
Introduction To Computing Systems
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781260150537
Author: PATT, Yale N., Patel, Sanjay J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 19E
Shown below is a byte-addressible memory consisting of eight locations, and its associated MAR and MDR. Both MAR and MDR consist of flip-flops that are latched at the start of each clock cycle based on the values on their corresponding input lines. A memory read is initiated every cycle, and the data is available by the end of that cycle.
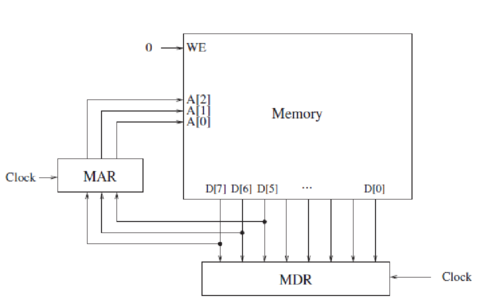
Just before the start of cycle 1, MAR contains 000, MDR contains 00010101, and the contents of each memory location is as shown.

a. What do MAR and MDR contain just before the end of cycle 1?
MAR:  MDR:
MDR: 
b. What does MDR contain just before the end of cycle 4?
MDR: 
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Dijkstra's Algorithm (part 1). Consider the network shown below, and Dijkstra’s link-state algorithm. Here, we are interested in computing the least cost path from node E (note: the start node here is E) to all other nodes using Dijkstra's algorithm. Using the algorithm statement used in the textbook and its visual representation, complete the "Step 0" row in the table below showing the link state algorithm’s execution by matching the table entries (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv) with their values. Write down your final [correct] answer, as you‘ll need it for the next question.
4. |z + 5 - 5i| = 7
14.
dz,
C: |z❘
C: |z❘ = 0.6
ze² - 2iz
H
Chapter 4 Solutions
Introduction To Computing Systems
Ch. 4 - Prob. 1ECh. 4 - Prob. 2ECh. 4 - What is misleading about the name program counter?...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4ECh. 4 - Prob. 5ECh. 4 - What are the two components of an instruction?...Ch. 4 - Prob. 7ECh. 4 - The FETCH phase of the instruction cycle does two...Ch. 4 - Prob. 10ECh. 4 - State the phases of the instruction cycle, and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285867168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285867168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:9781305080195
Author:Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:Cengage Learning

C++ for Engineers and Scientists
Computer Science
ISBN:9781133187844
Author:Bronson, Gary J.
Publisher:Course Technology Ptr


Microsoft Visual C#
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337102100
Author:Joyce, Farrell.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781285867168
Author:Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781305627482
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Instruction Format (With reference to address); Author: ChiragBhalodia;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lNdy8HREvgo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY