
For its first 2 decades of existence, the NBA’s Orlando Magic basketball team set seat prices for its 41-game home
But when Anthony Perez, director of business strategy, finished his MBA at the University of Florida, he developed a valuable database of ticket sales. Analysis of the data led him to build a
Studying individual sales of Magic tickets on the open Stub Hub marketplace during the prior season, Perez determined the additional potential sales revenue the Magic could have made had they charged prices the fans had proven they were willing to pay on Stub Hub. This became his dependent variable, y, in a multiple-regression model.
He also found that three variables would help him build the “true market” seat price for every game. With his model, it was possible that the same seat in the arena would have as many as seven different prices created at season onset—sometimes higher than expected on average and sometimes lower.
The major factors he found to be statistically significant in determining how high the demand for a game ticket, and hence, its price, would be were:
► The day of the week (x1)
► A rating of how popular the opponent was (x2)
► The time of the year (x3)
For the day of the week, Perez found that Mondays were the least-favored game days (and he assigned them a value of 1). The rest of the weekdays increased in popularity, up to a Saturday game, which he rated a 6. Sundays and Fridays received 5 ratings, and holidays a 3 (refer to the footnote in Table 4.2).

Fernado Medina
TABLE 4.2 Data for Last Year’s Magic Ticket Sales Pricing Model
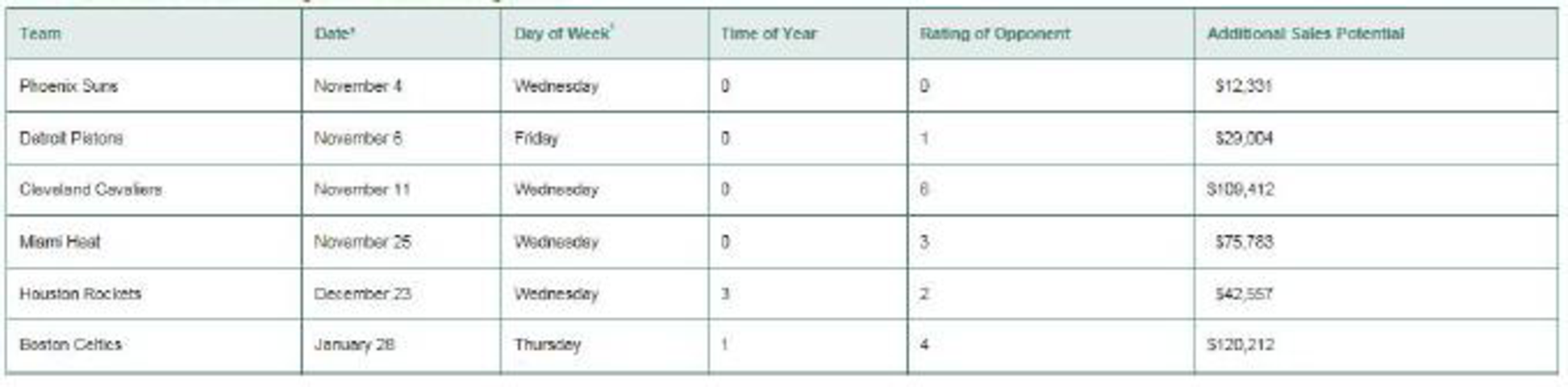
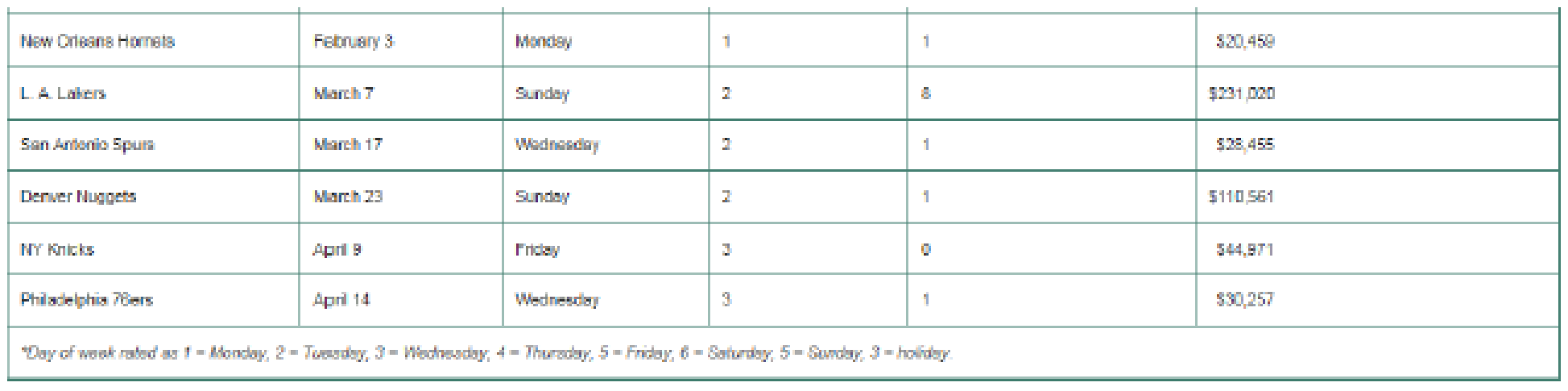
His ratings of opponents, done just before the start of the season, were subjective and range from a low of 0 to a high of 8. A very high-rated team in that particular season may have had one or more superstars on its roster, or have won the NBA finals the prior season, making it a popular fan draw.
