
Concept explainers
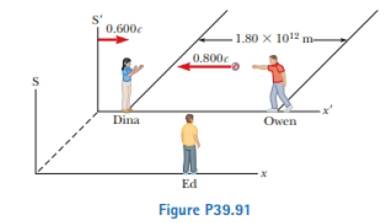
Owen and Dina are at rest in frame S.’ which is moving at 0.600c with respect to frame S. They play a game of catch while Ed. at rest in frame S, watches the action (Fig. P39.91). Owen throws the ball to Dina at 0.800c (according to Owen), and their separation (measured in S') is equal to 1.80 × 1012 m. (a) According to Dina, how fast is the ball moving? (b) According to Dina, what time interval is required for the ball to reach her? According to Ed, (c) how far apart are Owen and Dina, (d) how fast is the ball moving, and (e) what time interval is required for the ball to reach Dina?
(a)
The speed of ball according to Dina.
Answer to Problem 39.91CP
The speed of ball according to Dina is 0.800c.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The frame S′ which is moving at 0.600c with respect to the frame S. The speed of ball is 0.800c with respect to Owen. The distance between Owen and Dina is 1.80×1012 m.
If both persons are in same frame then the velocity of ball will be same for both persons.
Owen and Dina are in same frame S and Owen throws the ball to the Dina with speed of 0.800c, then the speed of the ball with respect to the Dina is 0.800c.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of ball according to Dina is 0.800c.
(b)
The time interval is required for the ball to reach Dina.
Answer to Problem 39.91CP
The time interval is required for the ball to reach Dina is 7.51×103 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The frame S′ which is moving at 0.600c with respect to the frame S. The speed of ball is 0.800c with respect to Owen. The distance between Owen and Dina is 1.80×1012 m.
Write the expression for time taken by the ball to reach Dina.
t=LPu
Here,
t is the time taken by the ball.
LP is the distance between Owen and Dina.
u is the speed of the ball.
Substitute 0.800c for u and 1.80×1012 m for LP in above equation.
t=1.80×1012 m0.800c
The speed of the light is,
c=3.0×108 m/s
Substitute 3.0×108 m/s for c in above equation to find the time interval.
t=1.80×1012 m(0.800)(3.0×108 m/s)=7.51×103 s
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time interval is required for the ball to reach Dina is 7.51×103 s.
(c)
The distance between Owen and Dina with respect to Ed.
Answer to Problem 39.91CP
The distance between Owen and Dina with respect to Ed is 1.44×1012 m.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The frame S′ which is moving at 0.600c with respect to the frame S. The speed of ball is 0.800c with respect to Owen. The distance between Owen and Dina is 1.80×1012 m.
Write the expression of distance between Owen and Dina with respect to the other frame S′.
L=LP√1−v2c2
Here,
L is the distance between Owen and Dina with respect to Ed.
v is the speed of frame S′.
Substitute 0.600c for v and 1.80×1012 m for LP in above equation.
L=(1.80×1012 m)√1−(0.600c)2c2=(1.80×1012 m)(0.8)=1.44×1012 m
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance between Owen and Dina with respect to Ed is 1.44×1012 m.
(d)
The speed of the ball with respect to Ed.
Answer to Problem 39.91CP
The speed of the ball with respect to Ed is 0.385c.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The frame S′ which is moving at 0.600c with respect to the frame S. The speed of ball is 0.800c with respect to Owen. The distance between Owen and Dina is 1.80×1012 m.
Write the expression of speed of the ball with respect to the other frame S′.
u′=u−v1−uvc2
Here,
u′ is the speed of ball with respect to Ed.
Substitute 0.600c for v and 0.800c for u in above equation.
u′=0.800c−0.600c1−(0.800c)(0.600c)c2=0.200c1−0.48=0.3846c≈0.385c
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of the ball with respect to Ed is 0.385c.
(e)
The time interval required for the ball to reach Dina with respect to Ed.
