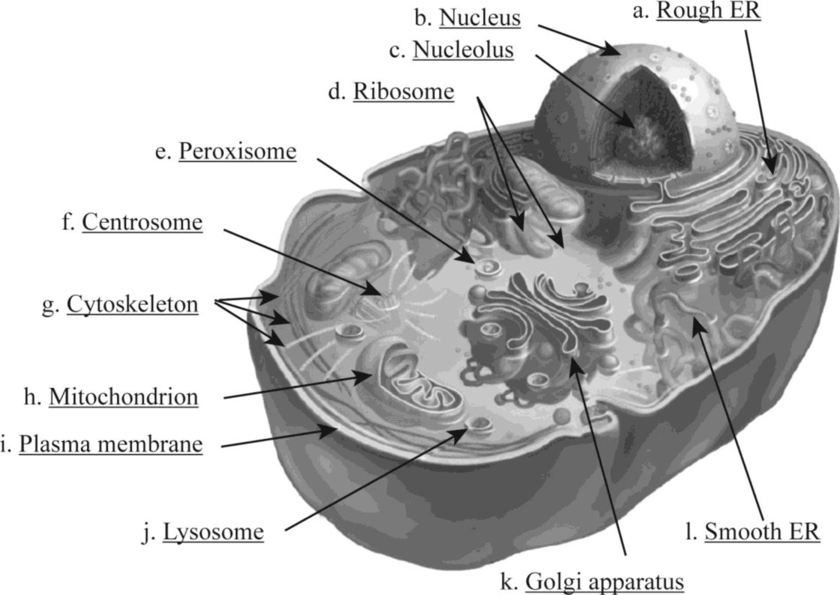
Fig. 1: Structure of an animal cell
The functions of various organelles are very specific.
- a. Rough ER: It is a network of membranous sacs and tubes; its external surface is attached with the ribosome. It helps in protein processing and secretion. Also, the addition of carbohydrate with protein occurs to produce glycoprotein, which helps in the production of a new membrane within the cell.
- b. Nucleus: It is a membrane-bound organelle covered by the nuclear envelope. The nucleus contains the nucleolus and chromatin material. The chromatin material consists of DNA and proteins.
- c. Nucleolus: It is a core region in the nucleus where components of the ribosome assemble.
- d. Ribosome: It is a non-membranous structure found in the cytoplasm of the cell. It is the core organelle for protein synthesis. It can be found free or attached with the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- e. Peroxisome: It is a specialized single membrane–bound vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell. It produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product and converts it to water.
- f. Centrosome: The formation of microtubules initiates at the centrosome. It contains a pair of centrioles.
- g. Cytoskeleton: It consists of a network of fibrous substances within the cytoplasm of a cell. The cytoskeleton consists of three main fibers called microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. It helps in providing rigidity and gives structural support to the cell.
- h. Mitochondrion: It is double membrane–bound organelle. It is important for cellular respiration and energy generation in the form of ATP. The two phospholipid bilayer membranes enclosed with the mitochondria play a great role in functioning of mitochondria. It is also called as the “power house” of the cell.
- i. Plasma membrane: It is the protective compartment of the cell. It is composed of a lipid bilayer.
- j. Lysosome: It is a single membrane–bound organelle. It is the storage unit of hydrolytic enzymes. Breakdown of indigested substances takes place in lysosomes, and cell organelles are recycled here.
- k. Golgi apparatus: It is a single membrane–bound organelle stack of the flattened membranous sac. It is the active unit of modification, sorting, and secretion of cell products.
