
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780136538820
Author: Taylor
Publisher: INTER PEAR
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 1CC
Label the structures in this diagram of an animal cell. Review the functions of each of these organelles.
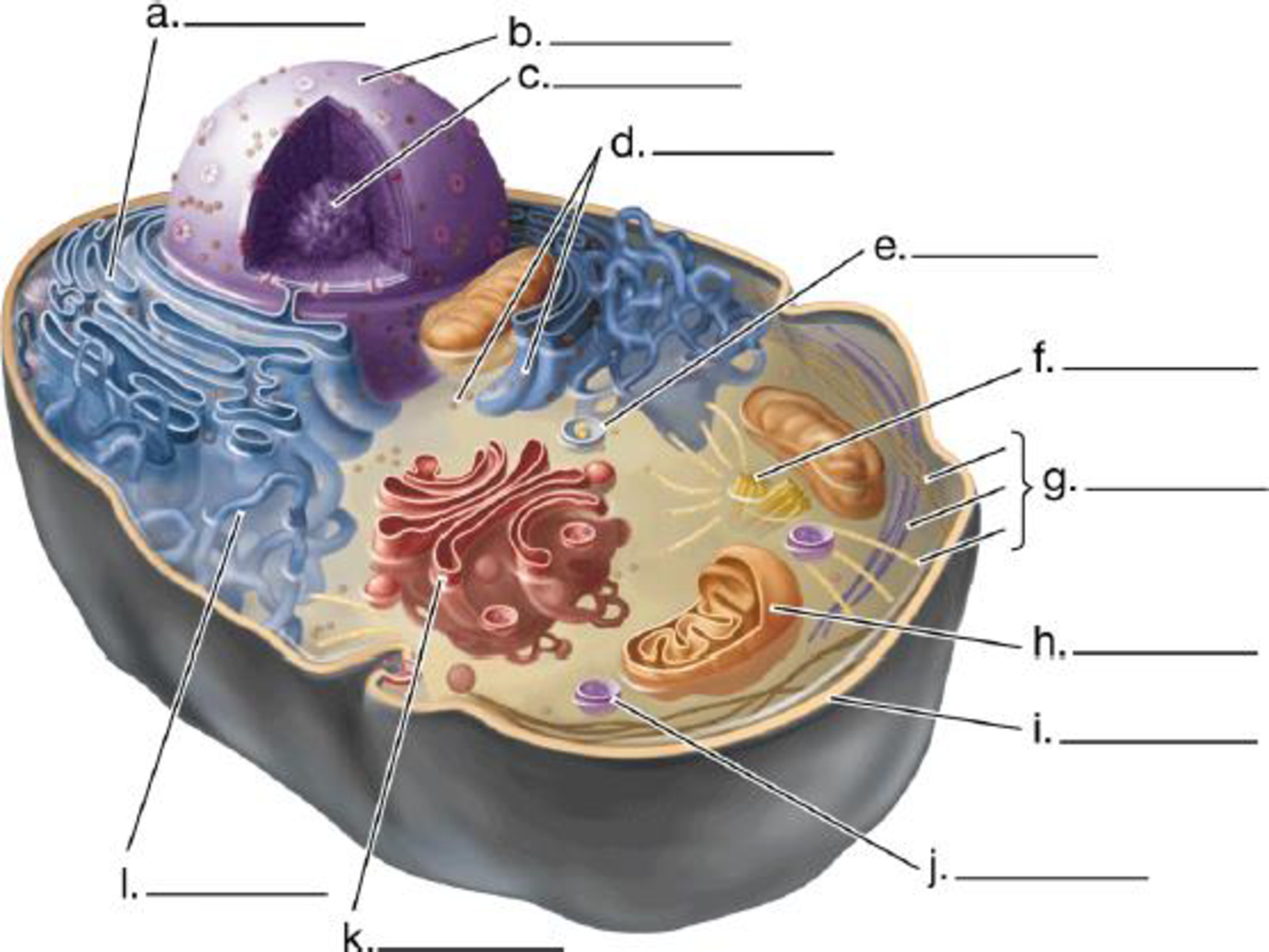
Expert Solution & Answer
Summary Introduction
To review: The structures and functions of each of the organelles in the given animal cell.