Answer to Problem 39.91CP
The time interval required for the ball to reach Dina with respect to Ed.
is 4.88×103 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The frame S′ which is moving at 0.600c with respect to the frame S. The speed of ball is 0.800c with respect to Owen. The distance between Owen and Dina is 1.80×1012 m.
Write the expression for time taken by the ball to reach Dina with respect to Ed.
t′=γ(t−vLPc2) (1)
Here,
t′ is time taken by the ball to reach Dina with respect to Ed.
γ is the Lorentz factor.
Write the expression for the Lorentz factor.
γ=1√1−v2c2
Substitute 1√1−v2c2 for γ in equation (1).
t′=1√1−v2c2(t−vLPc2)
Substitute 0.600c for v, 3.0×108 m/s for c, 7.51×103 s for t and 1.80×1012 m for LP in above equation.
t′=1√1−(0.600c)2c2(7.51×103 s−(0.600c)(1.80×1012 m)c2)=1.25(7.51×103 s−1.08 m3.0×108 m/s)=4.88×103 s
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time interval required for the ball to reach Dina with respect to Ed.
is 4.88×103 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 39 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- Please draw a sketch and a FBDarrow_forwardAnswer everything or don't answer at allarrow_forwardPart A: kg (a) Water at 20 °C (p = 998.3 and v = 1 × 10-6 m²/s) flows through a galvanised m³ iron pipe (k = 0.15 mm) with a diameter of 25 mm, entering the room at point A and discharging at point C from the fully opened gate valve B at a volumetric flow rate of 0.003 m³/s. Determine the required pressure at A, considering all the losses that occur in the system described in Figure Q1. Loss coefficients for pipe fittings have been provided in Table 1. [25 marks] (b) Due to corrosion within the pipe, the average flow velocity at C is observed to be V2 m/s after 10 years of operation whilst the pressure at A remains the same as determined in (a). Determine the average annual rate of growth of k within the pipe. [15 marks] 4₁ Figure Q1. Pipe system Page 2 25 mmarrow_forward
- For an independent study project, you design an experiment to measure the speed of light. You propose to bounce laser light off a mirror that is 53.5 km due east and have it detected by a light sensor that is 119 m due south of the laser. The first problem is to orient the mirror so that the laser light reflects off the mirror and into the light sensor. (a) Determine the angle that the normal to the mirror should make with respect to due west.(b) Since you can read your protractor only so accurately, the mirror is slightly misaligned and the actual angle between the normal to the mirror and due west exceeds the desired amount by 0.003°. Determine how far south you need to move the light sensor in order to detect the reflected laser light.arrow_forwardA mirror hangs 1.67 m above the floor on a vertical wall. A ray of sunlight, reflected off the mirror, forms a spot on the floor 1.41 m from the wall. Later in the day, the spot has moved to a point 2.50 m from the wall. (a) What is the change in the angle of elevation of the Sun, between the two observations?arrow_forwardIt is not (theta 1i) or (pi/2 - theta 2i)arrow_forward
- Assume the helium-neon lasers commonly used in student physics laboratories have power outputs of 0.250 mW. (a) If such a laser beam is projected onto a circular spot 3.40 mm in diameter, what is its intensity (in watts per meter squared)? 27.5 W/m² (b) Find the peak magnetic field strength (in teslas). 8.57e-7 X T (c) Find the peak electric field strength (in volts per meter). 144 V/marrow_forwardIdentify the most likely substancearrow_forwardA proton moves at 5.20 × 105 m/s in the horizontal direction. It enters a uniform vertical electric field with a magnitude of 8.40 × 103 N/C. Ignore any gravitational effects. (a) Find the time interval required for the proton to travel 6.00 cm horizontally. 83.33 ☑ Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. ns (b) Find its vertical displacement during the time interval in which it travels 6.00 cm horizontally. (Indicate direction with the sign of your answer.) 2.77 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. mm (c) Find the horizontal and vertical components of its velocity after it has traveled 6.00 cm horizontally. 5.4e5 V × Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. I + [6.68e4 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each…arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