- l. Smooth ER: It is a network of membranous sacs and tubes but not attached with the ribosome. It helps in detoxification and lipid synthesis. It helps in folding of protein and transferring of the synthesized protein.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Biology with eText -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- Luke recently moved to a new apartment and wants to grow houseplants but isn't sure which room will be the best fit for them. Apply your knowledge of the scientific method to recommend a strategy for Luke to follow when determining the ideal location for houseplants in his new apartment.arrow_forwardA farmer has noticed that his soybean plants produce more beans in some years than others. He claims to always apply the same amount of fertilizer to the plants, but he suspects the difference in crop yield may have something to do with the amount of water the crops receive. The farmer has observed that the soybeans on his farm usually receive between 0 to 0.5 inches of water per day, but he is unsure of the optimal average daily amount of water with which to irrigate. 1. State a question that addresses the farmer’s problem 2. Conduct online research on “soybean crop irrigation" and record a brief summary of the findings 3. Construct a testable hypothesis and record i 4. Design an experiment to test the hypothesis and describe the procedures, variables, and data to be collected 5. What is the purpose of a control group in an experiment? What would the control groups be for each of your designed experiments in this exercise? 6. Describe the data that would be recorded in each of the…arrow_forwardA farmer has noticed that his soybean plants produce more beans in some years than others. He claims to always apply the same amount of fertilizer to the plants, but he suspects the difference in crop yield may have something to do with the amount of water the crops receive. The farmer has observed that the soybeans on his farm usually receive between 0 to 0.5 inches of water per day, but he is unsure of the optimal average daily amount of water with which to irrigate. 1. State a question that addresses the farmer’s problem 2. Conduct online research on “soybean crop irrigation" and record a brief summary of the findings 3. Construct a testable hypothesis and record i 4. Design an experiment to test the hypothesis and describe the procedures, variables, and data to be collectedarrow_forward
- A pharmaceutical company has developed a new weight loss drug for adults. Preliminary tests show that the drug seems to be fairly effective in about 75% of test subjects. The drug company thinks that the drug might be most effective in overweight individuals, but they are unsure to whom they should market the product. Use the scientific method to address the pharmaceutical company’s needs: State a research question that addresses the pharmaceutical company's problem Conduct online research on “Body Mass Index” categories and record a brief summary Construct a testable hypothesis and record in Design an experiment to test the hypothesis and describe the procedures, variables, and data to be collected What is the purpose of a control group in an experiment? What would the control groups be for each of your designed experiments in this exercise? Describe the data that would be recorded in each of the experiments you designed. Would it be classified as quantitative or…arrow_forwardPatients with multiple sclerosis frequently suffer from blurred vision. Drug X was developed to reduce blurred vision in healthy patients, but the effectiveness had not been tested on those suffering from multiple sclerosis. A study was conducted to determine if Drug X is effective at reducing blurry vision in multiple sclerosis patients. To be considered effective, a drug must reduce blurred vision by more than 30% in patients. Researchers predicted that a 20 mg dose of the drug would be effective for treating blurred vision in multiple sclerosis patients by reducing blurred vision by more than 30%. Drug X was administered to groups of multiple sclerosis patients at three doses (10 mg/day, 20 mg/day, 30 mg/day) for three weeks. A fourth group of patients was given a placebo containing no drug X for the same length of time. Vision clarity was measured for each patient before and after the three-week period using a standard vision test. The results were analyzed and graphed (See Figure…arrow_forwardSvp je voulais demander l aide pour mon exercicearrow_forward
- Imagine that you are a clinical geneticist. Your colleague is an oncologist who wants your help explaining the basics of genetics to their patient, who will be undergoing genetic testing in the coming weeks for possible acute myeloid leukemia (AML) induced by the radiation she had several years ago for breast cancer. Write a 1,050- to 1,225-word memo to your colleague. Include the following in your memo: An explanation of the molecular structure of DNA and RNA, highlighting both similarities and differences A description of the processes of transcription and translation An explanation of the differences between leading and lagging strands and how the DNA is replicated in each strand Reponses to the following common questions patients might ask about this type of genetic testing and genetic disorder: Does AML run in families? What genes are tested for?arrow_forwardRespond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What are some potential consequences that could result if the processes of replication, transcription, and translation don’t function correctly? Provide an example of how you might explain these consequences in terms that patients might understand.arrow_forwardanswer questions 1-10arrow_forward
- Answer Question 1-9arrow_forwardEx: Mr. Mandarich wanted to see if the color of light shined on a planthad an effect on the number of leaves it had. He gathered a group ofthe same species of plants, gave them the same amount of water, anddid the test for the same amount of time. Only the color of light waschanged. IV:DV:Constants:Control Gr:arrow_forwardethical considerations in medical imagingarrow_forward
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