Introduction:
A cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of living organisms. It is bounded by a cell membrane. Cells contain different organelles. Each organelle has its own specific features and functions. Each cellular organelle possesses different structural peculiarities.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
Fig. 1 shows various structural organelles of an animal cell.
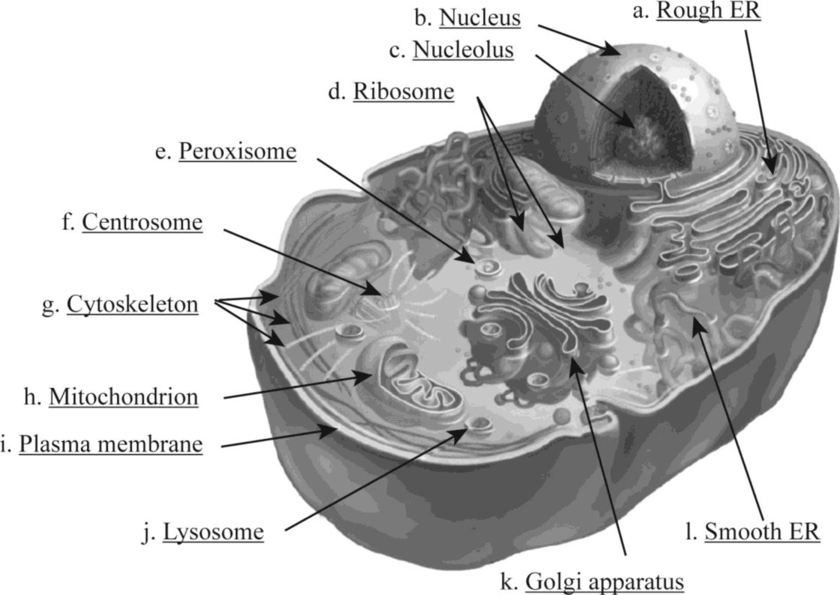
Fig. 1: Structure of an animal cell
The functions of various organelles are very specific.
- a. Rough ER: It is a network of membranous sacs and tubes; its external surface is attached with the ribosome. It helps in protein processing and secretion. Also, the addition of carbohydrate with protein occurs to produce glycoprotein, which helps in the production of a new membrane within the cell.
- b. Nucleus: It is a membrane-bound organelle covered by the nuclear envelope. The nucleus contains the nucleolus and chromatin material. The chromatin material consists of DNA and proteins.
- c. Nucleolus: It is a core region in the nucleus where components of the ribosome assemble.
- d. Ribosome: It is a non-membranous structure found in the cytoplasm of the cell. It is the core organelle for protein synthesis. It can be found free or attached with the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- e. Peroxisome: It is a specialized single membrane–bound vesicle found in the cytoplasm of the cell. It produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product and converts it to water.
- f. Centrosome: The formation of microtubules initiates at the centrosome. It contains a pair of centrioles.
- g. Cytoskeleton: It consists of a network of fibrous substances within the cytoplasm of a cell. The cytoskeleton consists of three main fibers called microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. It helps in providing rigidity and gives structural support to the cell.
- h. Mitochondrion: It is double membrane–bound organelle. It is important for cellular respiration and energy generation in the form of ATP. The two phospholipid bilayer membranes enclosed with the mitochondria play a great role in functioning of mitochondria. It is also called as the “power house” of the cell.
- i. Plasma membrane: It is the protective compartment of the cell. It is composed of a lipid bilayer.
- j. Lysosome: It is a single membrane–bound organelle. It is the storage unit of hydrolytic enzymes. Breakdown of indigested substances takes place in lysosomes, and cell organelles are recycled here.
- k. Golgi apparatus: It is a single membrane–bound organelle stack of the flattened membranous sac. It is the active unit of modification, sorting, and secretion of cell products.