Finally, Perez believed that the NBA season could be divided into four periods in popularity:
► Early games (which he assigned 0 scores)
► Games during the Christmas season (assigned a 3)
► Games until the All-Star break (given a 2)
► Games leading into the play-offs (scored with a 3)
The first year Perez built his multiple-regression model, the dependent variable y, which was a “potential premium revenue score,” yielded an R2 =.86 with this equation:
Table 4.2 illustrates, for brevity in this case study, a sample of 12 games that year (out of the total 41 home game regular season), including the potential extra revenue per game (y) to be expected using the variable pricing model.
A leader in NBA variable pricing, the Orlando Magic have learned that regression analysis is indeed a profitable forecasting tool.
1. Use the data in Table 4.2 to build a regression model with day of the week as the only independent variable.
4. What additional independent variables might you suggest to include in Perez’s model?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Mylab Operations Management With Pearson Etext -- Access Card -- For Operations Management: Sustainability And Supply Chain Management (13th Edition)
- Choose one major approach to job design, and then discuss how best that approach can be utilized in either your current or previous employer, including a discussion of its strengths and weaknesses.arrow_forwardThe results of your four plans will provide an indicative EOQ value. State this value and discuss in a precise manner, why it is not the exact, true value. Additional calculations in the form of plans E, F etc. may also assist your explanation of the EOQ and can be includedarrow_forwardi). Complete the table assuming a Level production plan. ii) Comment on your results and explain whether at this stage, you consider a Level plan is a suitable approach for this particular business. Your comment should include reference to a calculated ‘fill rate’.arrow_forward
- In the following sawtooth inventory profile diagram, two inventory plans with different order quantities (Q) and different frequencies of delivery are shown; order quantity for Plan A = 200 units and Plan B = 50 units. i). Total demand (D) is 350 units, the holding cost per unit (Ch) is equal to (£0.8) and the ordering cost per order (Co) is (£12.5). Calculate the total costs for each plan and state which one is more preferable along with the reason why. ii). There is a stark difference in the composition of the total costs of Plans A and B. Explain this difference and why it occurs. Use the breakdown of costs for each plan to help illustrate your answer.arrow_forwardi). Complete the table for a Chase production plan. ii). Explain whether a Level or Chase plan is more suitable for the demand pattern experienced by this particular business, which incidentally relies on highly skilled workers in the production process. Assume a starting workforce of 7 and that fractional workers are permissible. You should support your answer with numerical data derived from Table 3. In comparing the costs, state any other assumptions made.arrow_forwardi). Complete for a Chase production plan. ii). Explain whether a Level or Chase plan is more suitable for the demand pattern experienced by this particular business, which incidentally relies on highly skilled workers in the production process. Assume a starting workforce of 7 and that fractional workers are permissible.arrow_forward
- Complete the table for a Chase production plan.arrow_forwardHow much can the garden centre expect to sell during each quarter of next year (Year 3) accounting for seasonality? Your forecast must make use of seasonal indices. All workings must be shown in full. (NOTE: Please round your calculations to three decimal places).arrow_forwardPS.53 Brother I.D. Ricks is a faculty member at BYU-Idaho whose grandchildren live in Oklahoma and California. He and his wife would like to visit their grandchildren at least once a year in these states. They currently have one vehicle with well over 100,000 miles on it, so they want to buy a newer vehicle with fewer miles and that gets better gas mileage. They are considering two options: (1) a new subcompact car that would cost $18,750 to purchase or (2) a used sedan that would cost $12,750.They anticipate that the new subcompact would get 37 miles per gallon (combined highway and around town driving) while the sedan would get 26 miles per gallon. Based on their road tripping history they expect to drive 13,000 miles per year. For the purposes of their analysis they are assuming that gas will cost $2.93 per gallon.Question: How many miles would the Ricks need to drive before the cost of these two options would be the same? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) (Hint:…arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,


