
Concept explainers
The police often use a device called a Breatkalyzer to test drivers suspected of being drunk. In one type of device, the breath of a driver suspected of driving under the influence of alcohol is bubbled through an orange solution containing potassium dichromate
(a) Classify each of the species in the Breathalyzer reaction as a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte, (b) Write the ionic and net ionic equations for the Breathahzer reaction. (c) Determine the oxidation number of each element in the overall equation. (d) One manufacturer of Breathalyzers specifies a potassium dichromate concentration of 0.025 percent weight per volume
Interpretation:
The reactants and products in breathalyzer are to be classified as strong, weak, or non-electrolyte, the ionic and the net ionic equation for the reaction are to be represented, and the oxidation state of each element is to be determined in the reaction. The concentration of potassium dichromate in molarity is to be expressed and the volume of stock solution of
Concept introduction:
An electrolyte is a compound which dissociates into its corresponding ions when dissolved in water and conducts electricity. Electrolytes can be strong, weak, or non-electrolyte. The classification of the type of electrolyte is based on the formation of the ions when the electrolyte is dissolved in water.
An ionic reaction always follows the law of conservation of mass, according to which, when a chemical reaction occurs, the mass of ions in products should be equal to the mass of ions in reactants.
Oxidation number is the net charge on an element involved in the formation of a compound in a reaction. It is also known as oxidation state.
The concentration of a solution in terms of molarity is determined as follows:
Here,
Dilution is the process by which a less concentrated solution can be prepared from a more concentrated solution. But, the number of moles of solute remains the same in the original solution and the dilution. So, the concentration or volume of dilution can be determined as follows:
Here,
in ml,
Answer to Problem 159AP
Solution:
a)
b)
Ionic equation for breathalyzer is as follows:
The net ionic equation is as follows:
c)
Oxidation states of reactants and products are:
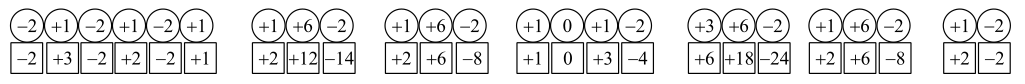
d)
The molar concentration of
e)
The volume of
f)
The molarity of
Explanation of Solution
a)
Given information: The reaction for breathalyzer is as follows:
a) Classify each of the species in the Breathalyzer reaction as a strong electrolyte, weak electrolite or nonelectrolyte.
b) The ionic and net ionic equations for the Breathalyzer reaction.
The ionic equation for the breathalyzer reaction is as follows:
The net ionic equation for the breathalyzer reaction is as follows:
c) The oxidation number of each element in the overall equation.
The oxidation numbers of elements in
The oxidation numbers of elements in
The oxidation numbers of elements in
The oxidation numbers of elements in
The oxidation numbers of elements in
The oxidation numbers of elements in
The oxidation numbers of elements in
d) The concentration in terms of molarity for the reaction
The concentration of
The molecular weight of
Substitute the values in the equation as follows:
e) The volume of
The concentration of stock solution is
Consider the two solutions, the stock solution is solution
Rearranging the equation to calculate the volume as follows:
f) The molarity of each ion in a
Potassium dichromate form the following ions on dissolution:
So, the concentration of these ions is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