- l. Smooth ER: It is a network of membranous sacs and tubes but not attached with the ribosome. It helps in detoxification and lipid synthesis. It helps in folding of protein and transferring of the synthesized protein.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Your goal is to produce black seeds resistant to mold. So you make the same cross again (between a homozygous black seeded, mold susceptible parent and a homozygous white seeded and mold resistant parent), and, again, advance progeny by SSD to create 100 F10 generation plants.
Based on the information you obtained from your first crossing experiment (Question #4), how many F10 plants would you expect to have black seeds and be resistant to mold?
Assume that a toxin produced by the mold fungus has been isolated. Only mold resistant seeds will germinate in the presence of the toxin. Could you use this toxin screening procedure to have segregation distortion work in your favor in the F2 generation? Explain your answer.
Info from Question 4
a. P Locus (Seed Color):
Hypothesis: The null hypothesis (H₀) is that seed color is controlled by alleles at a single locus.
Observed Data:
Total white seeds: 45 (resistant plants) + 6 (susceptible plants) = 51
Total black seeds: 7 (resistant…
10. Consider the following enzyme and its substrate where the "+" and "-" indicate cations and
anions, respectively. Explain which of the following inhibitors could inhibit this enzyme?
Which type of inhibitor would it be and why? (Video 5-2)
Substrate
Enzyme
Potential inhibitors
Using Punnett Squares Punnett squares are one good
way to predict the outcome of genetic crosses. Punnett
squares use mathematical probability to help predict the
genotype and phenotype combinations in genetic crosses. The
number of possible alleles from each parent determines the
number of rows and columns in the Punnett square.
Independent Assortment
KEY QUESTION How do alleles segregate when more than
one gene is involved?
Mendel wondered if the segregation of one pair of alleles
affects another pair. For example, does the gene that
determines the shape of a seed affect the gene for seed color?
This type of experiment is known as a two-factor, or dihybrid,
cross because it involves two different genes. Single-gene
crosses are monohybrid crosses.
Visual Reading Tool: Two-Factor Cross: F₂
The Punnett square shows the
results of self-crossing the F,
generation of a cross between
round yellow peas and wrinkled
green peas.
1. List the different genotypes in
the F, generation. What is the…
Chapter 4 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
Ch. 4 - Label the structures in this diagram of an animal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2TYKCh. 4 - Prob. 3TYKCh. 4 - Which of the following clues would tell you...Ch. 4 - Prob. 5TYKCh. 4 - What four cellular components are shared by...Ch. 4 - Describe two different ways in which cilia can...Ch. 4 - In which cell would you find the most lysosomes?...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9TYKCh. 4 - Prob. 10TYK
Ch. 4 - In which cell would you find the most...Ch. 4 - In what ways do the internal membranes of a...Ch. 4 - Is this statement true or false? Animal cells have...Ch. 4 - Describe the structure of the plasma membrane of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15TYKCh. 4 - Describe the pathway of the protein hormone...Ch. 4 - How might the phrase ingested but not digested be...Ch. 4 - Cilia are found on cells in almost every organ of...Ch. 4 - SCIENTIFIC THINKING Microtubules often produce...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CHAPTER 12 LESSON 2 Applying Mendel's Principles READING TOOL Connect to Visuals Before you read, preview Figure 12-7. Try to infer the purpose of this diagram. As you read, compare your inference to the text. After you read, revise your statement if needed or write a new one about the diagram's purpose. Take notes on the lines provided. Then view the Punnett square and answer the questions below regarding the genotypes and phenotypes. Inference: Revision: Parent 2 rryy Gametes F ry Parent 1 RRYY Gametes RY RrYy The F, generation are all RrYy. 1. What is the phenotype of parent 1?. 2. What is the genotype of parent 1? 3. What is the phenotype of parent 2? 4. What is the genotype of parent 2? 5. What is the phenotype of the F, offspring?. 6. What is the genotype of the F, offspring?. 7. What kind of cross does this figure describe? 144 Chanter 12 Introduction to Genetice Copyright Pearson Education Inc. or its affiliator. All rights reserved.arrow_forwardHow is the term enzyme related to the term proteinarrow_forwardCan very low temperatures cause proteins to denature? Explain why or why not?arrow_forward
- Humans consider themselves amazingly clever and innovative, constantly developing "new" ways of altering the world around us. As material consumption has increased, many have turned to the ideas of recycling and reuse as a means to minimize some negative aspects of our modern consumerism. Mother Nature though is the ultimate innovator and, more importantly, the ultimate recycler.arrow_forwardH gene assorts independently from the I gene. Both on autosomes. One man and one woman, both of HhIAIB genotype. Determine the blood type of progeny and fractions out of 16arrow_forwardAlleles at the P locus control seed color. Plants which are pp have white seeds, white flowers and no pigment in vegetative parts. Plants which are P_ have black seeds, purple flowers and may have varying degrees of pigment on stems and leaves. Seed color can be assessed, visually, based on if the seed is white or not white A gene for mold resistance has been reported and we want to determine its inheritance and whether it is linked to P. For the purposes of this exercise, we will assume that resistance is controlled by a single locus M, and M_ plants are resistant and mm plants are susceptible. Resistance can be measured, under greenhouse conditions, 2 weeks after planting, by injecting each seedling with a spore suspension. After two weeks, the seedlings can be rated as resistant or susceptible, based on whether or not tissue is actively sporulating. For this exercise we will use seed and data from the F10 generation of a recombinant inbred population produced using single seed…arrow_forward
- Linkage in common bean Alleles at the P locus control seed color. Plants which are pp have white seeds, white flowers and no pigment in vegetative parts. Plants which are P_ have black seeds, purple flowers and may have varying degrees of pigment on stems and leaves. Seed color can be assessed, visually, based on if the seed is white or not white A gene for mold resistance has been reported and we want to determine its inheritance and whether it is linked to P. For the purposes of this exercise, we will assume that resistance is controlled by a single locus M, and M_ plants are resistant and mm plants are susceptible. Resistance can be measured, under greenhouse conditions, 2 weeks after planting, by injecting each seedling with a spore suspension. After two weeks, the seedlings can be rated as resistant or susceptible, based on whether or not tissue is actively sporulating. For this exercise we will use seed and data from the F10 generation of a recombinant inbred population…arrow_forwardAlleles at the P locus control seed color. Plants which are pp have white seeds, white flowers and no pigment in vegetative parts. Plants which are P_ have black seeds, purple flowers and may have varying degrees of pigment on stems and leaves. Seed color can be assessed, visually, based on if the seed is white or not white A gene for mold resistance has been reported and we want to determine its inheritance and whether it is linked to P. For the purposes of this exercise, we will assume that resistance is controlled by a single locus M, and M_ plants are resistant and mm plants are susceptible. Resistance can be measured, under greenhouse conditions, 2 weeks after planting, by injecting each seedling with a spore suspension. After two weeks, the seedlings can be rated as resistant or susceptible, based on whether or not tissue is actively sporulating. For this exercise we will use seed and data from the F10 generation of a recombinant inbred population produced using single seed…arrow_forwardcan you help? I think its B but not surearrow_forward
- Skip to main content close Homework Help is Here – Start Your Trial Now! arrow_forward search SEARCH ASK Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BUY Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition) 11th Edition ISBN: 9780134580999 Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn Publisher: PEARSON 1 The Human Body: An Orientation expand_moreChapter 1 : The Human Body: An Orientation Chapter Questions expand_moreSection: Chapter Questions Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,... format_list_bulletedProblem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,... See similar textbooks Bartleby Related Questions Icon Related questions Bartleby Expand Icon bartleby Concept explainers bartleby Question Draw a replication bubble with two replication forks.blue lines are DNA single strands and red lines are RNA single strands.indicate all 3' and 5’ ends on all DNA single…arrow_forwardProvide an answerarrow_forwardQuestion 4 1 pts Which of the following would be most helpful for demonstrating alternative splicing for a new organism? ○ its proteome and its transcriptome only its transcriptome only its genome its proteome and its genomearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning




Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Dissection Basics | Types and Tools; Author: BlueLink: University of Michigan Anatomy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-_B17pTmzto;License: Standard youtube license